Diabetes Metab J.
2018 Feb;42(1):74-81. 10.4093/dmj.2018.42.1.74.
Lack of Evidence of the Role of APOA5 3’UTR Polymorphisms in Iranian Children and Adolescents with Metabolic Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Genetics, Faculty of Basic Sciences, Shahrekord University, Shahrekord, Iran.
- 2Research Institute of Biotechnology, Shahrekord University, Shahrekord, Iran.
- 3Pediatric Inherited Diseases Research Center, Research Institute for Primordial Prevention of Non-communicable Disease, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. pnikpour@med.mui.ac.ir
- 4Department of Genetics and Molecular Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran.
- 5Child Growth and Development Research Center, Research Institute for Primordial Prevention of Non-communicable Disease, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran.
- KMID: 2409188
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.1.74
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a complex and multifactorial disorder characterized by insulin resistance, dyslipidaemia, hyperglycemia, abdominal obesity, and elevated blood pressure. The apolipoprotein A5 (APOA5) gene variants have been reported to correlate with two major components of MetS, including low levels of high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and high levels of triglyceride. In the present study, we explored the associations between five single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of APOA5 gene and the MetS risk.
METHODS
In a case-control design, 120 Iranian children and adolescents with/without MetS were genotyped by polymerase chain reaction-sequencing for these SNPs. Then, we investigated the association of SNPs, individually or in haplotype constructs, with MetS risk.
RESULTS
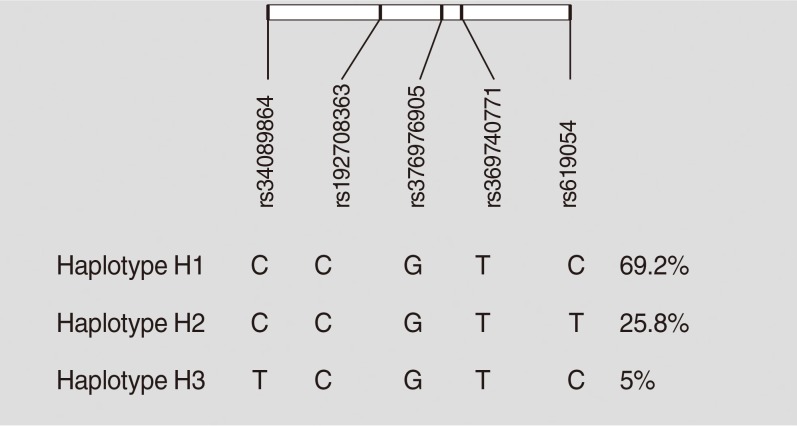
The rs34089864 variant and H1 haplotype (harboring the two major alleles of rs619054 and rs34089864) were associated with HDL-C levels. However, there was no significant association between different haplotypes/individual SNPs and MetS risk.
CONCLUSION
These results presented no association of APOA5 3'UTR SNPs with MetS. Further studies, including other polymorphisms, are required to investigate the involvement of APOA5 gene in the genetic susceptibility to MetS in the pediatric age group.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Is Diabetes & Metabolism Journal Eligible to Be Indexed in MEDLINE?
Sun Huh
Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(6):472-474. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0089.
Reference
-
1. Pollex RL, Hegele RA. Genetic determinants of the metabolic syndrome. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2006; 3:482–489. PMID: 16932765.
Article2. Roche HM, Phillips C, Gibney MJ. The metabolic syndrome: the crossroads of diet and genetics. Proc Nutr Soc. 2005; 64:371–377. PMID: 16048671.
Article3. Chien KL, Hsu HC, Chen YC, Su TC, Lee YT, Chen MF. Association between sequence variant of c.553 G > T in the apolipoprotein A5 gene and metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and carotid atherosclerosis. Transl Res. 2009; 154:133–141. PMID: 19665689.4. Nilsson SK, Heeren J, Olivecrona G, Merkel M. Apolipoprotein A-V: a potent triglyceride reducer. Atherosclerosis. 2011; 219:15–21. PMID: 21831376.
Article5. Zhang Z, Peng B, Gong RR, Gao LB, Du J, Fang DZ, Song YY, Li YH, Ou GJ. Apolipoprotein A5 polymorphisms and risk of coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis. Biosci Trends. 2011; 5:165–172. PMID: 21914952.
Article6. Alexander R, Lodish H, Sun L. MicroRNAs in adipogenesis and as therapeutic targets for obesity. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011; 15:623–636. PMID: 21355787.
Article7. Heneghan HM, Miller N, Kerin MJ. Role of microRNAs in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Obes Rev. 2010; 11:354–361. PMID: 19793375.
Article8. Hu Z, Bruno AE. The influence of 3’UTRs on microRNA function inferred from human SNP data. Comp Funct Genomics. 2011; 2011:910769. PMID: 22110399.
Article9. Ye Q, Zhao X, Xu K, Li Q, Cheng J, Gao Y, Du J, Shi H, Zhou L. Polymorphisms in lipid metabolism related miRNA binding sites and risk of metabolic syndrome. Gene. 2013; 528:132–138. PMID: 23911300.
Article10. Ziebarth JD, Bhattacharya A, Chen A, Cui Y. PolymiRTS Database 2.0: linking polymorphisms in microRNA target sites with human diseases and complex traits. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012; 40:D216–D221. PMID: 22080514.
Article11. Jorgensen AB, Frikke-Schmidt R, West AS, Grande P, Nordestgaard BG, Tybjaerg-Hansen A. Genetically elevated non-fasting triglycerides and calculated remnant cholesterol as causal risk factors for myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2013; 34:1826–1833. PMID: 23248205.12. Pare G, Serre D, Brisson D, Anand SS, Montpetit A, Tremblay G, Engert JC, Hudson TJ, Gaudet D. Genetic analysis of 103 candidate genes for coronary artery disease and associated phenotypes in a founder population reveals a new association between endothelin-1 and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Am J Hum Genet. 2007; 80:673–682. PMID: 17357073.13. Silander K, Alanne M, Kristiansson K, Saarela O, Ripatti S, Auro K, Karvanen J, Kulathinal S, Niemela M, Ellonen P, Vartiainen E, Jousilahti P, Saarela J, Kuulasmaa K, Evans A, Perola M, Salomaa V, Peltonen L. Gender differences in genetic risk profiles for cardiovascular disease. PLoS One. 2008; 3:e3615. PMID: 18974842.
Article14. Salehi S, Emadi-Baygi M, Rezaei M, Kelishadi R, Nikpour P. Identification of a new single-nucleotide polymorphism within the apolipoprotein A5 gene, which is associated with metabolic syndrome. Adv Biomed Res. 2017; 6:24. PMID: 28401071.
Article15. Kelishadi R, Ardalan G, Gheiratmand R, Adeli K, Delavari A, Majdzadeh R. Caspian Study Group. Paediatric metabolic syndrome and associated anthropometric indices: the CASPIAN Study. Acta Paediatr. 2006; 95:1625–1634. PMID: 17129973.
Article16. National High. Update on the 1987 task force report on high blood pressure in children and adolescents: a working group report from the national high blood pressure education program. Pediatrics. 1996; 98(4 Pt 1):649–658. PMID: 8885941.17. Bao L, Zhou M, Wu L, Lu L, Goldowitz D, Williams RW, Cui Y. PolymiRTS Database: linking polymorphisms in microRNA target sites with complex traits. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007; 35:D51–D54. PMID: 17099235.
Article18. Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS, Sander C. The microRNA.org resource: targets and expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008; 36:D149–D153. PMID: 18158296.
Article19. Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005; 120:15–20. PMID: 15652477.
Article20. Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics. 2005; 21:263–265. PMID: 15297300.
Article21. Lin DY, Zeng D, Millikan R. Maximum likelihood estimation of haplotype effects and haplotype-environment interactions in association studies. Genet Epidemiol. 2005; 29:299–312. PMID: 16240443.
Article22. Lin DY, Zeng D. Likelihood-based inference on haplotype effects in genetic association studies. J Am Stat Assoc. 2006; 101:89–104.
Article23. Dorfmeister B, Cooper JA, Stephens JW, Ireland H, Hurel SJ, Humphries SE, Talmud PJ. The effect of APOA5 and APOC3 variants on lipid parameters in European Whites, Indian Asians and Afro-Caribbeans with type 2 diabetes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007; 1772:355–363. PMID: 17197160.
Article24. Lai CQ, Demissie S, Cupples LA, Zhu Y, Adiconis X, Parnell LD, Corella D, Ordovas JM. Influence of the APOA5 locus on plasma triglyceride, lipoprotein subclasses, and CVD risk in the Framingham Heart Study. J Lipid Res. 2004; 45:2096–2105. PMID: 15342688.
Article25. Martinelli N, Trabetti E, Bassi A, Girelli D, Friso S, Pizzolo F, Sandri M, Malerba G, Pignatti PF, Corrocher R, Olivieri O. The −1131 T>C and S19W APOA5 gene polymorphisms are associated with high levels of triglycerides and apolipoprotein C-III, but not with coronary artery disease: an angiographic study. Atherosclerosis. 2007; 191:409–417. PMID: 16682041.26. Nabika T, Nasreen S, Kobayashi S, Masuda J. The genetic effect of the apoprotein AV gene on the serum triglyceride level in Japanese. Atherosclerosis. 2002; 165:201–204. PMID: 12417270.
Article27. Kao JT, Wen HC, Chien KL, Hsu HC, Lin SW. A novel genetic variant in the apolipoprotein A5 gene is associated with hypertriglyceridemia. Hum Mol Genet. 2003; 12:2533–2539. PMID: 12915450.
Article28. Grallert H, Sedlmeier EM, Huth C, Kolz M, Heid IM, Meisinger C, Herder C, Strassburger K, Gehringer A, Haak M, Giani G, Kronenberg F, Wichmann HE, Adamski J, Paulweber B, Illig T, Rathmann W. APOA5 variants and metabolic syndrome in Caucasians. J Lipid Res. 2007; 48:2614–2621. PMID: 17768309.
Article29. Pullinger CR, Aouizerat BE, Movsesyan I, Durlach V, Sijbrands EJ, Nakajima K, Poon A, Dallinga-Thie GM, Hattori H, Green LL, Kwok PY, Havel RJ, Frost PH, Malloy MJ, Kane JP. An apolipoprotein A-V gene SNP is associated with marked hypertriglyceridemia among Asian-American patients. J Lipid Res. 2008; 49:1846–1854. PMID: 18441017.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents
- Metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents
- Therapeutic approaches to obesity and metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents
- Clinical Predictive Factors for Metabolic Syndrome in Obese Children and Adolescents
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome among Children and Adolescents in Korea