J Vet Sci.
2017 Sep;18(3):273-281. 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.3.273.
Phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes of Salmonella enterica isolated from pet dogs and cats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Unit in Microbial Food Safety and Antimicrobial Resistance, Department of Veterinary Public Health, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok 10330, Thailand. rchuanchuen@yahoo.com
- 2Center for Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring in Foodborne Pathogens (in cooperation with WHO), Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok 10330, Thailand.
- 3Research Group for Prevention Technology in Livestock, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen 40002, Thailand.
- 4Department of Veterinary Biosciences, Faculty of Animal Sciences and Veterinary Medicine, Nong Lam University, Ho Chi Minh 70000, Vietnam.
- KMID: 2412444
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.3.273
Abstract
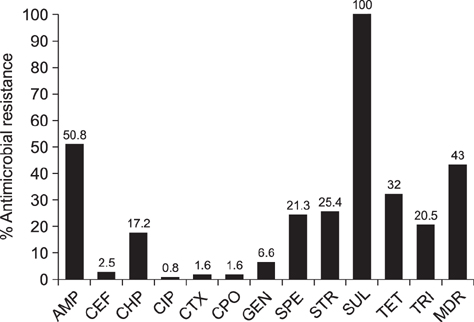
- Salmonella enterica isolates (n = 122), including 32 serotypes from 113 dogs and 9 cats, were obtained from household dogs (n = 250) and cats (n = 50) during 2012-2015. The isolates were characterized by serotyping, antimicrobial resistance phenotyping and genotyping, and virulence gene screening. Serovars Weltevreden (15.6%) and Typhimurium (13.9%) were the most common. The majority (43%) of the isolates were multidrug resistant. The dog isolates (12.3%) harbored class 1 integrons, of which the dfrA12-aadA2 cassette was most frequent (66.7%). The only class integron in serovar Albany was located on a conjugative plasmid. Two ESBL-producing isolates (i.e., a serovar Krefeld and a serovar Enteritridis) carried bla(TEM) and bla(CTX-M), and the bla(TEM) gene in both was horizontally transferred. Of the plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes tested, only qnrS (4.9%) was detected. Most Salmonella isolates harbored invA (100%), prgH (91.8%), and sipB (91%). Positive associations between resistance and virulence genes were observed for bla(PSE-1)/orgA, cmlA/spaN, tolC, and sul1/tolC (p < 0.05). The results suggest that companion dogs and cats are potential sources of S. enterica strains that carry resistance and virulence genes and that antimicrobial use in companion animals may select for the examined Salmonella virulence factors.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Anti-Bacterial Agents/therapeutic use
Cat Diseases/drug therapy/microbiology
Cats
Dog Diseases/drug therapy/microbiology
Dogs
Drug Resistance, Bacterial/genetics
Integrons/genetics
Microbial Sensitivity Tests/veterinary
Polymerase Chain Reaction/veterinary
Salmonella Infections, Animal/drug therapy/*microbiology
Salmonella enterica/drug effects/*genetics/pathogenicity
Serotyping/veterinary
Virulence Factors/*genetics
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bangtrakulnonth A, Pornreongwong S, Pulsrikarn C, Sawanpanyalert P, Hendriksen RS, Lo Fo Wong DMA, Aarestrup FM. Salmonella serovars from humans and other sources in Thailand, 1993-2002. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004; 10:131–136.2. Beceiro A, Tomás M, Bou G. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence: a successful or deleterious association in the bacterial world? Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013; 26:185–230.
Article3. Boerlin P, Travis R, Gyles CL, Reid-Smith R, Janecko N, Lim H, Nicholson V, McEwen SA, Friendship R, Archambault M. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes of Escherichia coli isolates from swine in Ontario. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005; 71:6753–6761.
Article4. Chen S, Cui S, McDermott PF, Zhao S, White DG, Paulsen I, Meng J. Contribution of target gene mutations and efflux to decreased susceptibility of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium to fluoroquinolones and other antimicrobials. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007; 51:535–542.
Article5. Chen S, Zhao S, White DG, Schroeder CM, Lu R, Yang H, McDermott PF, Ayers S, Meng J. Characterization of multiple-antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella serovars isolated from retail meats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004; 70:1–7.
Article6. Chiu CH, Ou JT. Rapid identification of Salmonella serovars in feces by specific detection of virulence genes, invA and spvC, by an enrichment broth culture-multiplex PCR combination assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1996; 34:2619–2622.
Article7. Chu C, Chiu CH, Wu WY, Chu CH, Liu TP, Ou JT. Large drug resistance virulence plasmids of clinical isolates of Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001; 45:2299–2303.
Article8. Chuanchuen R, Ajariyakhajorn K, Koowatananukul C, Wannaprasat W, Khemtong S, Samngamnim S. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes in Salmonella enterica isolates from dairy cows. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010; 7:63–69.
Article9. Chuanchuen R, Khemtong S, Padungtod P. Occurrence of qacE/qacEΔ1 genes and their correlation with class 1 integrons in Salmonella enterica isolates from poultry and swine. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2007; 38:855–862.10. Chuanchuen R, Padungtod P. Antimicrobial resistance genes in Salmonella enterica isolates from poultry and swine in Thailand. J Vet Med Sci. 2009; 71:1349–1355.
Article11. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals; Approved Standard-Fourth edition. CLSI document VET01-04. Wayne: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2013.12. D'Ortenzio E, Weill FX, Ragonneau S, Lebon JA, Renault P, Pierre V. First report of a Salmonella enterica serovar Weltevreden outbreak on Reunion Island, France, August 2007. Euro Surveill. 2008; 13:pii: 18949.13. Ekkapobyotin C, Padungtod P, Chuanchuen R. Antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter coli isolates from swine. Int J Food Microbiol. 2008; 128:325–328.14. Fluit AC. Towards more virulent and antibiotic-resistant Salmonella? FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2005; 43:1–11.15. Galanis E, Lo Fo, Patrick ME, Binsztein N, Cieslik A, Chalermchikit T, Aidara-Kane A, Ellis A, Angulo FJ, Wegener HC. World Health Organization Global Salm-Surv. Web-based surveillance and global Salmonella distribution, 2000-2002. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006; 12:381–388.16. Gordis L. Estimating risk: is there an association?. Epidemiology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier;2009. p. 201–214.17. Guardabassi L, Schwarz S, Lloyd DH. Pet animals as reservoirs of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004; 54:321–332.18. Hasman H, Mevius D, Veldman K, Olesen I, Aarestrup FM. β-Lactamases among extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-resistant Salmonella from poultry, poultry products and human patients in The Netherlands. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005; 56:115–121.
Article19. Heinitz ML, Ruble RD, Wagner DE, Tatini SR. Incidence of Salmonella in fish and seafood. J Food Prot. 2000; 63:579–592.20. Herrero A, Rodicio MR, González-Hevia MA, Mendoza MC. Molecular epidemiology of emergent multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium strains carrying the virulence resistance plasmid pUO-StVR2. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006; 57:39–45.
Article21. Hsu SC, Chiu TH, Pang JC, Hsuan-Yuan CH, Chang GN, Tsen HY. Characterisation of antimicrobial resistance patterns and class 1 integrons among Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis strains isolated from humans and swine in Taiwan. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006; 27:383–391.
Article22. International Organization for Standardization (ISO). ISO 6579:2002(en). Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuffs-Horizontal method for the detection of Salmonella spp. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization;2002.23. Jay-Russell MT, Hake AF, Bengson Y, Thiptara A, Nguyen T. Prevalence and characterization of Escherichia coli and Salmonella strains isolated from stray dog and coyote feces in a major leafy greens production region at the United States-Mexico border. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e113433.24. Khemtong S, Chuanchuen R. Class 1 integrons and Salmonella genomic island 1 among Salmonella enterica isolated from poultry and swine. Microb Drug Resist. 2008; 14:65–70.
Article25. Lay KK, Koowattananukul C, Chansong N, Chuanchuen R. Antimicrobial resistance, virulence, and phylogenetic characteristics of Escherichia coli isolates from clinically healthy swine. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2012; 9:992–1001.
Article26. Leonard EK, Pearl DL, Finley RL, Janecko N, Reid-Smith RJ, Peregrine AS, Weese JS. Comparison of antimicrobial resistance patterns of Salmonella spp. and Escherichia coli recovered from pet dogs from volunteer households in Ontario (2005-06). J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012; 67:174–181.
Article27. Lévesque C, Piché L, Larose C, Roy PH. PCR mapping of integrons reveals several novel combinations of resistance genes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995; 39:185–191.
Article28. Li R, Lai J, Wang Y, Liu S, Li Y, Liu K, Shen J, Wu C. Prevalence and characterization of Salmonella species isolated from pigs, ducks and chickens in Sichuan Province, China. Int J Food Microbiol. 2013; 163:14–18.
Article29. Lin D, Chen K, Wai-Chi Chan E, Chen S. Increasing prevalence of ciprofloxacin-resistant food-borne Salmonella strains harboring multiple PMQR elements but not target gene mutations. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:14754.
Article30. Ling JM, Chan EW, Lam AW, Cheng AF. Mutations in topoisomerase genes of fluoroquinolone-resistant salmonellae in Hong Kong. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003; 47:3567–3573.
Article31. Marshall BM, Levy SB. Food animals and antimicrobials: impacts on human health. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011; 24:718–733.
Article32. Park CH, Robicsek A, Jacoby GA, Sahm D, Hooper DC. Prevalence in the United States of aac(6′)-Ib-cr encoding a ciprofloxacin-modifying enzyme. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006; 50:3953–3955.
Article33. Pedersen K, Pedersen K, Jensen H, Finster K, Jensen VF, Heuer OE. Occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from diagnostic samples from dogs. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007; 60:775–781.
Article34. Piddock LJ, Ricci V, McLaren I, Griggs DJ. Role of mutation in the gyrA and parC genes of nalidixic-acid-resistant Salmonella serotypes isolated from animals in the United Kingdom. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1998; 41:635–641.
Article35. Robicsek A, Jacoby GA, Hooper DC. The worldwide emergence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006; 6:629–640.
Article36. Rushdy AA, Mabrouk MI, Abu-Sef FAH, Kheiralla ZH, Abdel-All SM, Saleh NM. Contribution of different mechanisms to the resistance to fluoroquinolones in clinical isolates of Salmonella enterica. Braz J Infect Dis. 2013; 17:431–437.
Article37. Sackett DL, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Down with odds ratios. Evid Based Med. 1996; 1:164–166.38. Sahm DF, Thornsberry C, Mayfield DC, Jones ME, Karlowsky JA. Multidrug-resistant urinary tract isolates of Escherichia coli: prevalence and patient demographics in the United States in 2000. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001; 45:1402–1406.
Article39. Seepersadsingh N, Adesiyun AA, Seebaransingh R. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella spp. in non-diarrhoeic dogs in Trinidad. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2004; 51:337–342.
Article40. Skyberg JA, Logue CM, Nolan LK. Virulence genotyping of Salmonella spp. with multiplex PCR. Avian Dis. 2006; 50:77–81.41. Stephenson S, Brown PD, Holness A, Wilks M. The emergence of qnr-mediated quinolone resistance among Enterobacteriaceae in Jamaica. West Indian Med J. 2010; 59:241–244.42. Strahilevitz J, Jacoby GA, Hooper DC, Robicsek A. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance: a multifaceted threat. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009; 22:664–689.
Article43. Thong KL, Goh YL, Radu S, Noorzaleha S, Yasin R, Koh YT, Lim VKE, Rusul G, Puthucheary SD. Genetic diversity of clinical and environmental strains of Salmonella enterica serotype Weltevreden isolated in Malaysia. J Clin Microbiol. 2002; 40:2498–2503.
Article44. Torkan S, Khamesipour F, Anyanwu MU. Detection of virulence and antibacterial resistance genes in Salmonella isolates from diarrhoeic dogs in Iran. Rev Med Vet (Toulouse). 2015; 166:221–228.45. Tsai HJ, Huang HC, Lin CM, Lien YY, Chou CH. Salmonellae and campylobacters in household and stray dogs in northern Taiwan. Vet Res Commun. 2007; 31:931–939.
Article46. Ulaya W, Hang'ombe BM, Zulu V, Nalubamba K, Mulenga E, Isogai H, Isogai E. Distribution of virulence genes and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella isolated from dogs and chickens in Zambia. Int J Agro Vet Med Sci. 2012; 6:360–367.
Article47. Wannaprasat W, Padungtod P, Chuanchuen R. Class 1 integrons and virulence genes in Salmonella enterica isolates from pork and humans. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011; 37:457–461.
Article48. Yamane K, Wachino J, Suzuki S, Arakawa Y. Plasmid-mediated qepA gene among Escherichia coli clinical isolates from Japan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008; 52:1564–1566.
Article49. Zgurskaya HI, Nikaido H. Bypassing the periplasm: reconstitution of the AcrAB multidrug efflux pump of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96:7190–7195.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Virulence gene profiles and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella Brancaster from chicken
- Quinolone susceptibility and genetic characterization of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica isolated from pet turtles
- A Virulent Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Phage SE2 with a Strong Bacteriolytic Activity of Planktonic and Biofilmed Cells
- Molecular Mechanisms of Salmonella Pathogenicity
- Genomic Characteristics and Identification of Salmonella enterica serovars Typhi and Paratyphi A Using Multiplex PCR