Korean J Gastroenterol.
2018 Mar;71(3):162-167. 10.4166/kjg.2018.71.3.162.
Severe Intraperitoneal Hemorrhage from Pseudoaneurysm after a Large-volume Paracentesis, Successfully Treated with Microcoil Embolization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. rshdrryu@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2407673
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2018.71.3.162
Abstract
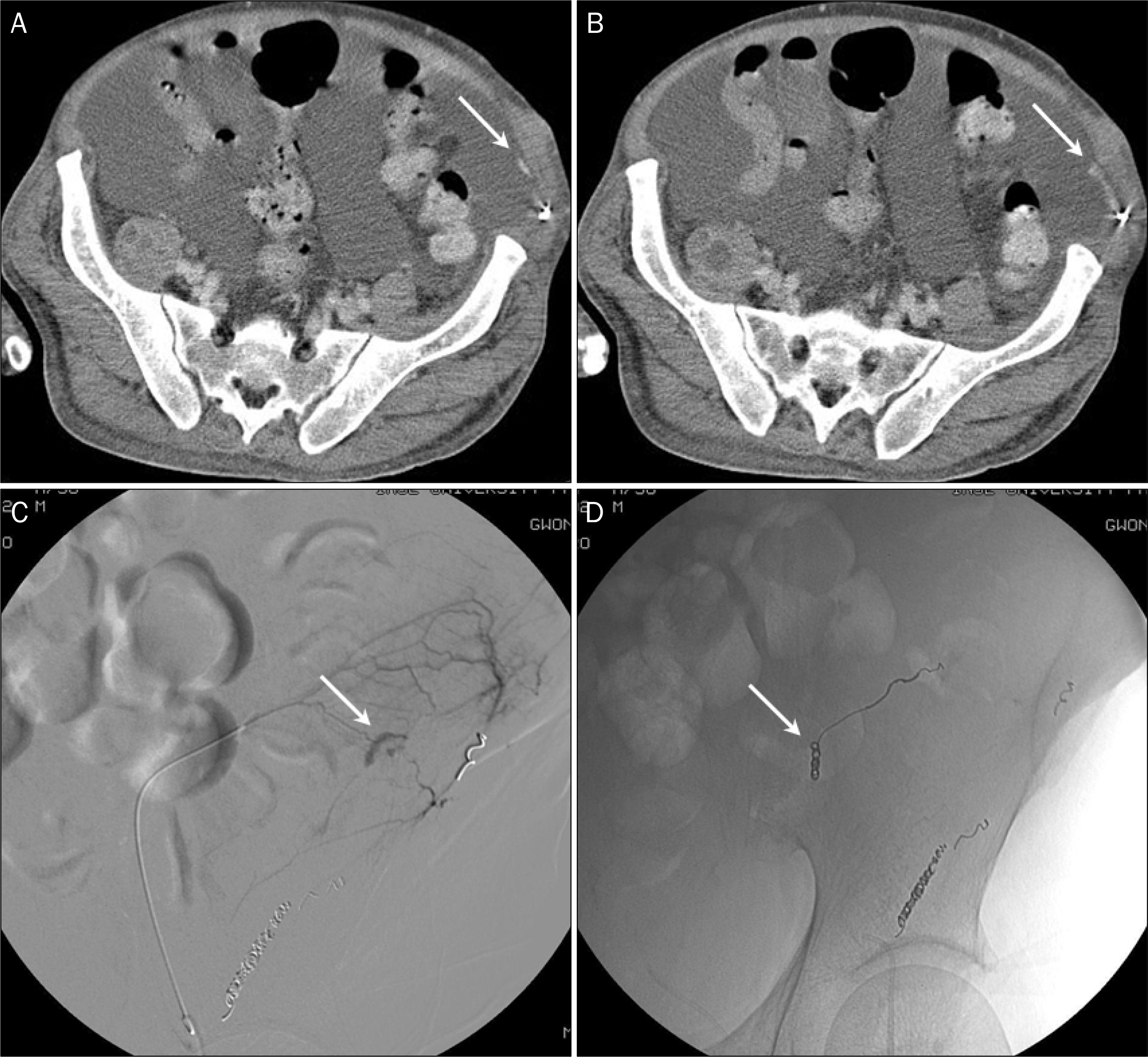
- Large-volume paracentesis-induced intraperitoneal hemorrhage due to pseudoaneurysm formation is rarely reported. Here, we present a 56-year-old man with alcoholic liver cirrhosis admitted for massive ascites. Large-volume paracentesis was performed. Three days later, he became pale and complained of dyspnea and abdominal distention with hypotension. Percutaneous iliac angiography revealed contrast media leakage from a branch of the left circumflex iliac artery with pseudoaneurysm. He was successfully treated with microcoil embolization. Several days later, ascitic fluid increased and large-volume paracentesis was performed again. Two days later, his hemoglobin level suddenly decreased. An abdominal computed tomography scan showed new active bleeding at the left lower lateral peritoneal cavity, just anterior to the metalic coils. Percutaneous iliac angiography revealed contrast media extravasation from a branch of the left inferior epigastric artery with formation of collateral vessel. Percutaneous embolization was successfully performed again. After coil embolization, there were no further bleeding episodes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aneurysm, False*
Angiography
Ascites
Ascitic Fluid
Contrast Media
Dyspnea
Embolization, Therapeutic
Epigastric Arteries
Extravasation of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Materials
Hemorrhage*
Humans
Hypotension
Iliac Artery
Liver Cirrhosis
Liver Cirrhosis, Alcoholic
Middle Aged
Paracentesis*
Peritoneal Cavity
Contrast Media
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Runyon BA. Paracentesis of ascitic fluid. A safe procedure. Arch Intern Med. 1986; 146:2259–2261.
Article2. Runyon BA. Practice Guidelines Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). Management of adult abdominals with ascites due to cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2004; 39:841–856.3. Lam EY, McLafferty RB, Taylor LM Jr, et al. Inferior epigastric abdominal pseudoaneurysm: a complication of paracentesis. J Vasc Surg. 1998; 28:566–569.4. Ferrer JV, Soriano P, Zazpe C, Vicente F, Herrera J, Lera JM. Pseudoaneurysm of the inferior epigastric artery. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Arch Surg. 1996; 131:102–103.5. Gage TS, Sussman SK, Conard FU 3rd, Hull D, Bartus SA. Pseudoaneurysm of the inferior epigastric artery: diagnosis and percutaneous treatment. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990; 155:529–530.
Article6. Runyon BA. Ascites and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Feldman M, Friedman LS, Sleisenger MH, editors. Sleisenger & Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Management. Volume. 2:7th ed.Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Company;2002. p. 1517–1542.
Article7. Pache I, Bilodeau M. Severe haemorrhage following abdominal paracentesis for ascites in patients with liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005; 21:525–529.
Article8. Martinet O, Reis ED, Mosimann F. Delayed hemoperitoneum abdominal large-volume paracentesis in a patient with cirrhosis and ascites. Dig Dis Sci. 2000; 45:357–358.9. Arnold C, Haag K, Blum HE, Rössle M. Acute hemoperitoneum abdominal large-volume paracentesis. Gastroenterology. 1997; 113:978–982.10. Webster ST, Brown KL, Lucey MR, Nostrant TT. Hemorrhagic abdominals of large volume abdominal paracentesis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996; 91:366–368.11. Lin S, Wang M, Zhu Y, et al. Hemorrhagic complications following abdominal paracentesis in acute on chronic liver failure: a propensity score analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e2225.12. Lin CH, Shih FY, Ma MH, Chiang WC, Yang CW, Ko PC. Should bleeding tendency deter abdominal paracentesis? Dig Liver Dis. 2005; 37:946–951.
Article13. Grabau CM, Crago SF, Hoff LK, et al. Performance standards for therapeutic abdominal paracentesis. Hepatology. 2004; 40:484–488.
Article14. Sobkin PR, Bloom AI, Wilson MW, et al. Massive abdominal wall hemorrhage from injury to the inferior epigastric artery: a abdominal review. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008; 19:327–332.15. Makund A, Kumar Dp, Condati NK, Bhadoria AS, Sarin SK. Efficacy and safety of ultrasound guided percutaneous glue abdominal in iatrogenic haemorrhagic complications of abdominal and thoracocentesis in cirrhotic patients. Br J Radiol. 2018; 91:20170259.16. Mallory A, Schaefer JW. Complications of diagnostic paracentesis in patients with liver disease. JAMA. 1978; 239:628–630.
Article17. Park SW, Choe WH, Lee CH, et al. Transcatheter embolization of a pseudoaneurysm of the inferior epigastric artery with N-butyl cyanoacrylate. Br J Radiol. 2008; 81:e64–e67.
Article18. Takase K, Kazama T, Abe K, et al. Pseudoaneurysm of the inferior epigastric artery successfully treated by ultrasound-guided compression. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2004; 27:520–522.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Splanchnic Artery Pseudoaneurysm: Transcatheter Embolization
- Embolization of gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm caused by chronic pancreatitis: a case report
- A Case of the Ruptured Pseudoaneurysm of Gastroduodenal Artery Treated by Transcatheter Embolization
- Pseudoaneurysm of uterine artery causing intra-abdominal and vaginal bleeding after cervical conization
- Therapeutic Embolization for Pseudoaneurysm of the LateralInferior Genicular Artery after Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Case Report