Perinatology.
2018 Mar;29(1):27-32. 10.14734/PN.2018.29.1.27.
Echocardiographic Flow Pattern of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Infants with Respiratory Distress: Compared with Other Echocardiographic Parameters
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cbmin@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2409109
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/PN.2018.29.1.27
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The different patterns of ductal shunt flow by Doppler echocardiography are useful for the diagnosis and prediction of risk of hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), especially growing or pulsatile patterns. We examined whether the ductal flow patterns might represent a reliable guide for PDA management in preterm infants with respiratory distress, using a comparison of traditional echocardiographic parameters.
METHODS
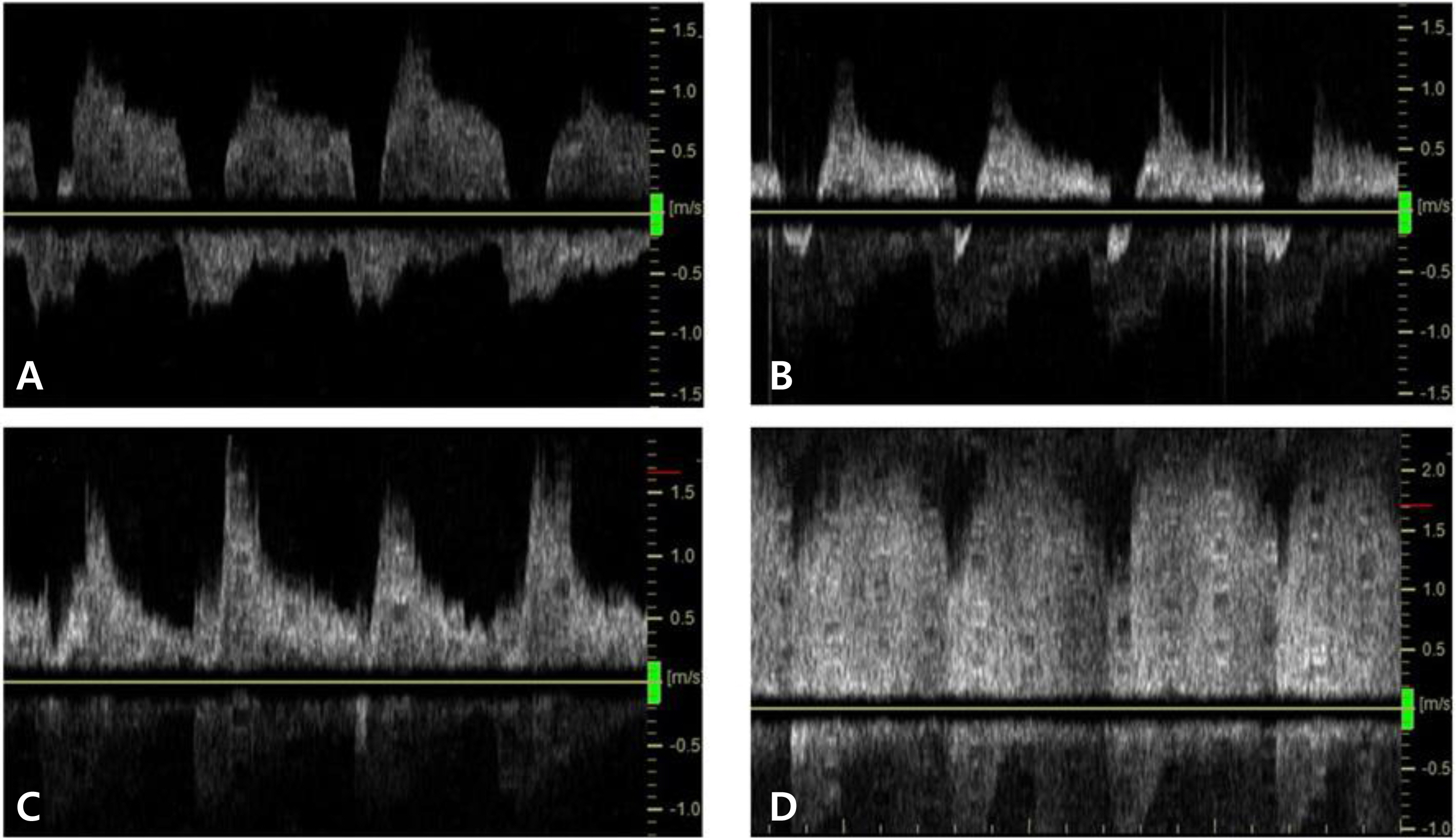
Thirty-one preterm infants with gestational age of 25-34 weeks who required respiratory supports were studied. Serial echocardiographic evaluations were performed within the first week after birth. Four ductal flow patterns were identified such as pulmonary hypertension pattern, growing pattern, pulsatile pattern and closing pattern and compared with other echocardiographic indices.
RESULTS
One hundred five echocardiographic evaluations were done. The ductal diameter varied widely within each pattern but was significantly associated with ductal flow pattern: median diameter was greatest in the pulmonary hypertension pattern, progressively narrowed across the growing and pulsatile patterns, and was smallest in the closing pattern. The ratio of the ductal diameter to weight, the ratio of the left atrial to aortic root diameter and the diastolic flow velocity in left pulmonary artery of the growing and pulsatile patterns were significantly higher than those of the pulmonary hypertension and closing patterns.
CONCLUSION
Echocardiographic Doppler assessment of shunt flow pattern is useful for diagnosis of hemodynamically significant PDA in premature infants, especially in the growing or pulsatile pattern. The addition of ductal flow pattern assessment to traditional echocardiographic measures may further enhance the clinical diagnostic capacity of echocardiography for PDA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Skinner J. Diagnosis of patent ductus arteriosus. Semin Neonatol. 2001. 6:49–61.
Article2). El Hajjar M., Vaksmann G., Rakza T., Kongolo G., Storme L. Severity of the ductal shunt: a comparison of different markers. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2005. 90:F419–22.
Article3). McNamara PJ., Sehgal A. Towards rational management of the patent ductus arteriosus: the need for disease staging. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2007. 92:F424–7.
Article4). Sehgal A., McNamara PJ. Does echocardiography facilitate determination of hemodynamic significance attributable to the ductus arteriosus? Eur J Pediatr. 2009. 168:907–14.
Article5). Sehgal A., Paul E., Menahem S. Functional echocardiography in staging for ductal disease severity: role in predicting outcomes. Eur J Pediatr. 2013. 172:179–84.6). Su BH., Watanabe T., Shimizu M., Yanagisawa M. Echocardiographic assessment of patent ductus arteriosus shunt flow pattern in premature infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1997. 77:F36–40.
Article7). Tavera MC., Bassareo PP., Biddau R., Montis S., Neroni P., Tumbarello R. Role of echocardiography on the evaluation of patent ductus arteriosus in newborns. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2009. 22(Suppl 3):10–3.
Article8). Sasi A., Deorari A. Patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. Indian Pediatr. 2011. 48:301–8.
Article9). Choi BM., Lee KH., Eun BL., Yoo KH., Hong YS., Son CS, et al. Utility of rapid B-type natriuretic peptide assay for diagnosis of symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 2005. 115:e255–61.
Article10). Shin J., Lee EH., Lee JH., Choi BM., Hong YS. Individualized ibuprofen treatment using serial B-type natriuretic peptide measurement for symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus in very preterm infants. Korean J Pediatr. 2017. 60:175–80.
Article11). Su BH., Peng CT., Tsai CH. Echocardiographic flow pattern of patent ductus arteriosus: a guide to indomethacin treatment in premature infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1999. 81:F197–200.
Article12). Su BH., Lin HC., Chiu HY., Hsieh HY., Chen HH., Tsai YC. Comparison of ibuprofen and indometacin for early-targeted treatment of patent ductus arteriosus in extremely premature infants: a randomised controlled trial. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2008. 93:F94–9.
Article13). Takami T., Yoda H., Kawakami T., Yamamura H., Nakanishi T., Nakazawa M, et al. Usefulness of indomethacin for patent ductus arteriosus in fullterm infants. Pediatr Cardiol. 2007. 28:46–50.
Article14). Condo M., Evans N., Bellu R., Kluckow M. Echocardiographic assessment of ductal significance: retrospective comparison of two methods. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2012. 97:F35–8.
Article15). Visconti LF., Morhy SS., Deutsch AD., Tavares GM., Wilberg TJ., Rossi Fde S. Clinical and echocardiographic characteristics associated with the evolution of the ductus arteriosus in the neonate with birth weight lower than 1,500g. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2013. 11:317–23.16). Occhipinti F., De Carolis MP., De Rosa G., Bersani I., Lacerenza S., Cota F, et al. Correlation analysis between echocardiographic flow pattern and N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide for early targeted treatment of patent ductus arteriosus. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014. 27:1800–4.
Article17). Dix L., Molenschot M., Breur J., de Vries W., Vijlbrief D., Groenendaal F, et al. Cerebral oxygenation and echocardiographic parameters in preterm neonates with a patent ductus arteriosus: an observational study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2016. 101:F520–6.
Article18). Lista G., Bianchi S., Mannarino S., Schena F., Castoldi F., Stronati M, et al. Velocity time integral for right upper pulmonary vein in VLBW infants with patent ductus arteriosus. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2016. 71:580–5.
Article19). Bapat R., Aggarwal S., Natarajan G. A right-to-left or bidirectional ductal shunt in preterm neonates: grave implication? Am J Perinatol. 2011. 28:709–14.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation of B-type natriuretic peptide levels and echocardiographic parameters in preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus
- Hemodynamic Effects on Systemic Blood Flow and Ductal Shunting Flow after Loading Dose of Intravenous Caffeine in Preterm Infants according to the Patency of Ductus Arteriosus
- Usefulness of Pasma Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Concentration in the Diagnosis of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Infants
- Reliability of Diastolic Flow Velocity of the Left Pulmonary Artery for the Diagnosis of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Infants
- Evaluation of echocardiographic markers in dogs with patent ductus arteriosus after ductal closure