Clin Orthop Surg.
2018 Mar;10(1):41-46. 10.4055/cios.2018.10.1.41.
Prevalence of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis Diagnosed by Whole Spine Computed Tomography: A Preliminary Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology, Cheju Halla General Hospital, Jeju, Korea. mingy9879@gmail.com
- KMID: 2405481
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.1.41
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) is characterized by ossification of the enthesis. The diagnosis has been mainly based on the chest or whole spine lateral plain film. Recently, chest or thoracolumbar computed tomography (CT) has been reported to be more reliable for the diagnosis of DISH. The purposes of this study were to investigate the prevalence and location of DISH and evaluate the prevalence of comorbidities, such as ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) and ossification of the ligamentum flavum (OLF), using whole spine CT.
METHODS
Whole spine CT scans of patients over 16 years of age who were examined at Cheju Halla General Hospital between February 2011 and December 2016 were reviewed for this study. The diagnosis of DISH was made according to the modified Resnick criteria. The prevalence of DISH in each age decade and its location were evaluated. Also, the prevalence of OPLL and OLF in DISH patients was investigated.
RESULTS
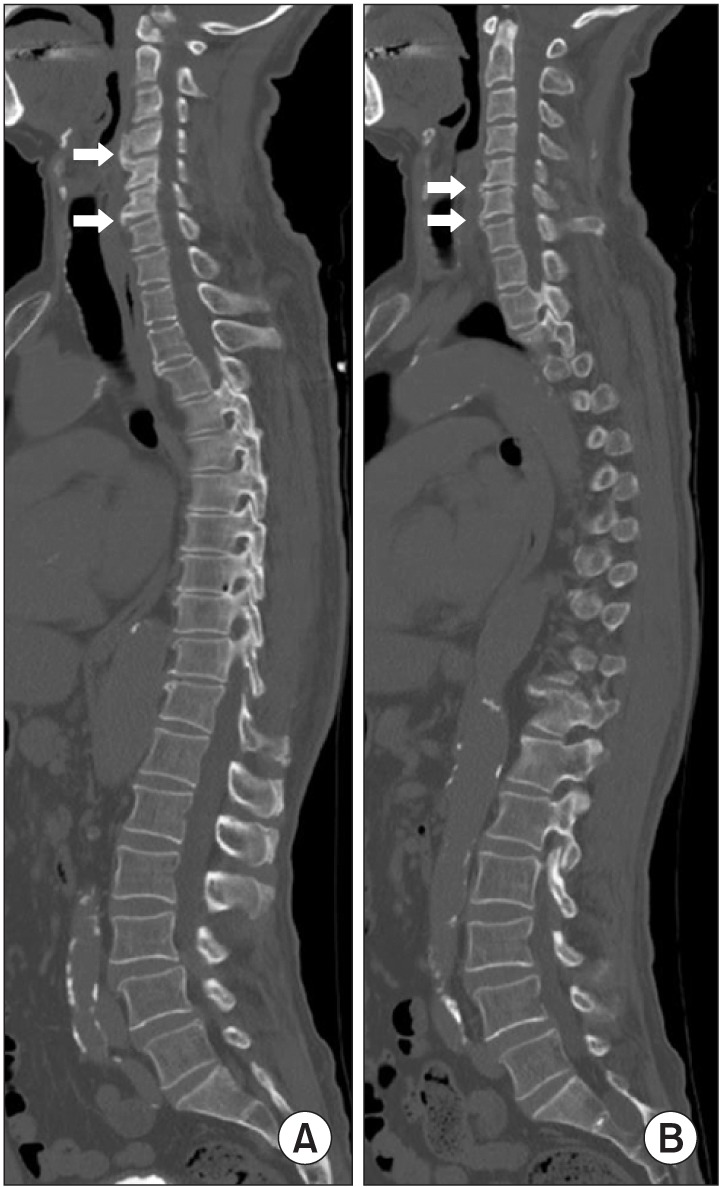
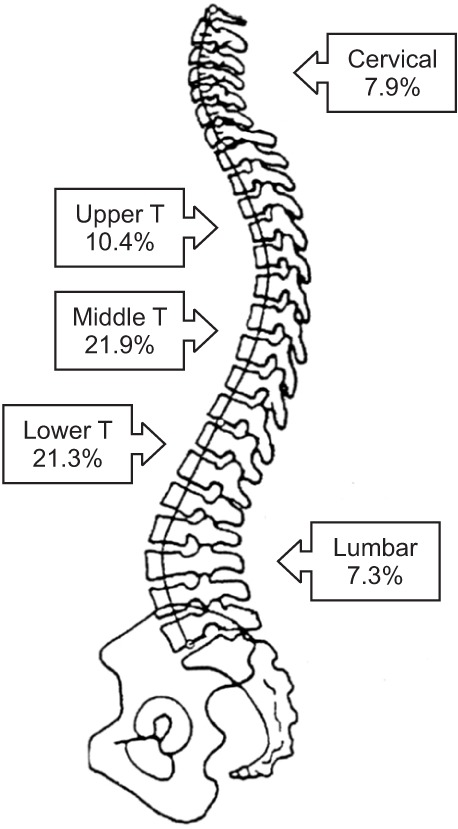
The overall incidence of DISH was 24.4% (40 of 164 cases). There was no case of DISH in patients in their 40s and younger. The percentile incidences of DISH in patients in their fifth, sixth, seventh, eighth, and ninth decades were 20.0% (4 of 20 cases), 32.3% (10 of 31 cases), 40.0% (10 of 25 cases), 34.5% (10 of 29 cases), and 27.3% (6 of 22 cases), respectively. A strong positive correlation between the age decade and the incidence of DISH was noted (r = 0.853, p = 0.007). DISH patients had higher incidences of OLF (22.5%) and OPLL (37.5%). The most common location of DISH was the middle thoracic spine (90.0%) followed by the lower thoracic spine (87.5%). There was one case of DISH involving only the cervical spine.
CONCLUSIONS
The incidence of DISH diagnosed by CT was higher than we expected. Whole spine CT can be a valuable modality to evaluate the location of DISH in the cervical and lumbar spine and the comorbidity rates of OLF and OPLL.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Forestier J, Rotes-Querol J. Senile ankylosing hyperostosis of the spine. Ann Rheum Dis. 1950; 9(4):321–330. PMID: 14800245.
Article2. Resnick D, Niwayama G. Radiographic and pathologic features of spinal involvement in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Radiology. 1976; 119(3):559–568. PMID: 935390.
Article3. Mader R, Novofestovski I, Adawi M, Lavi I. Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk in patients with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 38(5):361–365. PMID: 18304611.
Article4. Sinha R, Aggarwal N, Dutta S, Choudhury A, Ghosh SK, Guha D. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis involving cervical and lumbar spine presenting with dysphagia: a case report. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2017; 29(93):233–236. PMID: 28819624.5. Moriwaki M, Hase H, Fujioka S, et al. Prolonged dysphagia due to a combination of cerebral hemorrhage and diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: a case report. NMC Case Rep J. 2016; 3(3):75–79. PMID: 28664003.
Article6. Yamada K, Toyoda H, Terai H, Takahashi S, Nakamura H. Spinopelvic alignment of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2014; 23(6):1302–1308. PMID: 24413742.
Article7. Mader R, Verlaan JJ, Buskila D. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: clinical features and pathogenic mechanisms. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013; 9(12):741–750. PMID: 24189840.
Article8. Westerveld LA, Verlaan JJ, Oner FC. Spinal fractures in patients with ankylosing spinal disorders: a systematic review of the literature on treatment, neurological status and complications. Eur Spine J. 2009; 18(2):145–156. PMID: 18791749.
Article9. Kobayashi H, Otani K, Watanabe K, et al. Vertebral fracture at the caudal end of a surgical fusion for thoracic vertebral fracture in a patient with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Fukushima J Med Sci. 2017; 63(2):112–115. PMID: 28680006.
Article10. Vaishya R, Vijay V, Nwagbara IC, Agarwal AK. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH): a common but less known cause of back pain. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2017; 8(2):191–196. PMID: 28721001.11. Katzman WB, Huang MH, Kritz-Silverstein D, Barrett-Connor E, Kado DM. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) and impaired physical function: the Rancho Bernardo Study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017; 65(7):1476–1481. PMID: 28369706.12. Mori K, Kasahara T, Mimura T, Nishizawa K, Nakamura A, Imai S. Prevalence of thoracic diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) in Japanese: results of chest CT-based cross-sectional study. J Orthop Sci. 2017; 22(1):38–42. PMID: 27697426.
Article13. Oudkerk SF, de Jong PA, Attrach M, et al. Diagnosis of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis with chest computed tomography: inter-observer agreement. Eur Radiol. 2017; 27(1):188–194. PMID: 27097788.
Article14. Hirasawa A, Wakao N, Kamiya M, et al. The prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in Japan: the first report of measurement by CT and review of the literature. J Orthop Sci. 2016; 21(3):287–290. PMID: 26948246.15. Toyoda H, Terai H, Yamada K, et al. Prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in patients with spinal disorders. Asian Spine J. 2017; 11(1):63–70. PMID: 28243371.
Article16. Weinfeld RM, Olson PN, Maki DD, Griffiths HJ. The prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) in two large American Midwest metropolitan hospital populations. Skeletal Radiol. 1997; 26(4):222–225. PMID: 9151370.
Article17. Kim SK, Choi BR, Kim CG, et al. The prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in Korea. J Rheumatol. 2004; 31(10):2032–2035. PMID: 15468371.18. Kagotani R, Yoshida M, Muraki S, et al. Prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) of the whole spine and its association with lumbar spondylosis and knee osteoarthritis: the ROAD study. J Bone Miner Metab. 2015; 33(2):221–229. PMID: 24623190.
Article19. Cassim B, Mody GM, Rubin DL. The prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in African blacks. Br J Rheumatol. 1990; 29(2):131–132. PMID: 2322769.20. Kiss C, O'Neill TW, Mituszova M, Szilagyi M, Poor G. The prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in a population-based study in Hungary. Scand J Rheumatol. 2002; 31(4):226–229. PMID: 12369655.
Article21. Westerveld LA, van Ufford HM, Verlaan JJ, Oner FC. The prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in an outpatient population in The Netherlands. J Rheumatol. 2008; 35(8):1635–1638. PMID: 18528963.22. Kuperus JS, de Gendt EE, Oner FC, et al. Classification criteria for diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: a lack of consensus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017; 56(7):1123–1134. PMID: 28371859.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dysphagia Due to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis of The Cervical Spine: A Case Report
- CT Findings of May–Thurner Syndrome in Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis: A Case Report
- Compression Fractures in the Setting of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis
- Progressive Paralysis of the Right Lower Extremity due to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis: A Case Report
- A Case of Dysphagia due to Cricopharyngeal Dysfunction and Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis