J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2017 Dec;24(4):211-220. 10.4184/jkss.2017.24.4.211.
Clinical and Radiographic Results of Artificial Disc Replacement Combined with Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Versus Two-Level Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion in Two-Level Cervical Disc Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital-affiliated to Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jshin2100@gmail.com
- KMID: 2408189
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2017.24.4.211
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Retrospective case-control study.
OBJECTIVES
To compare the clinical and radiographic outcomes of a hybrid construct (HC) of cervical artificial disc replacement (CADR) combined with anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) (group I) with 2-level ACDF (group II) in patients with 2-level cervical disc disease. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: ACDF is reported to potentially promote degenerative changes in the adjacent segment. CADR has been expected to reduce the risk of adjacent segment degeneration. However, its clinical course has yet to be sufficiently clarified.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
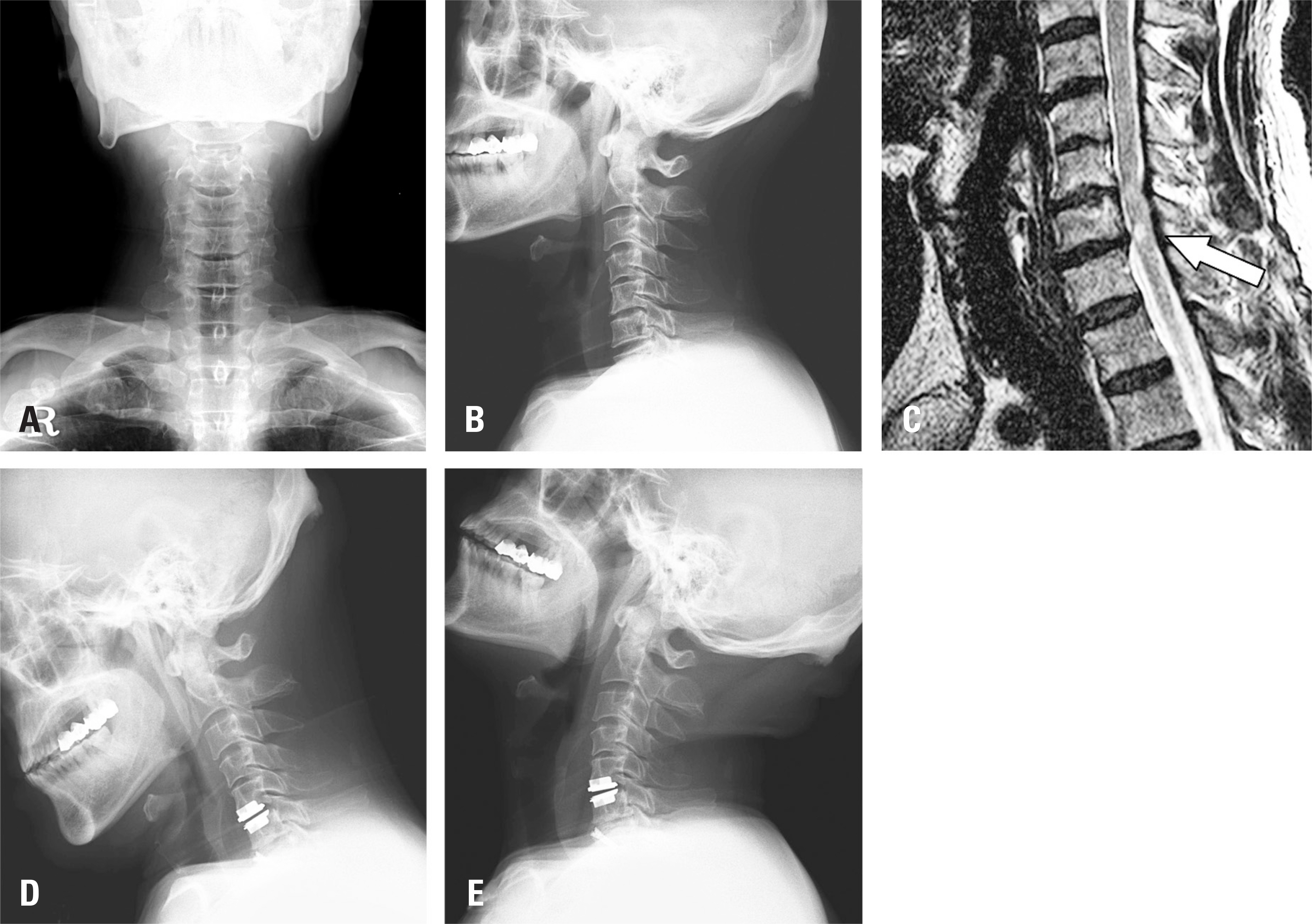
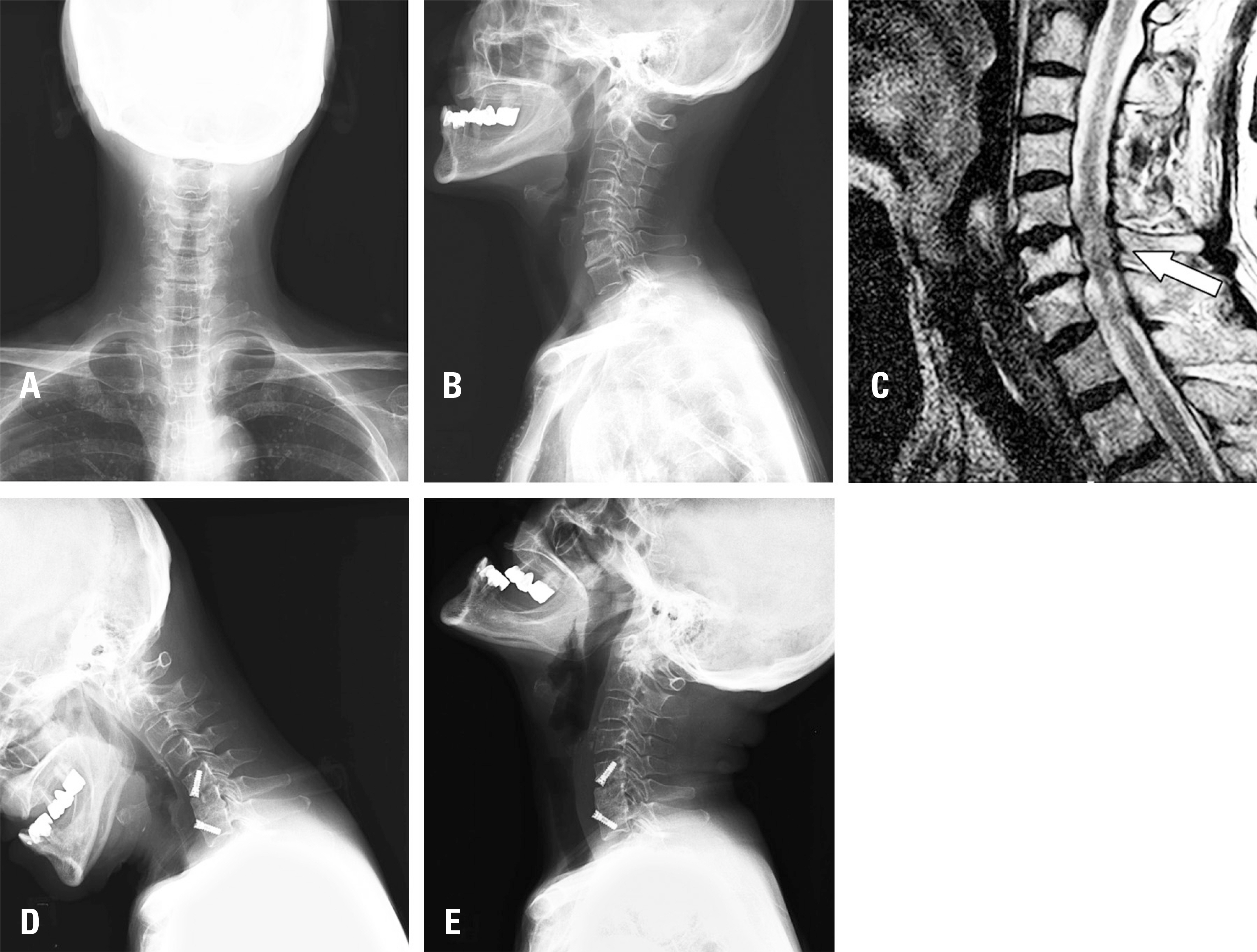
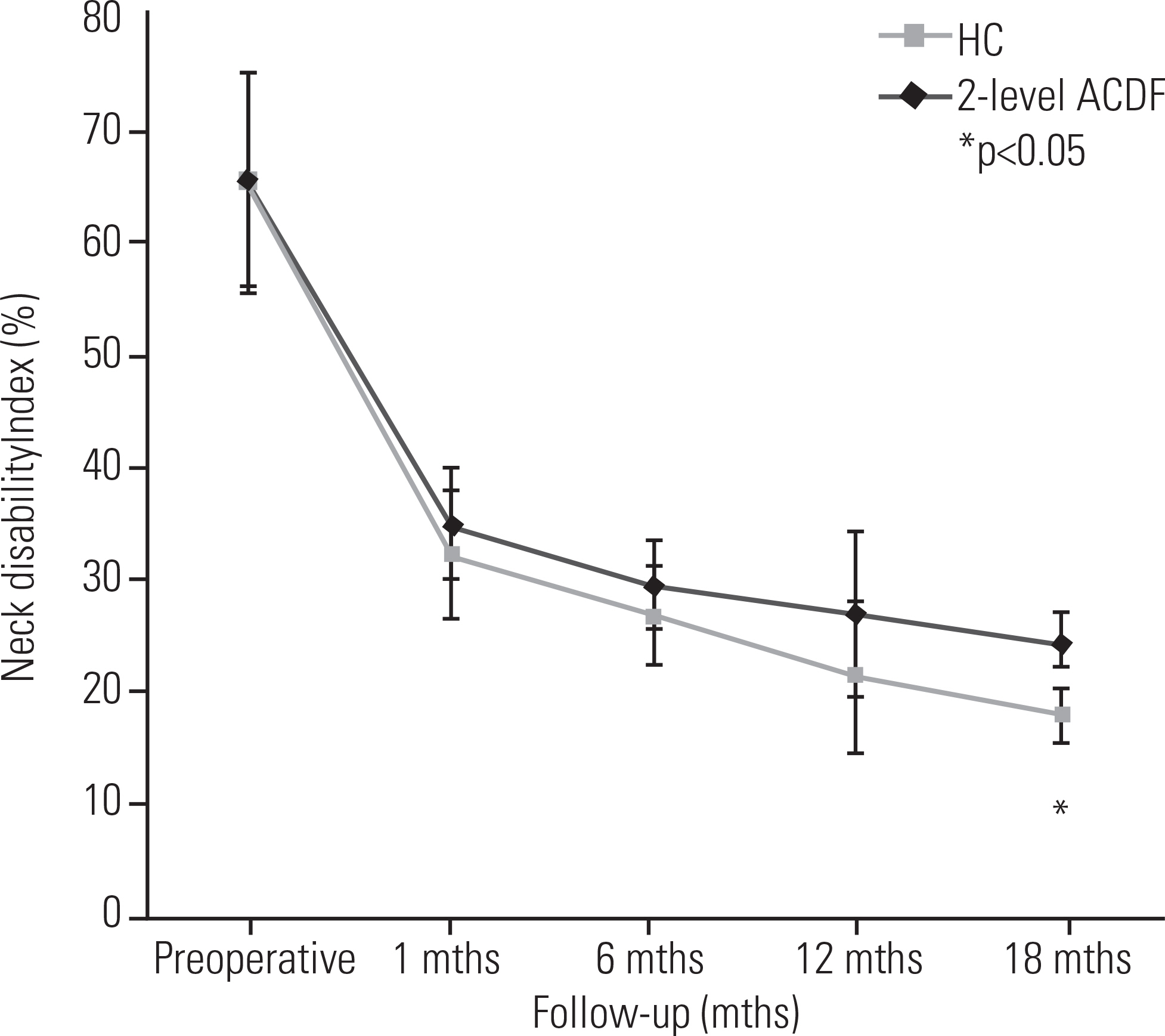
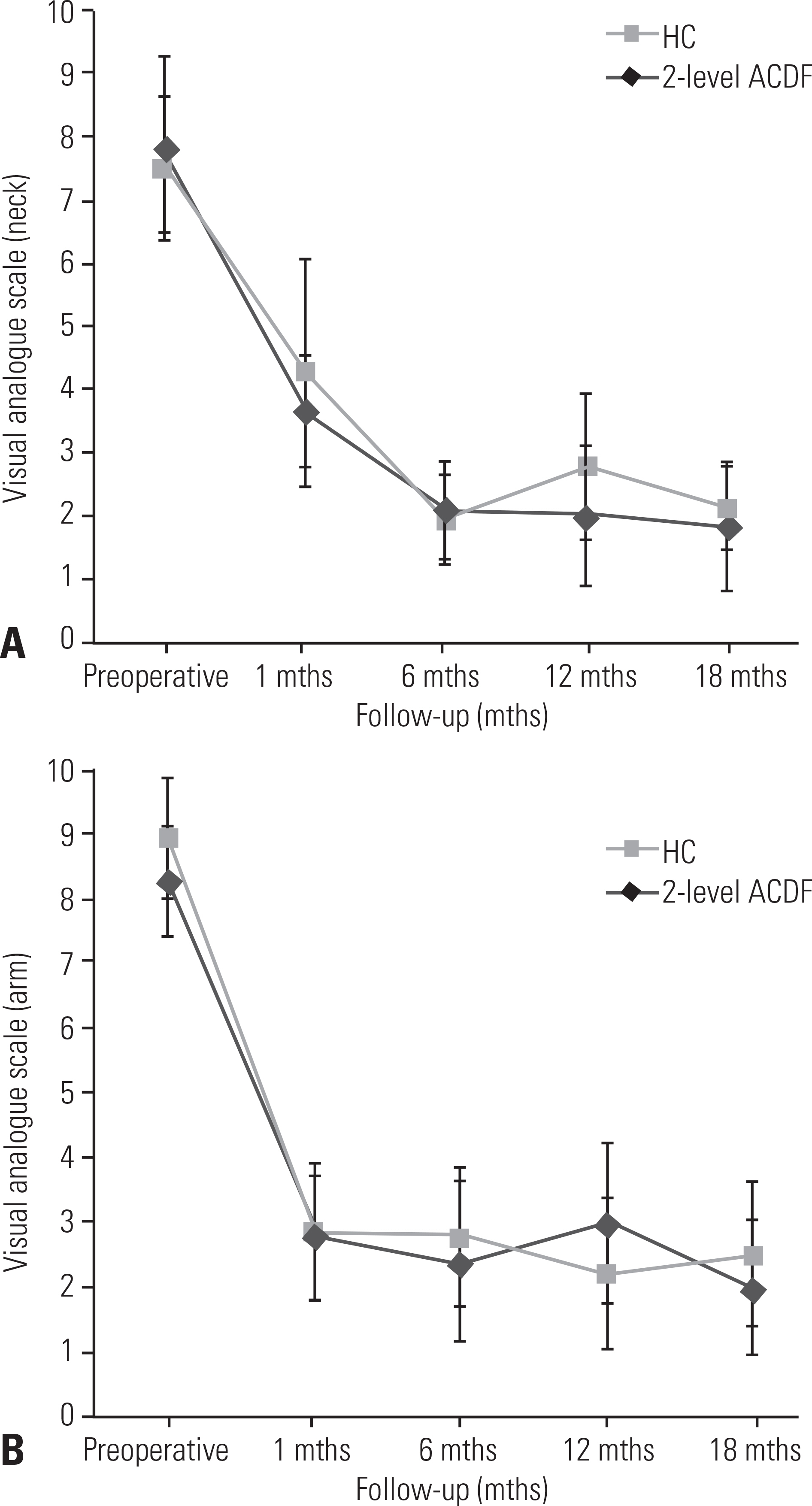
Twenty-six patients underwent 2-level cervical disc surgery. Single-level CADR combined with ACDF was performed in 14 patients. Twelve patients underwent 2-level ACDF. Clinical profiles were assessed using the neck disability index (NDI) and visual analogue scale scores of arm and neck pain. Dynamic lateral cervical radiographs were obtained preoperatively and at 1, 6, 12, and 18 months postoperatively. The range of motion (ROM) of the overall cervical spine (C2-7) and the adjacent segments was measured.
RESULTS
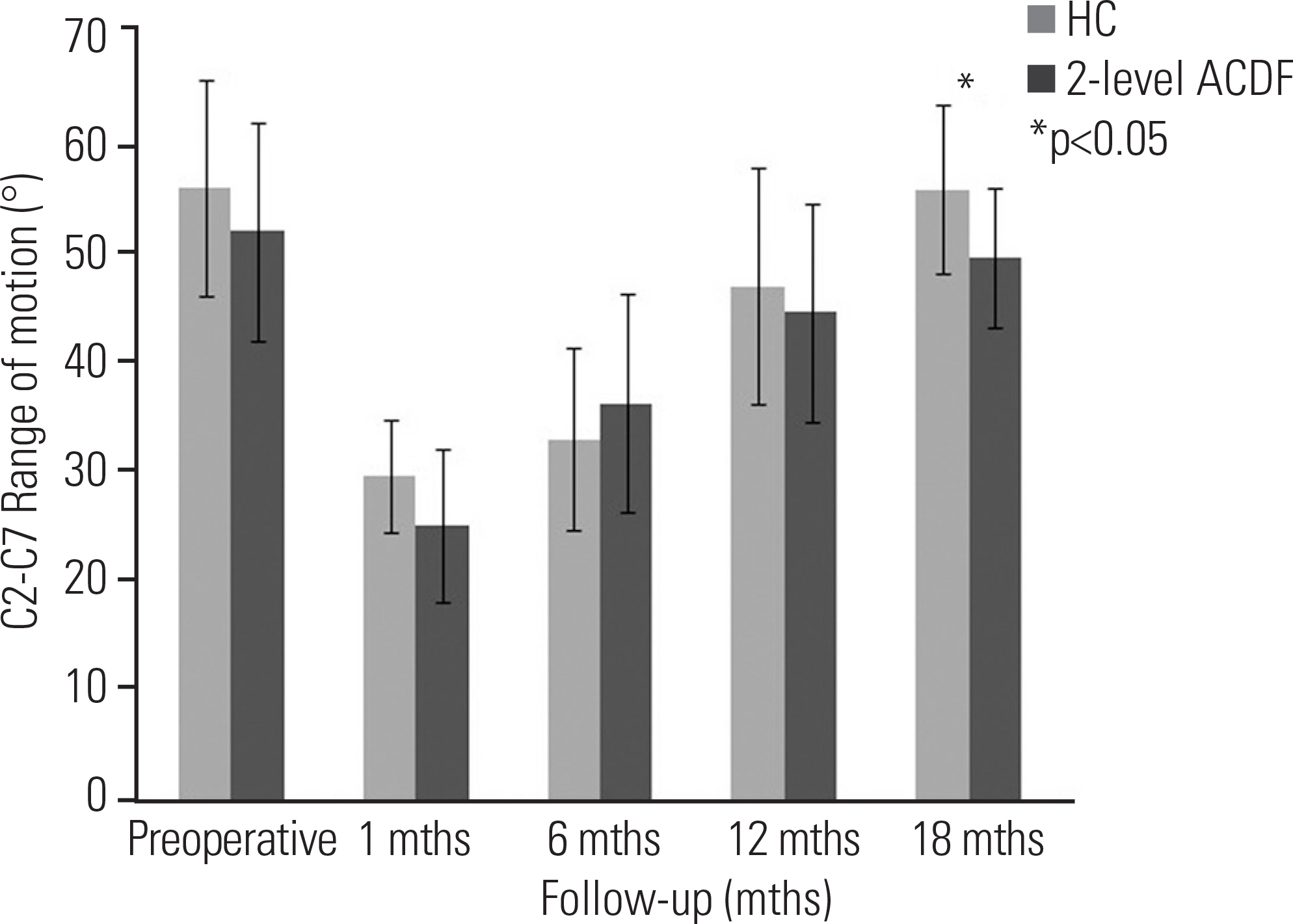
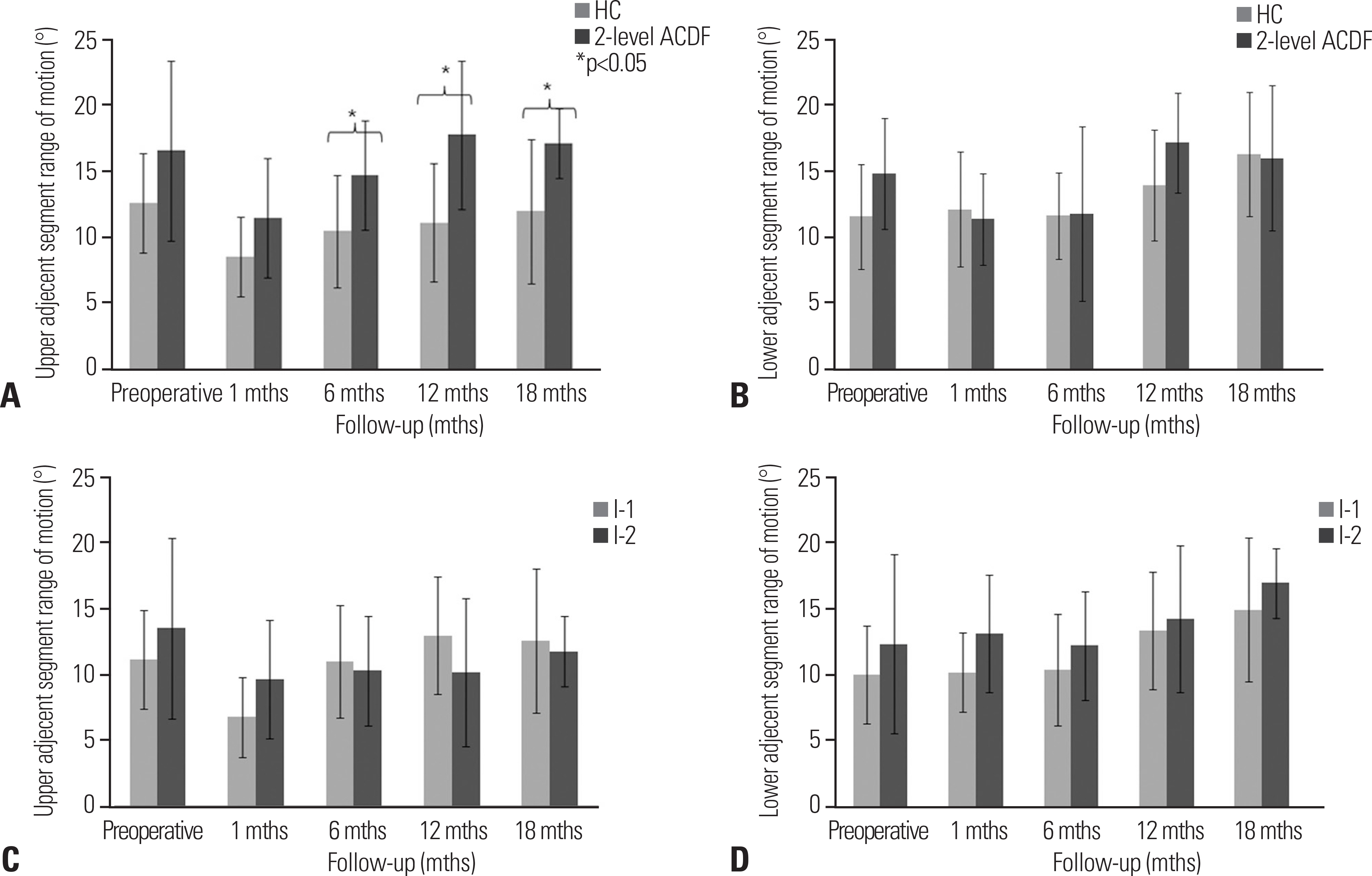
Group I showed superior NDI 18 months postoperatively (p < 0.05). The mean C2-7 ROM of both groups recovered to the preoperative ROM. At 18 months postoperatively, the C2-7 ROM of group I was higher than that of group II (p < 0.05). The superior adjacent segment ROM was higher in group II (p < 0.05), starting at 6 months. The inferior adjacent segment ROM showed no significant difference between the groups (p>0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The HC group showed comparable clinical and radiographic outcomes to those of the 2-level ACDF group. HC can be used selectively in the treatment of patients with 2-level cervical disc disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bohlman HH, Emery SE, Goodfellow DB, et al. Robinson anterior cervical discectomy and arthrodesis for cervical radiculopathy. Long-term follow-up of one hundred and twenty-two patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993 Sep; 75(9):1298–307. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-199309000-00005.
Article2. Hilibrand AS, Carlson GD, Palumbo MA, et al. Radiculopathy and myelopathy at segments adjacent to the site of a previous anterior cervical arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999 Apr; 81(4):519–28. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-199904000-00009.
Article3. Cheng L, Nie L, Zhang L, et al. Fusion versus Bryan Cervical Disc in two-level cervical disc disease: a prospective, randomised study. Int Orthop. 2009 Oct; 33(5):1347–51. DOI: 10.1007/s00264-008-0655-3.
Article4. DiAngelo DJ, Foley KT, Vossel KA, et al. Anterior cervical plating reverses load transfer through multilevel strut-grafts. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000 Apr 1; 25(7):783–95. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-200004010-00005.
Article5. Emery SE, Bohlman HH, Bolesta MJ, et al. Anterior cervical decompression and arthrodesis for the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Two to seventeen-year followup. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998 Jul; 80(7):941–51. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-199807000-00002.
Article6. Liu F, Cheng J, Komistek RD, et al. In vivo evaluation of dynamic characteristics of the normal, fused, and disc replacement cervical spines. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007 Nov 1; 32(23):2578–84. DOI: 10.1097/brs.0b013e318158cdf8.
Article7. Pickett GE, Rouleau JP, Duggal N. Kinematic analysis of the cervical spine following implantation of an artificial cervical disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005 Sep 1; 30(17):194954. DOI: 10.1097/01.brs.0000176320.82079.ce.
Article8. Sasso RC, Smucker JD, Hacker RJ, et al. Artificial disc versus fusion: a prospective, randomized study with 2-year follow-up on 99 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007 Dec 15; 32(26):2933–40. discussion 2941-2. DOI: 10.1097/brs.0b013e31815d0034.9. Yi S, Kim SH, Shin HC, et al. Cervical arthroplasty in a patient with Klippel-Feil syndrome. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2007 Aug; 149(8):805–9. DOI: 10.1007/s00701-007-1115-7.
Article10. Yi S, Shin HC, Kim KN, et al. Modified techniques to prevent sagittal imbalance after cervical arthroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007 Aug 15; 32(18):1986–91. DOI: 10.1097/brs.0b013e318133fb99.
Article11. Satomi K, Ogawa J, Ishii Y, et al. Short-term complications and long-term results of expansive open-door laminoplasty for cervical stenotic myelopathy. Spine J. 2001 Jan-Feb; 1(1):26–30. DOI: 10.1016/s1529-9430 (01)00008-0.
Article12. Moatz B, Tortolani PJ. Cervical disc arthroplasty: Pros and cons. Surg Neurol Int. 2012; 3(3 Suppl):216–24. DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.98582.
Article13. Matsunaga S, Kabayama S, Yamamoto T, et al. Strain on intervertebral discs after anterior cervical decompression and fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999 Apr 1; 24(7):670–5. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-199904010-00011.
Article14. Dmitriev AE, Cunningham BW, Hu N, et al. Adjacent level intradiscal pressure and segmental kinematics following a cervical total disc arthroplasty: an in vitro human cadaveric model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005 May 15; 30(10):116572. DOI: 10.1097/01.brs.0000162441.23824.95.15. Hilibrand AS, Yoo JU, Carlson GD, et al. The success of anterior cervical arthrodesis adjacent to a previous fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997 Jul 15; 22(14):1574–9. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-199707150-00009.
Article16. Hilibrand AS, Robbins M. Adjacent segment degeneration and adjacent segment disease: the consequences of spinal fusion? Spine J. 2004 Nov-Dec; 4(6 Suppl):190–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.spinee.2004.07.007.
Article17. Schwab JS, Diangelo DJ, Foley KT. Motion compensation associated with single-level cervical fusion: where does the lost motion go? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006 Oct 1; 31(21):2439–48. DOI: 10.1097/01. brs.0000239125.54761.23.
Article18. Park DH, Ramakrishnan P, Cho TH, et al. Effect of lower two-level anterior cervical fusion on the superior adjacent level. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007 Sep; 7(3):336–40. DOI: 10.3171/spi-07/09/336.
Article19. Sekhon LH. Two-level artificial disc placement for spondylotic cervical myelopathy. J Clin Neurosci. 2004 May; 11(4):412–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.jocn.2003.10.001.
Article20. Cho BY, Lim J, Sim HB, et al. Biomechanical analysis of the range of motion after placement of a two-level cervical ProDisc-C versus hybrid construct. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010 Sep 1; 35(19):1769–76. DOI: 10.1097/brs.0b013e3181c225fa.
Article21. Mummaneni PV, Burkus JK, Haid RW, et al. Clinical and radiographic analysis of cervical disc arthroplasty compared with allograft fusion: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007 Mar; 6(3):198–209. DOI: 10.3171/spi.2007.6.3.198.
Article22. Gore DR, Sepic SB. Anterior cervical fusion for degenerated or protruded discs. A review of one hundred forty-six patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1984 Oct; 9(7):667–71.23. Ishihara H, Kanamori M, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical interbody fusion. Spine J. 2004 Nov-Dec; 4(6):624–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.spinee.2004.04.011.
Article24. Ausman JI. Evaluation of motion produced in adjacent segments after use of an anterior cervical cage or artificial cervical disc: evaluation of a recently published study in the Journal of Neurosurgery Spine 2005. Surg Neurol. 2006 May; 65(5):522–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.surneu.2006.02.030.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Comparison of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion versus Fusion Combined with Artificial Disc Replacement for Treating 3-Level Cervical Spondylotic Disease
- Anterior Cervical Discectomy
- Total Cervical Disc Replacement using Artificial Disc in Cervical Disc Herniations
- Recycling of Cervical Artificial Disc for the Symptomatic Adjacent Segment Disorder Combined with Instability on Total Disc Replacement Area: A Case Report
- Analysis of Noninstrumented Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Interbody Fusion in Degenerative Cervical Disease