Korean Circ J.
2018 Jan;48(1):24-35. 10.4070/kcj.2017.0194.
Bioresorbable Scaffolds in Coronary Intervention: Unmet Needs and Evolution
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Cardio-Thoracic-Vascular Department, Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria “Policlinico-Vittorio Emanuele†and Department of General Surgery and Medical-Surgical Specialties, University of Catania, Catania, Italy. dcapodanno@gmail.com
- KMID: 2405043
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2017.0194
Abstract
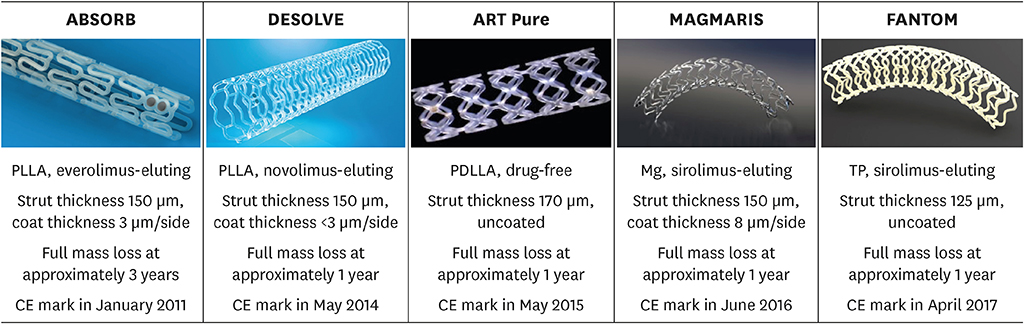
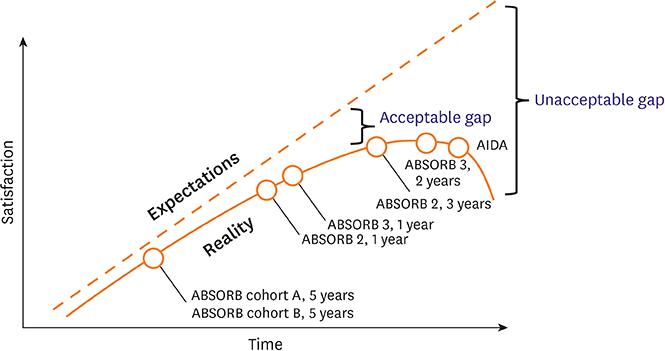
- Bioresorbable scaffolds (BRS) represent a novel paradigm in the 40-year history of interventional cardiology. Restoration of cyclic pulsatility and physiologic vasomotion, adaptive vascular remodeling, plaque regression, and removal of the trigger for late adverse events are expected BRS benefits over current metallic drug-eluting stents. However, first-generation BRS devices have significant manufacturing limitations and rely on optimal implantation technique to avoid experiencing an excess of clinical events. There are currently at least 22 BRS devices in different stages of development, including many trials of device iterations with thinner (<150 µm) struts than first-generation BRS. This article reviews the outcomes of commercially available and potentially upcoming BRS, focusing on the most recent stages of clinical development and future directions for each scaffold type.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Palmerini T, Biondi-Zoccai G, Della Riva D, et al. Stent thrombosis with drug-eluting stents: is the paradigm shifting? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013; 62:1915–1921.2. Kereiakes DJ, Onuma Y, Serruys PW, Stone GW. Bioresorbable vascular scaffolds for coronary revascularization. Circulation. 2016; 134:168–182.
Article3. Capodanno D, Angiolillo DJ. Antiplatelet therapy after implantation of bioresorbable vascular scaffolds: a review of the published data, practical recommendations, and future directions. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017; 10:425–437.4. Capodanno D. Bioresorbable scaffolds: clinical outcomes and considerations. Interv Cardiol Clin. 2016; 5:357–363.5. Capodanno D, Gori T, Nef H, et al. Percutaneous coronary intervention with everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffolds in routine clinical practice: early and midterm outcomes from the European multicentre GHOST-EU registry. EuroIntervention. 2015; 10:1144–1153.
Article6. Serruys PW, Chevalier B, Dudek D, et al. A bioresorbable everolimus-eluting scaffold versus a metallic everolimus-eluting stent for ischaemic heart disease caused by de-novo native coronary artery lesions (ABSORB II): an interim 1-year analysis of clinical and procedural secondary outcomes from a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2015; 385:43–54.
Article7. Kimura T, Kozuma K, Tanabe K, et al. A randomized trial evaluating everolimus-eluting Absorb bioresorbable scaffolds vs. everolimus-eluting metallic stents in patients with coronary artery disease: ABSORB Japan. Eur Heart J. 2015; 36:3332–3342.
Article8. Gao R, Yang Y, Han Y, et al. Bioresorbable vascular scaffolds versus metallic stents in patients with coronary artery disease: ABSORB China Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015; 66:2298–2309.9. Ellis SG, Kereiakes DJ, Metzger DC, et al. Everolimus-eluting bioresorbable scaffolds for coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:1905–1915.
Article10. Cassese S, Byrne RA, Ndrepepa G, et al. Everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffolds versus everolimus-eluting metallic stents: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet. 2016; 387:537–544.
Article11. Stone GW, Gao R, Kimura T, et al. 1-year outcomes with the Absorb bioresorbable scaffold in patients with coronary artery disease: a patient-level, pooled meta-analysis. Lancet. 2016; 387:1277–1289.
Article12. Serruys PW, Chevalier B, Sotomi Y, et al. Comparison of an everolimus-eluting bioresorbable scaffold with an everolimus-eluting metallic stent for the treatment of coronary artery stenosis (ABSORB II): a 3 year, randomised, controlled, single-blind, multicentre clinical trial. Lancet. 2016; 388:2479–2491.
Article13. Wykrzykowska JJ, Kraak RP, Hofma SH, et al. Bioresorbable scaffolds versus metallic stents in routine PCI. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376:2319–2328.
Article14. Ali ZA, Serruys PW, Kimura T, et al. 2-year outcomes with the Absorb bioresorbable scaffold for treatment of coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of seven randomised trials with an individual patient data substudy. Lancet. 2017; 390:760–772.
Article15. Nef HM, Wiebe J, Foin N, et al. A new novolimus-eluting bioresorbable coronary scaffold: present status and future clinical perspectives. Int J Cardiol. 2017; 227:127–133.
Article16. Verheye S, Ormiston JA, Stewart J, et al. A next-generation bioresorbable coronary scaffold system: from bench to first clinical evaluation: 6- and 12-month clinical and multimodality imaging results. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014; 7:89–99.17. Abizaid A, Costa RA, Schofer J, et al. Serial multimodality imaging and 2-year clinical outcomes of the novel DESolve novolimus-eluting bioresorbable coronary scaffold system for the treatment of single de novo coronary lesions. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2016; 9:565–574.18. Haude M, Erbel R, Erne P, et al. Safety and performance of the DRug-Eluting Absorbable Metal Scaffold (DREAMS) in patients with de novo coronary lesions: 3-year results of the prospective, multicentre, first-in-man BIOSOLVE-I trial. EuroIntervention. 2016; 12:e160–6.
Article19. Haude M, Erbel R, Erne P, et al. Safety and performance of the drug-eluting absorbable metal scaffold (DREAMS) in patients with de-novo coronary lesions: 12 month results of the prospective, multicentre, first-in-man BIOSOLVE-I trial. Lancet. 2013; 381:836–844.
Article20. Fajadet J, Haude M, Joner M, et al. Magmaris preliminary recommendation upon commercial launch: a consensus from the expert panel on 14 April 2016. EuroIntervention. 2016; 12:828–833.
Article21. Haude M, Ince H, Abizaid A, et al. Safety and performance of the second-generation drug-eluting absorbable metal scaffold in patients with de-novo coronary artery lesions (BIOSOLVE-II): 6 month results of a prospective, multicentre, non-randomised, first-in-man trial. Lancet. 2016; 387:31–39.
Article22. Haude M, Ince H, Abizaid A, et al. Sustained safety and performance of the second-generation drug-eluting absorbable metal scaffold in patients with de novo coronary lesions: 12-month clinical results and angiographic findings of the BIOSOLVE-II first-in-man trial. Eur Heart J. 2016; 37:2701–2709.23. Haude M, Ince H, Kische S, et al. Sustained safety and clinical performance of a drug-eluting absorbable metal scaffold up to 24 months: pooled outcomes of BIOSOLVE-II and BIOSOLVE-III. EuroIntervention. 2017; 13:432–439.
Article24. Seth A, Onuma Y, Costa R, et al. First-in-human evaluation of a novel poly-L-lactide based sirolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold for the treatment of de novo native coronary artery lesions: MeRes-1 trial. EuroIntervention. 2017; 13:415–423.
Article25. Tenekecioglu E, Serruys PW, Onuma Y, et al. Randomized comparison of Absorb bioresorbable vascular scaffold and Mirage microfiber sirolimus-eluting scaffold using multimodality imaging. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017; 10:1115–1130.
Article26. Zhang YJ, Wang XZ, Fu G, et al. Clinical and multimodality imaging results at 6 months of a bioresorbable sirolimus-eluting scaffold for patients with single de novo coronary artery lesions: the NeoVas first-in-man trial. EuroIntervention. 2016; 12:1279–1287.
Article27. Wu Y, Shen L, Ge L, et al. Six-month outcomes of the XINSORB bioresorbable sirolimus-eluting scaffold in treating single de novo lesions in human coronary artery. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2016; 87:Suppl 1. 630–637.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Early experience and favorable clinical outcomes of everolimus-eluting bioresorbable scaffolds for coronary artery disease in Korea
- Current Status of Coronary Stent
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Versus Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting for Revascularization of Left Main Coronary Artery Disease
- Surface Functionalization of Three-Dimensional Printed Scaffold for Biomedical Application
- Optical Coherence Tomography and Stent Boost Imaging Guided Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffold Overlapping for Coronary Chronic Total Occlusion Lesion