J Rheum Dis.
2018 Apr;25(2):144-147. 10.4078/jrd.2018.25.2.144.
Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Combined with Erosive Arthritis was Treated Successfully with Tocilizumab: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rheumatology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. nakhada@naver.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2408933
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2018.25.2.144
Abstract
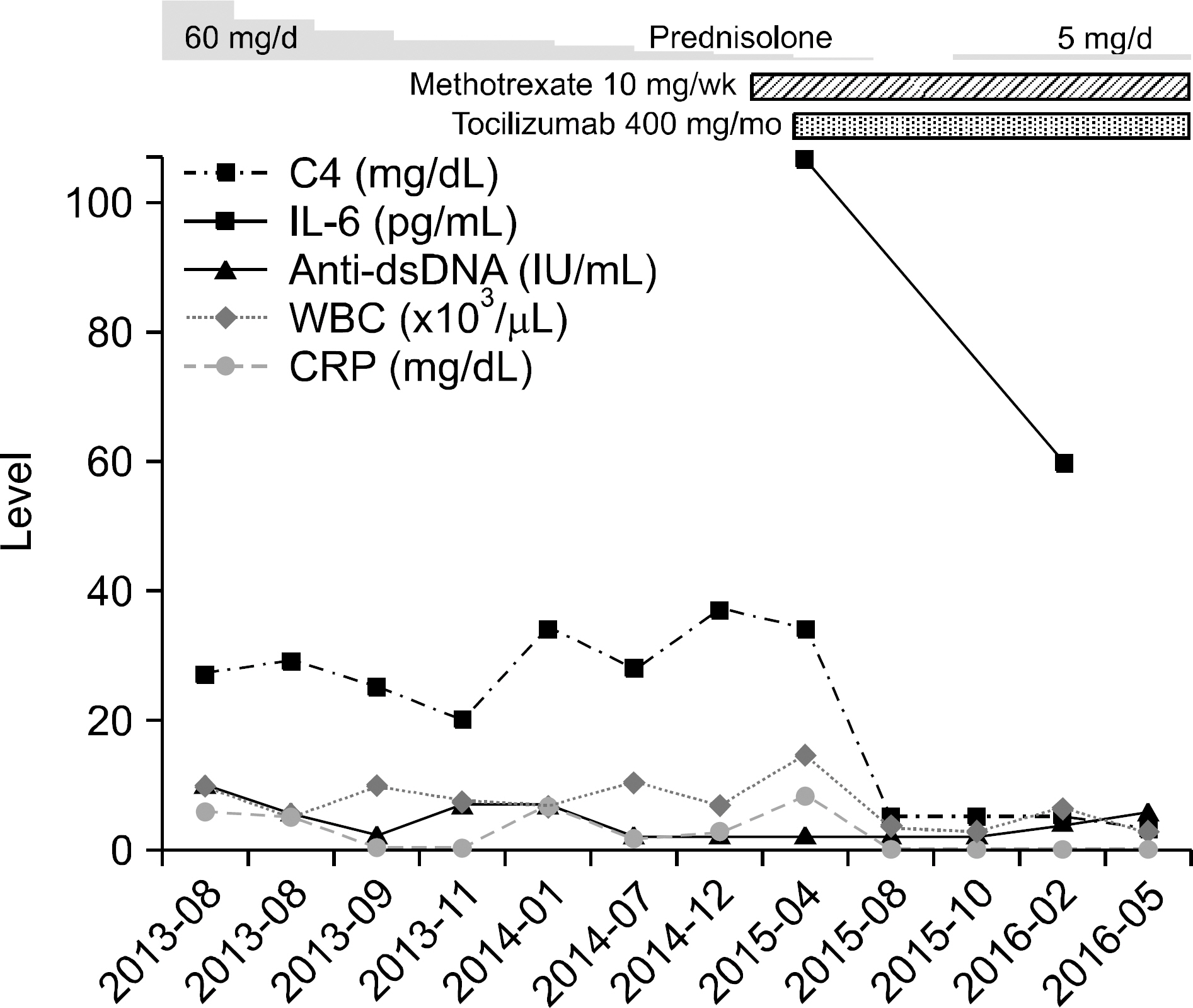
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a systemic autoimmune inflammatory disease that frequently involves the joints at some stage during the disease course. Although lupus arthritis is usually non-erosive, approximately 5% of patients develop erosions. This paper reports a patient with SLE combined with erosive arthritis, who was treated successfully with tocilizumab. A 20-year-old female, who was first diagnosed with SLE at the age of 13 years, had been admitted frequently to hospital with disease flare-ups during the previous 3 years. Despite aggressive treatment, her arthritis became aggravated, particularly in both wrists and the right knee. Radiologically, erosive arthritis was noted in the wrists.The serum interleukin (IL)-6 level was elevated significantly along with the other inflammatory markers. After the tocilizumab treatment, the arthritis subsided with a normalization of the IL-6 level, suggesting that tocilizumab may be a suitable treatment for lupus erosive arthritis if the IL-6 level is high.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aptekar RG, Lawless OJ, Decker JL. Deforming non-erosive arthritis of the hand in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974; (100):120–4.
Article2. Richter Cohen M, Steiner G, Smolen JS, Isenberg DA. Erosive arthritis in systemic lupus erythematosus: analysis of a distinct clinical and serological subset. Br J Rheumatol. 1998; 37:421–4.
Article3. Fernández A, Quintana G, Rondón F, Restrepo JF, Sánchez A, Matteson EL, et al. Lupus arthropathy: a case series of patients with rhupus. Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 25:164–7.
Article4. Amezcua-Guerra LM, Márquez-Velasco R, Bojalil R. Erosive arthritis in systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with high serum C-reactive protein and anticyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies. Inflamm Res. 2008; 57:555–7.
Article5. Chun HY, Chung JW, Kim HA, Yun JM, Jeon JY, Ye YM, et al. Cytokine IL-6 and IL-10 as biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Immunol. 2007; 27:461–6.
Article6. Linker-Israeli M, Deans RJ, Wallace DJ, Prehn J, Ozeri-Chen T, Klinenberg JR. Elevated levels of endogenous IL-6 in systemic lupus erythematosus. A putative role in pathogenesis. J Immunol. 1991; 147:117–23.7. Klashman DJ, Martin RA, Martínez-Maza O, Stevens RH. In vitro regulation of B cell differentiation by interleukin-6 and soluble CD23 in systemic lupus erythematosus B cell subpopulations and antigen-induced normal B cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1991; 34:276–86.
Article8. Alarcón-Segovia D, Abud-Mendoza C, Diaz-Jouanen E, Iglesias A, De los Reyes V, Hernández-Ortiz J. Deforming arthropathy of the hands in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1988; 15:65–9.9. Nzeusseu Toukap A, Galant C, Theate I, Maudoux AL, Lories RJ, Houssiau FA, et al. Identification of distinct gene expression profiles in the synovium of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 56:1579–88.
Article10. Budhram A, Chu R, Rusta-Sallehy S, Ioannidis G, Denburg JA, Adachi JD, et al. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide anti-body as a marker of erosive arthritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lupus. 2014; 23:1156–63.
Article11. Ball EM, Gibson DS, Bell AL, Rooney MR. Plasma IL-6 levels correlate with clinical and ultrasound measures of arthritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2014; 23:46–56.
Article12. Illei GG, Shirota Y, Yarboro CH, Daruwalla J, Tackey E, Takada K, et al. Tocilizumab in systemic lupus erythematosus: data on safety, preliminary efficacy, and impact on circulating plasma cells from an open-label phase I dos-age-escalation study. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:542–52.
Article13. Kamata Y, Minota S. Successful treatment of massive intractable pericardial effusion in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus with tocilizumab. BMJ Case Rep. 2012; DOI: DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2012-007834.
Article14. Makol A, Gibson LE, Michet CJ. Successful use of interleukin 6 antagonist tocilizumab in a patient with refractory cutaneous lupus and urticarial vasculitis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2012; 18:92–5.
Article15. García-Hernández FJ, González-León R, Castillo-Palma MJ, Ocaña-Medina C, Sánchez-Román J. Tocilizumab for treating refractory haemolytic anaemia in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012; 51:1918–9.16. Korkmaz HI, Krijnen PAJ, Ulrich MMW, de Jong E, van Zuijlen PPM, Niessen HWM. The role of complement in the acute phase response after burns. Burns. 2017; 43:1390–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adalimumab-induced Lupus Erythematosus Profundus in a Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient
- A Case of Rheumatoid Nodule in a Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patient
- A Case of Septic Arthritis Caused by Salmonella Group D in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- A Case of Transverse Myelitis as a First Manifestation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- A Ruptured Aneurysm in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Case Report