Clin Endosc.
2018 Mar;51(2):129-136. 10.5946/ce.2018.039.
Foreign Body Ingestion in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea. jihugy@chungbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2410978
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2018.039
Abstract
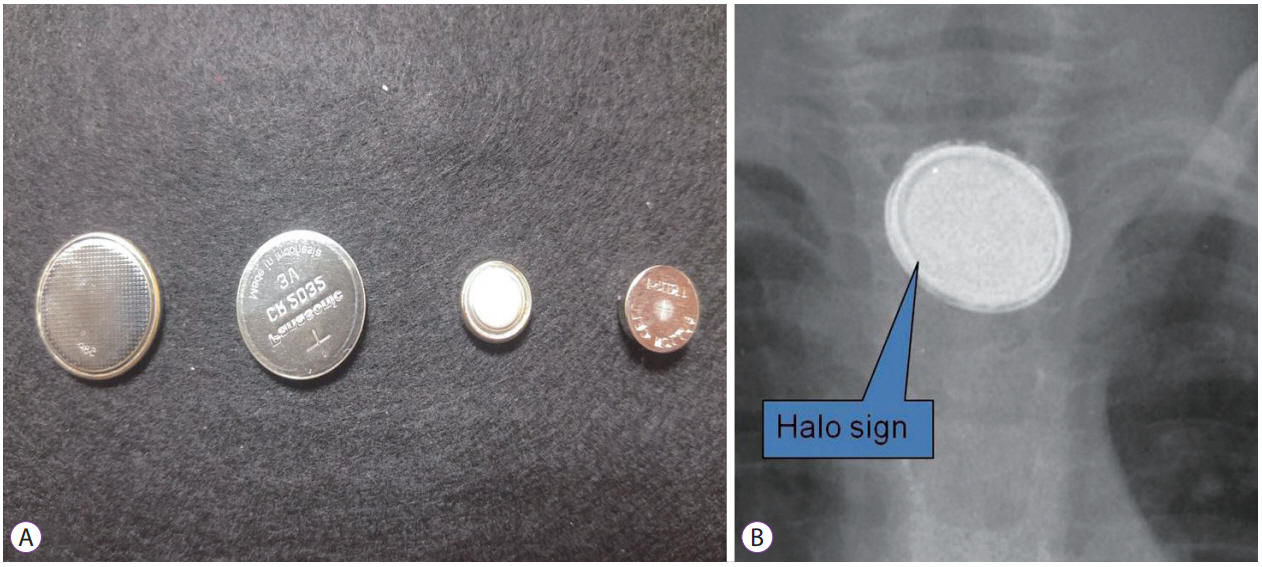
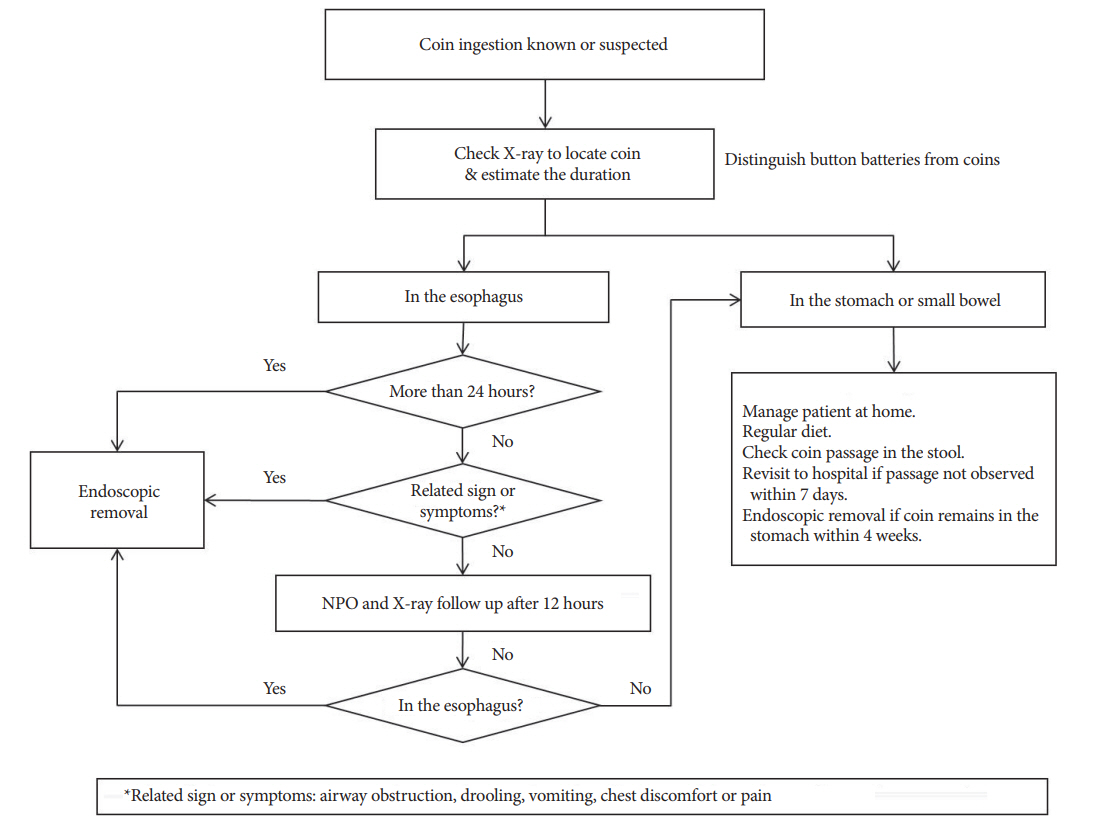
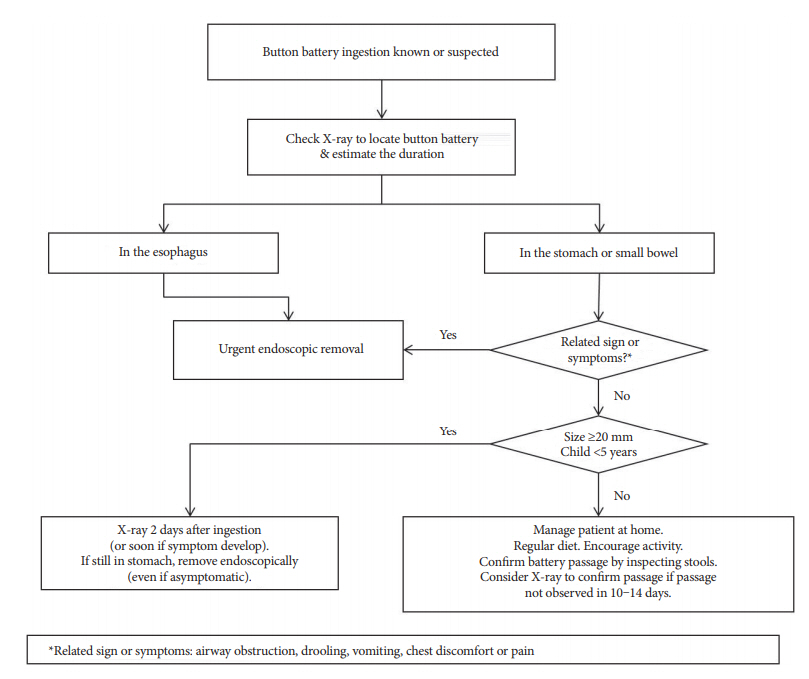
- Foreign body (FB) ingestion in children is common and most children are observed to be between 6 months and 3 years of age. Although most FBs in the gastrointestinal tract pass spontaneously without complications, endoscopic or surgical removal may be required in a few children. Thus, FB ingestion presents a significant clinical difficulty in pediatric gastroenterological practice. Parameters that need to be considered regarding the timing of endoscopic removal of ingested FBs in children are the children's age or body weight, the clinical presentation, time lapse since ingestion, time of last meal, type as well as size and shape of the FB, and its current location in the gastrointestinal tract. Esophageal button batteries require emergency removal regardless of the presence of symptoms because they can cause serious complications. Coins, magnets, or sharp FBs in the esophagus should be removed within 2 hours in symptomatic and within 24 hours in asymptomatic children. Among those presenting with a single or multiple magnets and a metallic FB that have advanced beyond the stomach, symptomatic children need a consultation with a pediatric surgeon for surgery, and asymptomatic children may be followed with serial X-rays to assess progression. Sharp or pointed, and long or large and wide FBs located in the esophagus or stomach require endoscopic removal.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Button Battery Ingestion in Children: A Specific Clinical Issue
Francesco Macchini, Elettra Vestri, Martina Ichino, Anna Morandi, Giorgio Fava, Ernesto Leva
Clin Endosc. 2018;51(6):602-603. doi: 10.5946/ce.2018.137.
Reference
-
1. Seo JK. Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal foreign bodies in children. Indian J Pediatr. 1999; 66(1 Suppl):S75–S80.2. Litovitz TL, Klein-Schwartz W, White S, et al. 2000 annual report of the American association of poison control centers toxic exposure surveillance system. Am J Emerg Med. 2001; 19:337–395.
Article3. Lee JH, Nam SH, Lee JH, Lee HJ, Choe YH. Spontaneous passage of gastrointestinal foreign bodies in children. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007; 10:157–165.
Article4. Alexander W, Kadish JA, Dunbar JS. Ingested foreign bodies in children. In : Kaufmann HJ, editor. Progress in pediatric radiology. 2nd ed. Chicago (IL): Yearbook Medical Publishers;1969. p. 256–285.5. Panieri E, Bass DH. The management of ingested foreign bodies in children--a review of 663 cases. Eur J Emerg Med. 1995; 2:83–87.6. Lim CW, Park MH, Do HJ, et al. Factors associated with removal of impactted fishbone in children, suspected ingestion. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2016; 19:168–174.
Article7. Brayer AF, Conners GP, Ochsenschlager DW. Spontaneous passage of coins lodged in the upper esophagus. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1998; 44:59–61.
Article8. Waltzman ML. Management of esophageal coins. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2006; 18:571–574.
Article9. Kramer RE, Lerner DG, Lin T, et al. Management of ingested foreign bodies in children: a clinical report of the NASPGHAN endoscopy committee. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015; 60:562–574.10. Chen X, Milkovich S, Stool D, van As AB, Reilly J, Rider G. Pediatric coin ingestion and aspiration. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2006; 70:325–329.
Article11. Waltzman ML, Baskin M, Wypij D, Mooney D, Jones D, Fleisher G. A randomized clinical trial of the management of esophageal coins in children. Pediatrics. 2005; 116:614–619.
Article12. Conners GP, Chamberlain JM, Ochsenschlager DW. Symptoms and spontaneous passage of esophageal coins. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1995; 149:36–39.
Article13. Chen MK, Beierle EA. Gastrointestinal foreign bodies. Pediatr Ann. 2001; 30:736–742.
Article14. Cheng W, Tam PK. Foreign-body ingestion in children: experience with 1,265 cases. J Pediatr Surg. 1999; 34:1472–1476.
Article15. ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Ikenberry SO, Jue TL, et al. Management of ingested foreign bodies and food impactions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73:1085–1091.
Article16. Litovitz T, Whitaker N, Clark L, White NC, Marsolek M. Emerging battery-ingestion hazard: clinical implications. Pediatrics. 2010; 125:1168–1177.
Article17. Litovitz T, Whitaker N, Clark L. Preventing battery ingestions: an analysis of 8648 cases. Pediatrics. 2010; 125:1178–1183.
Article18. Lee JH, Lee JH, Shim JO, Lee JH, Eun BL, Yoo KH. Foreign body ingestion in children: should button batteries in the stomach be urgently removed? Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2016; 19:20–28.
Article19. Hwang JB, Park MH, Choi SO, Park WH, Kim AS. How strong construction toy magnets are! A gastro-gastro-duodenal fistula formation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007; 44:291–292.
Article20. Lin CH, Chen AC, Tsai JD, Wei SH, Hsueh KC, Lin WC. Endoscopic removal of foreign bodies in children. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2007; 23:447–452.
Article21. Lee JH, Lee JS, Kim MJ, Choe YH. Initial location determines spontaneous passage of foreign bodies from the gastrointestinal tract in children. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2011; 27:284–289.
Article22. Hussain SZ, Bousvaros A, Gilger M, et al. Management of ingested magnets in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012; 55:239–242.
Article23. Tokar B, Cevik AA, Ilhan H. Ingested gastrointestinal foreign bodies: predisposing factors for complications in children having surgical or endoscopic removal. Pediatr Surg Int. 2007; 23:135–139.
Article24. McComas BC, van Miles P, Katz BE. Successful salvage of an 8-monthold child with an aortoesophageal fistula. J Pediatr Surg. 1991; 26:1394–1395.
Article25. Stricker T, Kellenberger CJ, Neuhaus TJ, Schwoebel M, Braegger CP. Ingested pins causing perforation. Arch Dis Child. 2001; 84:165–166.26. Aktay AN, Werlin SL. Penetration of the stomach by an accidentally ingested straight pin. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002; 34:81–82.
Article27. Palta R, Sahota A, Bemarki A, Salama P, Simpson N, Laine L. Foreign-body ingestion: characteristics and outcomes in a lower socioeconomic population with predominantly intentional ingestion. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69(3 Pt 1):426–433.
Article28. Paul RI, Christoffel KK, Binns HJ, Jaffe DM. Foreign body ingestions in children: risk of complication varies with site of initial health care contact. Pediatric practice research group. Pediatrics. 1993; 91:121–127.29. Ayantunde AA, Oke T. A review of gastrointestinal foreign bodies. Int J Clin Pract. 2006; 60:735–739.
Article30. Kim JK, Kim SS, Kim JI, et al. Management of foreign bodies in the gastrointestinal tract: an analysis of 104 cases in children. Endoscopy. 1999; 31:302–304.
Article31. Velitchkov NG, Grigorov GI, Losanoff JE, Kjossev KT. Ingested foreign bodies of the gastrointestinal tract: retrospective analysis of 542 cases. World J Surg. 1996; 20:1001–1005.
Article32. Zhang S, Cui Y, Gong X, Gu F, Chen M, Zhong B. Endoscopic management of foreign bodies in the upper gastrointestinal tract in South China: a retrospective study of 561 cases. Dig Dis Sci. 2010; 55:1305–1312.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ingested Foreign Body Trapped in the Appendix: A Case Report
- Ingested Gastrointestinal Foreign Body in Children: Retrospective Review in a Pediatric Emergency Department
- Prevention and management of foreign body ingestion and aspiration during the dental treatment
- The survey on foreign body ingestion and aspiration during the dental prosthetic treatment
- A Gastric Magnetic Foreign Body Incidentally Detected Several Years after Ingestion