J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2018 Mar;59(3):288-294. 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.3.288.
A Case of a Visual Field Defect with Optical Coherence Tomography Changes after Sildenafil Citrate Overdose
- Affiliations
-
- 1Siloam Eye Hospital, Seoul, Korea. genialtoday@naver.com
- 2The Institute of Vision Research, Department of Ophthalmology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2406965
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2018.59.3.288
Abstract
- PURPOSE
A case of a transient visual field defect and a change in spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) after an overdose of sildenafil citrate is described.
CASE SUMMARY
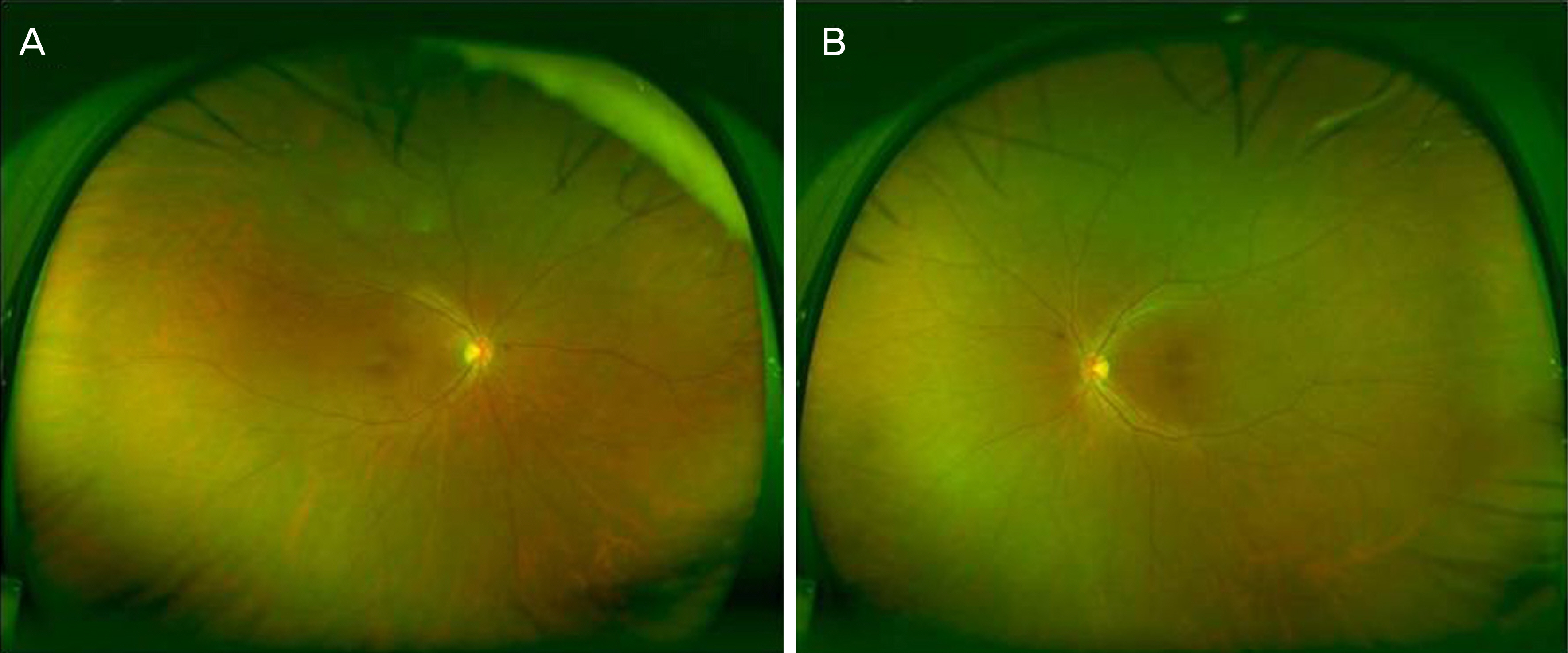
A 67-year-old male with no previous medical history presented with a bluish tinge and visual field defect in both eyes. He had consumed eight tablets of sildenafil citrate (800 mg) 3 days before the visit. His best-corrected visual acuity was 14/20 in the right eye and 20/20 in the left eye. No specific finding was noted on slit-lamp examination. Fundus examination and fundus photography revealed focal foveal hypopigmentation in both eyes. He underwent SD-OCT imaging with the Cirrus HD-OCT (Carl Zeiss Meditec, Oberkochen, Germany), and thickening of the ellipsoid zone and choroid was revealed by SD-OCT scans. He was advised not to take any more sildenafil citrate and was followed for 1 week after the first visit. Central scotomas of both eyes were revealed by a visual field test, and thickening of the ellipsoid zone and choroid remained. His eyes were re-evaluated 1 and 3 months after the first visit, and although the symptoms nearly disappeared, abnormalities in the visual field test and on SD-OCT remained, albeit with some degree of improvement. He revisited us 4 months after the first visit, at which time the visual field test and SD-OCT scans showed results within normal ranges.
CONCLUSIONS
Sildenafil citrate overdose can result in a color anomaly (bluish tinge), visual field defects, and thickening of the ellipsoid zone and choroid on SD-OCT scans.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Laties AM. Vision disorders and phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors: a review of the evidence to date. Drug Saf. 2009; 32:1–18.2). Marmor M. Sildenafil (Viagra) and ophthalmology. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999; 117:518–9.
Article3). Donahue SP, Taylor RJ. Pupil-sparing third nerve palsy associated with sildenafil citrate (Viagra). Am J Ophthalmol. 1998; 126:476–7.
Article4). Fraunfelder FW, Pomeranz HD, Egan RA. Nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy and sildenafil. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006; 124:733–4.
Article5). Tripathi A, O'Donnell NP. Branch retinal artery occlusion; another complication of sildenafil. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000; 84:934–5.
Article6). Jang YS, Ahn GS, Kim SD. Retinal hemorrhage associated with Viagra (sildenafil citrate). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:1340–4.7). Jung YH, Lee NY, Yim HB. A case of inferior rectus muscle enlargement after taking sildenafil citrate. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:382–6.
Article8). Lee WJ, Seong M. Bilateral simultaneous acute angle closure glaucoma following sexual intercourse aided by sildenafil citrate. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:1123–7.
Article9). Kim P, Kim SY. A case of transient color anomaly and persistent visual field defect after sildenafil citrate overdose. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015; 56:1473–8.
Article10). Coscas F, Coscas G, Zucchiatti I, et al. Optical coherence tomography in tadalafil-associated retinal toxicity. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2012; 22:853–6.
Article11). Allibhai ZA, Gale JS, Sheidow TS. Central serous chorioretinopathy in a patient taking sildenafil citrate. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2004; 35:165–7.
Article12). Murata M, Ideta H, Kawasaki T, Noda Y. A case of central serous chorioretinopathy after sildenafil(Viagra). Kyushu Ganka Gakkai. 2000; 42:727–30.13). Quiram P, Dumars S, Parwar B, Sarraf D. Viagra-associated serous macular detachment. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005; 243:339–44.
Article14). Kim DY, Silverman RH, Chan RV, et al. Measurement of choroidal perfusion and thickness following systemic sildenafilI(Viagra (R)). Acta Ophthalmol. 2013; 91:183–8.15). Bonini Filho M, Witkin A. Outer retinal layers as predictors of vision loss. Review of Ophthalmology. 2015; 4:78–83.16). Laties A, Ellis P, Koppiker N, et al. Visual function testing in patients and healthy volunteers receiving Viagra. Ophthalmic Res. 1998; 30(Suppl 1):177.17). Laties AM, Ellis P, Mollon JD. The effects of sildenafil citrate(Viagra (R)) on color discrimination in volunteers and patients with erectile dysfunction. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999; 40:S693.18). Schachat AP, Wilkinson CP, Hinton DR, et al. Ryan's Retina. 6th. Philadelphia: Elsevier Health Sciences;2017. p. 41.19). Curcio C, Allen KA, Sloan KR, et al. Distribution and morphology of human cone photoreceptors stained with anti-blue opsin. J Comp Neurol. 1991; 312:610–24.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Transient Color Anomaly and Persistent Visual Field Defect after Sildenafil Citrate Overdose
- Retinal Hemorrhage Associated with Viagra (sildenafil citrate)
- Asymptomatic Unexplained Visual Field Loss Diagnosed as Early Retinitis Pigmentosa without Pigmentation: A Case Report
- A Case Report of Occipital Lobe Epilepsy and Related Optical Coherence Tomography Findings
- The Optical Coherence Tomography Findings of Optic Tract Syndrome