Obstet Gynecol Sci.
2015 May;58(3):256-259. 10.5468/ogs.2015.58.3.256.
Pseudoaneurysm of uterine artery causing intra-abdominal and vaginal bleeding after cervical conization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea. sjeon@schmc.ac.kr
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2148940
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.2015.58.3.256
Abstract
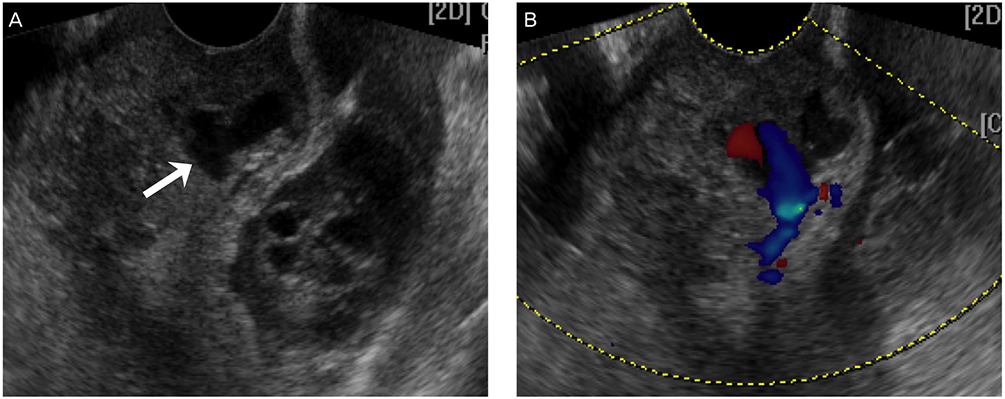
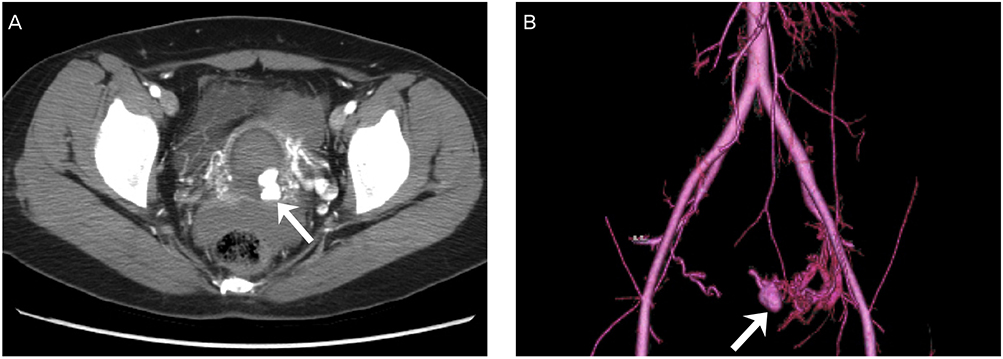
- Uterine arterial pseudoaneurysm is a very rare condition usually associated with postpartum hemorrhage. It almost never occurs after cervical conization; however, since ruptured pseudoaneurysm could be life threatening, we should consider the possibility of vascular injury such as pseudoaneurysm when we find a patient with vaginal bleeding after the process of surgical operation. Emergency arterial embolization is a well established therapeutic option to control the ruptured pseudoaneurysm. This is a case report of uterine arterial pseudoaneurysm causing intra-abdominal bleeding followed by cervical conization, which was successfully treated by uterine artery embolization.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Hemoperitoneum: a complication of loop electrosurgical excision procedure
Angela Cho, Sunwha Park, Soyun Park, Hye Sim Kang, Soon Sup Shim, Chul Min Park, Sung Yob Kim
Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2019;62(2):138-141. doi: 10.5468/ogs.2019.62.2.138.
Reference
-
1. Kurata H, Aoki Y, Tanaka K. Delayed, massive bleeding as an unusual complication of laser conization: a case report. J Reprod Med. 2003; 48:659–660.2. Marnela K, Saarelainen S, Palomaki O, Kirkinen P. Sonographic diagnosis of postpartum pseudoaneurysms of the uterine artery: a report of 2 cases. J Clin Ultrasound. 2010; 38:205–208.3. Chitra TV, Panicker S. Pseudoaneurysm of uterine artery: a rare cause of secondary postpartum hemorrhage. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2011; 61:641–644.4. Sharma AM, Burbridge BE. Uterine artery pseudoaneurysm in the setting of delayed postpartum hemorrhage: successful treatment with emergency arterial embolization. Case Rep Radiol. 2011; 2011:373482.5. Dohan A, Soyer P, Subhani A, Hequet D, Fargeaudou Y, Morel O, et al. Postpartum hemorrhage resulting from pelvic pseudoaneurysm: a retrospective analysis of 588 consecutive cases treated by arterial embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013; 36:1247–1255.6. Yeniel AO, Ergenoglu AM, Akdemir A, Eminov E, Akercan F, Karadadas N. Massive secondary postpartum hemorrhage with uterine artery pseudoaneurysm after cesarean section. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2013; 2013:285846.7. Kwon JH. Radiologic diagnosis and treatment of iatrogenic acquired uterine arteriovenous malformation. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2002; 46:483–490.8. Kwon JH, Kim GS. Obstetric iatrogenic arterial injuries of the uterus: diagnosis with US and treatment with transcatheter arterial embolization. Radiographics. 2002; 22:35–46.9. Zanati J, Sergent F, Clavier E, Marpeau L. Late post-conization hemorrhage and false aneurysm of the uterine pedicle. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2006; 35:725–728.10. Jain J, O'Leary S, Sarosi M. Uterine artery pseudoaneurysm after uterine cervical conization. Obstet Gynecol. 2014; 123:2 Pt 2 Suppl 2. 456–458.11. Dohan A, Soyer P, Subhani A, Hequet D, Fargeaudou Y, Morel O, et al. Postpartum hemorrhage resulting from pelvic pseudoaneurysm: a retrospective analysis of 588 consecutive cases treated by arterial embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013; 36:1247–1255.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Delayed postpartum hemoperitoneum due to uterine artery pseudoaneurysm rupture
- Spontaneous Pseudoaneurysm of the Uterine Artery during Pregnancy Treated by Direct Thrombin Injection: A Case Report
- Air in Vagina: Significance in the Staging of Uterine Cervical Carcinoma
- Vaginal Hemorrhage Associated with Decidualized Rectovaginal Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis during the Third Trimester of Pregnancy: A Case Report
- A Case using Uterine Artery Embolization for the Patient with Uterine Artery Bleeding after Transobturator Tape Operation