Clin Orthop Surg.
2016 Dec;8(4):428-436. 10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.428.
The Influence of Arthroscopic Remplissage for Engaging Hill-Sachs Lesions Combined with Bankart Repair on Redislocation and Shoulder Function Compared with Bankart Repair Alone
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea. everest@naver.com
- KMID: 2412326
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.428
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Recurrence of glenohumeral dislocation after arthroscopic Bankart repair can be associated with a large osseous defect in the posterosuperior part of the humeral head. Our hypothesis is that remplissage is more effective to prevent recurrence of glenohumeral instability without a severe motion deficit.
METHODS
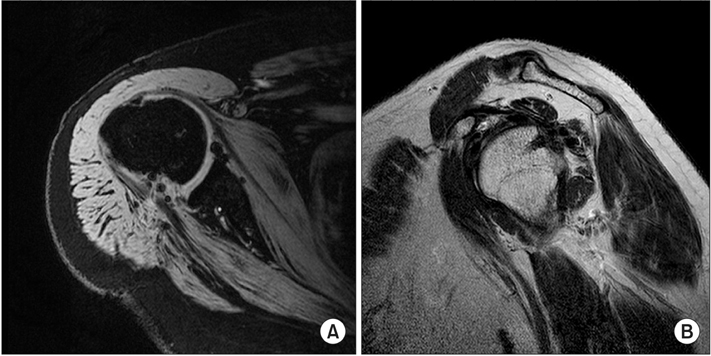
Engaging Hill-Sachs lesions were observed in 48 of 737 patients (6.5%). Twenty-four patients underwent arthroscopic Bankart repair combined with remplissage (group I) and the other 24 patients underwent arthroscopic Bankart repair alone (group II). Clinical outcomes were prospectively evaluated by assessing the range of motion. Complications, recurrence rates, and functional results were assessed utilizing the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons (ASES) score, Rowe score, and the Korean Shoulder Score for Instability (KSSI) score. Capsulotenodesis healing after remplissage was evaluated with magnetic resonance imaging.
RESULTS
The average ASES, Rowe, and KSSI scores were statistically significantly higher in group I than group II. The frequency of recurrence was statistically significantly higher in group II. The average loss in external rotation measured with the arm positioned at the side of the trunk was greater in group II and that in abduction was also higher in group II.
CONCLUSIONS
Compared to single arthroscopic Bankart repair, the remplissage procedure combined with arthroscopic Bankart repair was more effective to prevent the recurrence of anterior shoulder instability without significant impact on shoulder mobility in patients who had huge Hill-Sachs lesions.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
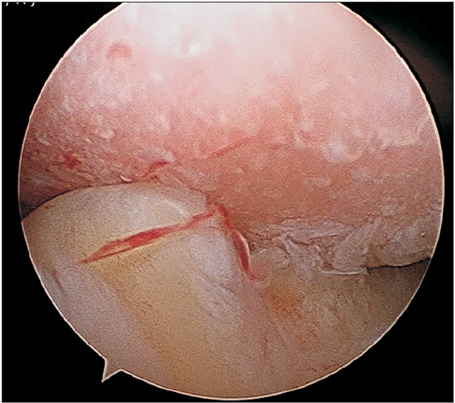
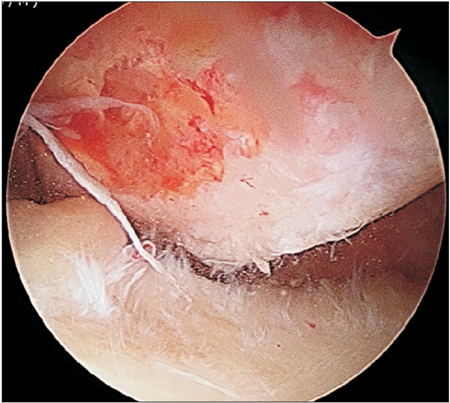
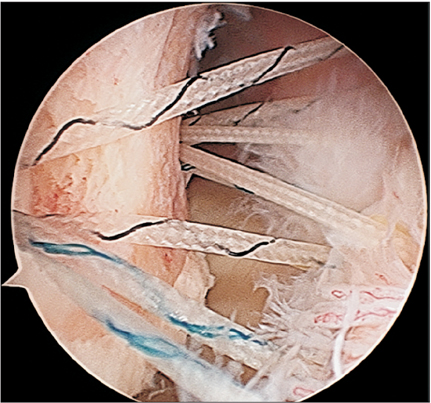
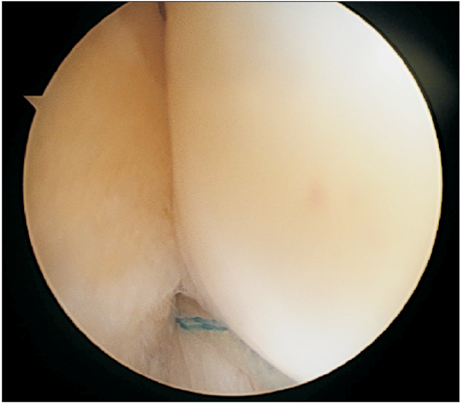
Figure
Reference
-
1. Burkhart SS, De Beer JF. Traumatic glenohumeral bone defects and their relationship to failure of arthroscopic Bankart repairs: significance of the inverted-pear glenoid and the humeral engaging Hill-Sachs lesion. Arthroscopy. 2000; 16(7):677–694.
Article2. Balg F, Boileau P. The instability severity index score: a simple pre-operative score to select patients for arthroscopic or open shoulder stabilisation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89(11):1470–1477.3. Connolly JF. Humeral head defects associated with shoulder dislocations: their diagnostic and surgical significance. Instr Course Lect. 1972; 21:42–54.4. Wolf EM, Pollack ME. Hill-Sachs "Remplissage": an arthroscopic solution for the engaging Hill-Sachs lesion. Arthroscopy. 2004; 20:Suppl 1. e14–e15.5. Purchase RJ, Wolf EM, Hobgood ER, Pollock ME, Smalley CC. Hill-Sachs "remplissage": an arthroscopic solution for the engaging Hill-Sachs lesion. Arthroscopy. 2008; 24(6):723–726.
Article6. Rowe CR, Patel D, Southmayd WW. The Bankart procedure: a long-term end-result study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978; 60(1):1–16.7. Tae SK, Rhee YG, Park TS, et al. The development and validation of an appraisal method for rotator cuff disorders: the Korean Shoulder Scoring System. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009; 18(5):689–696.
Article8. Boileau P, O'Shea K, Vargas P, Pinedo M, Old J, Zumstein M. Anatomical and functional results after arthroscopic Hill-Sachs remplissage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(7):618–626.
Article9. Lynch JR, Clinton JM, Dewing CB, Warme WJ, Matsen FA 3rd. Treatment of osseous defects associated with anterior shoulder instability. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009; 18(2):317–328.
Article10. Bushnell BD, Creighton RA, Herring MM. Bony instability of the shoulder. Arthroscopy. 2008; 24(9):1061–1073.
Article11. Weber BG, Simpson LA, Hardegger F. Rotational humeral osteotomy for recurrent anterior dislocation of the shoulder associated with a large Hill-Sachs lesion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984; 66(9):1443–1450.
Article12. Kronberg M, Brostrom LA. Proximal humeral osteotomy to correct the anatomy in patients with recurrent shoulder dislocations. J Orthop Trauma. 1991; 5(2):129–133.
Article13. Kazel MD, Sekiya JK, Greene JA, Bruker CT. Percutaneous correction (humeroplasty) of humeral head defects (Hill-Sachs) associated with anterior shoulder instability: a cadaveric study. Arthroscopy. 2005; 21(12):1473–1478.
Article14. Miniaci A, Berlet G. Recurrent anterior instability following failed surgical repair: allograft reconstruction of large humeral head defects [Abstract]. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001; 83:Suppl 1. 19–20.15. Kronberg M, Brostrom LA. Rotation osteotomy of the proximal humerus to stabilise the shoulder: five years' experience. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995; 77(6):924–927.
Article16. Re P, Gallo RA, Richmond JC. Transhumeral head plasty for large Hill-Sachs lesions. Arthroscopy. 2006; 22(7):798.e1–798.e4.
Article17. Chapovsky F, Kelly JD 4th. Osteochondral allograft transplantation for treatment of glenohumeral instability. Arthroscopy. 2005; 21(8):1007.
Article18. Haviv B, Mayo L, Biggs D. Outcomes of arthroscopic "remplissage": capsulotenodesis of the engaging large Hill-Sachs lesion. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011; 6:29.
Article19. Ko SH, Shin SM, Jo BG. Outcomes of minimally 1 year follow-up for the arthroscopic Remplissage technique with Hill-Sachs lesion. J Orthop. 2013; 10(1):41–45.
Article20. Elkinson I, Giles JW, Faber KJ, et al. The effect of the remplissage procedure on shoulder stability and range of motion: an in vitro biomechanical assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(11):1003–1012.
Article21. Franceschi F, Papalia R, Rizzello G, et al. Remplissage repair: new frontiers in the prevention of recurrent shoulder instability: a 2-year follow-up comparative study. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40(11):2462–2469.
Article22. Wolf EM, Arianjam A. Hill-Sachs remplissage, an arthroscopic solution for the engaging Hill-Sachs lesion: 2- to 10-year follow-up and incidence of recurrence. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014; 23(6):814–820.
Article23. Nourissat G, Kilinc AS, Werther JR, Doursounian L. A prospective, comparative, radiological, and clinical study of the influence of the "remplissage" procedure on shoulder range of motion after stabilization by arthroscopic Bankart repair. Am J Sports Med. 2011; 39(10):2147–2152.
Article24. Park MJ, Tjoumakaris FP, Garcia G, Patel A, Kelly JD 4th. Arthroscopic remplissage with Bankart repair for the treatment of glenohumeral instability with Hill-Sachs defects. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27(9):1187–1194.
Article25. Park MJ, Garcia G, Malhotra A, Major N, Tjoumakaris FP, Kelly JD 4th. The evaluation of arthroscopic remplissage by high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40(10):2331–2336.
Article26. McCabe MP, Weinberg D, Field LD, O'Brien MJ, Hobgood ER, Savoie FH 3rd. Primary versus revision arthroscopic reconstruction with remplissage for shoulder instability with moderate bone loss. Arthroscopy. 2014; 30(4):444–450.
Article27. Koo SS, Burkhart SS, Ochoa E. Arthroscopic double-pulley remplissage technique for engaging Hill-Sachs lesions in anterior shoulder instability repairs. Arthroscopy. 2009; 25(11):1343–1348.
Article28. Barlow B, Peace W, Metzger PK, Leonardelli D, Solomon DJ. Clinical grading of Hill-Sachs injuries: association with glenoid bone loss and clinical application of the "glenoid track" concept: when is there humeral head engagement? In : Proceedings of the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine 2010 Annual Meeting; 2010 Jul 15-18; Providence, RI. Rosemont, IL: American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine;2010.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Arthroscopic remplissage: history, indications, and clinical outcomes
- Arthroscopic Stabilization Using Remplissage Technique in Recurrent Shoulder Instability with Large Hill-Sachs Lesion
- Review in Remplissage on Anterior Shoulder Instability with Huge Hill-Sachs Lesion
- Hill-Sachs Lesion on MR Arthrography of the Shoulder: Relationship with Bankart Lesion on Arthroscopy and Frequency of Shoulder Dislocations
- Results According to Arthroscopic Repair Methods of Bankart Lesion (Operative Methods According to Labral Tear)