Korean J Radiol.
2018 Apr;19(2):209-222. 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.209.
Imaging Evaluation Following â¹â°Y Radioembolization of Liver Tumors: What Radiologists Should Know
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Korea. angiointervention@gmail.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Severance Hospital, Seoul 03722, Korea.
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Korea.
- KMID: 2404917
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.209
Abstract
- Radioembolization using beta-emitting yttrium-90 microspheres is being increasingly used for the treatment of primary and metastatic liver cancers. It is a form of intra-arterial brachytherapy which delivers intense radiation to liver tumors with little embolic effect; this mode of action results in unique post-treatment imaging findings. It is important to understand these imaging findings to avoid misinterpretation of tumor response and to determine further management of the disease. Herein, we discuss the current concepts for assessing tumor response, common post-treatment imaging features, and associated complications following radioembolization.
Keyword
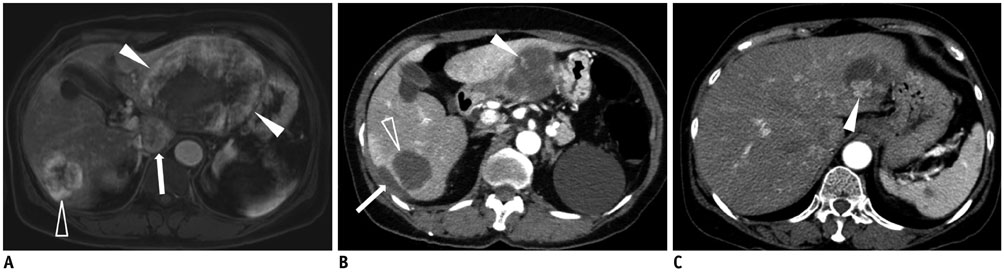
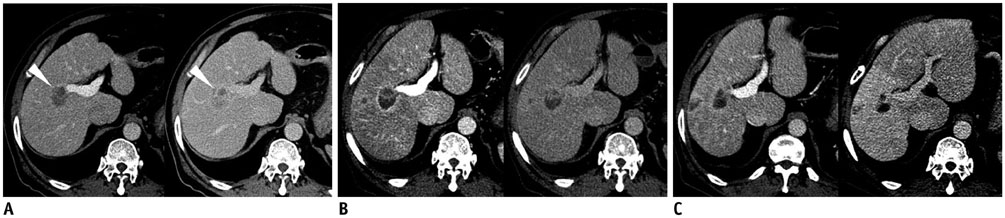
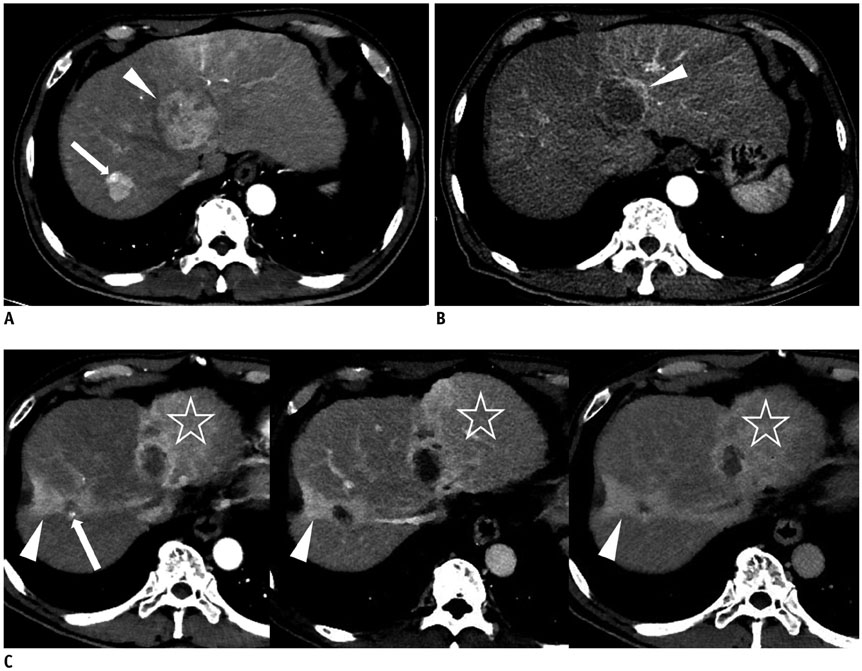
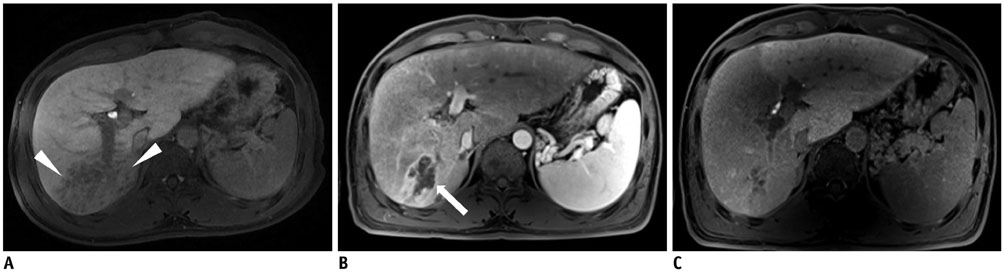
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: what clinicians need to know
Jin Woo Choi, Hyo-Cheol Kim
J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):4-13. doi: 10.17998/jlc.2022.01.16.
Reference
-
1. Sangro B, Iñarrairaegui M, Bilbao JI. Radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012; 56:464–473.
Article2. Lee EW, Alanis L, Cho SK, Saab S. Yttrium-90 selective internal radiation therapy with glass microspheres for hepatocellular carcinoma: current and updated literature review. Korean J Radiol. 2016; 17:472–488.
Article3. Lanza E, Donadon M, Poretti D, Pedicini V, Tramarin M, Roncalli M, et al. Transarterial therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer. 2016; 6:27–33.
Article4. Fidelman N, Kerlan RK Jr. Transarterial chemoembolization and (90)Y radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: review of current applications beyond intermediate-stage disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015; 205:742–752.5. Atassi B, Bangash AK, Bahrani A, Pizzi G, Lewandowski RJ, Ryu RK, et al. Multimodality imaging following 90Y radioembolization: a comprehensive review and pictorial essay. Radiographics. 2008; 28:81–99.6. Riaz A, Lewandowski RJ, Kulik LM, Mulcahy MF, Sato KT, Ryu RK, et al. Complications following radioembolization with yttrium-90 microspheres: a comprehensive literature review. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009; 20:1121–1130.
Article7. Coldwell D, Sangro B, Wasan H, Salem R, Kennedy A. General selection criteria of patients for radioembolization of liver tumors: an international working group report. Am J Clin Oncol. 2011; 34:337–341.8. Rosenbaum CE, Verkooijen HM, Lam MG, Smits ML, Koopman M, van Seeters T, et al. Radioembolization for treatment of salvage patients with colorectal cancer liver metastases: a systematic review. J Nucl Med. 2013; 54:1890–1895.
Article9. Kim HC. Radioembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2017; 23:109–114.
Article10. Kim DY, Han KH. Transarterial chemoembolization versus transarterial radioembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma: optimization of selecting treatment modality. Hepatol Int. 2016; 10:883–892.
Article11. Kim HC. Role of C-arm cone-beam CT in chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16:114–124.
Article12. Borggreve AS, Landman AJEMC, Vissers CMJ, De Jong , Lam MGEH, Monninkhof EM, et al. Radioembolization: is prophylactic embolization of hepaticoenteric arteries necessary? A systematic review. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2016; 39:696–670.
Article13. Camacho JC, Moncayo V, Kokabi N, Reavey HE, Galt JR, Yamada K, et al. (90)Y radioembolization: multimodality imaging pattern approach with angiographic correlation for optimized target therapy delivery. Radiographics. 2015; 35:1602–1618. quiz 316.
Article14. Kao YH, Hock Tan AE, Burgmans MC, Irani FG, Khoo LS, Gong Lo RH, et al. Image-guided personalized predictive dosimetry by artery-specific SPECT/CT partition modeling for safe and effective 90Y radioembolization. J Nucl Med. 2012; 53:559–566.
Article15. Roshan HR, Azarm A, Mahmoudian B, Islamian JP. Advances in SPECT for optimizing the liver tumors radioembolization using yttrium-90 microspheres. World J Nucl Med. 2015; 14:75–80.
Article16. Braat AJ, Smits ML, Braat MN, van den Hoven AF, Prince JF, de Jong HW, et al. 90Y hepatic radioembolization: an update on current practice and recent developments. J Nucl Med. 2015; 56:1079–1087.17. Uliel L, Royal HD, Darcy MD, Zuckerman DA, Sharma A, Saad NE. From the angio suite to the γ-camera: vascular mapping and 99mTc-MAA hepatic perfusion imaging before liver radioembolization--a comprehensive pictorial review. J Nucl Med. 2012; 53:1736–1747.
Article18. Kallini JR, Gabr A, Salem R, Lewandowski RJ. Transarterial radioembolization with yttrium-90 for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv Ther. 2016; 33:699–714.
Article19. Riaz A, Gates VL, Atassi B, Lewandowski RJ, Mulcahy MF, Ryu RK, et al. Radiation segmentectomy: a novel approach to increase safety and efficacy of radioembolization. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011; 79:163–171.
Article20. Padia SA, Kwan SW, Roudsari B, Monsky WL, Coveler A, Harris WP. Superselective yttrium-90 radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma yields high response rates with minimal toxicity. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014; 25:1067–1073.
Article21. Vouche M, Habib A, Ward TJ, Kim E, Kulik L, Ganger D, et al. Unresectable solitary hepatocellular carcinoma not amenable to radiofrequency ablation: multicenter radiology-pathology correlation and survival of radiation segmentectomy. Hepatology. 2014; 60:192–201.
Article22. Lewandowski RJ, Donahue L, Chokechanachaisakul A, Kulik L, Mouli S, Caicedo J, et al. (90) Y radiation lobectomy: outcomes following surgical resection in patients with hepatic tumors and small future liver remnant volumes. J Surg Oncol. 2016; 114:99–105.23. Vouche M, Lewandowski RJ, Atassi R, Memon K, Gates VL, Ryu RK, et al. Radiation lobectomy: time-dependent analysis of future liver remnant volume in unresectable liver cancer as a bridge to resection. J Hepatol. 2013; 59:1029–1036.
Article24. Lhommel R, Goffette P, Van den Eynde M, Jamar F, Pauwels S, Bilbao JI, et al. Yttrium-90 TOF PET scan demonstrates high-resolution biodistribution after liver SIRT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009; 36:1696.
Article25. Pasciak AS, Bourgeois AC, McKinney JM, Chang TT, Osborne DR, Acuff SN, et al. Radioembolization and the dynamic role of (90)Y PET/CT. Front Oncol. 2014; 4:38.
Article26. Bagni O, D’Arienzo M, Chiaramida P, Chiacchiararelli L, Cannas P, D’Agostini A, et al. 90Y-PET for the assessment of microsphere biodistribution after selective internal radiotherapy. Nucl Med Commun. 2012; 33:198–204.
Article27. Fowler KJ, Maughan NM, Laforest R, Saad NE, Sharma A, Olsen J, et al. PET/MRI of hepatic 90Y microsphere deposition determines individual tumor response. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2016; 39:855–864.
Article28. Cosimelli M, Golfieri R, Cagol PP, Carpanese L, Sciuto R, Maini CL, et al. Multi-centre phase II clinical trial of yttrium-90 resin microspheres alone in unresectable, chemotherapy refractory colorectal liver metastases. Br J Cancer. 2010; 103:324–331.
Article29. Hoffmann RT, Paprottka PM, Schön A, Bamberg F, Haug A, Dürr EM, et al. Transarterial hepatic yttrium-90 radioembolization in patients with unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: factors associated with prolonged survival. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2012; 35:105–116.
Article30. Salem R, Lewandowski RJ, Mulcahy MF, Riaz A, Ryu RK, Ibrahim S, et al. Radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma using Yttrium-90 microspheres: a comprehensive report of long-term outcomes. Gastroenterology. 2010; 138:52–64.
Article31. Keppke AL, Salem R, Reddy D, Huang J, Jin J, Larson AC, et al. Imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma after treatment with yttrium-90 microspheres. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 188:768–775.
Article32. Miller FH, Keppke AL, Reddy D, Huang J, Jin J, Mulcahy MF, et al. Response of liver metastases after treatment with yttrium-90 microspheres: role of size, necrosis, and PET. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 188:776–783.
Article33. Riaz A, Kulik L, Lewandowski RJ, Ryu RK, Giakoumis Spear G, Mulcahy MF, et al. Radiologic-pathologic correlation of hepatocellular carcinoma treated with internal radiation using yttrium-90 microspheres. Hepatology. 2009; 49:1185–1193.
Article34. Camacho JC, Kokabi N, Xing M, Prajapati HJ, El-Rayes B, Kim HS. Modified response evaluation criteria in solid tumors and European Association for The Study of the Liver criteria using delayed-phase imaging at an early time point predict survival in patients with unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma following yttrium-90 radioembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014; 25:256–265.
Article35. Chapiro J, Duran R, Lin M, Schernthaner R, Lesage D, Wang Z, et al. Early survival prediction after intra-arterial therapies: a 3D quantitative MRI assessment of tumour response after TACE or radioembolization of colorectal cancer metastases to the liver. Eur Radiol. 2015; 25:1993–2003.
Article36. Guo Y, Yaghmai V, Salem R, Lewandowski RJ, Nikolaidis P, Larson AC, et al. Imaging tumor response following liver-directed intra-arterial therapy. Abdom Imaging. 2013; 38:1286–1299.
Article37. Singh P, Anil G. Yttrium-90 radioembolization of liver tumors: what do the images tell us. Cancer Imaging. 2014; 13:645–657.
Article38. Shady W, Sotirchos VS, Do RK, Pandit-Taskar N, Carrasquillo JA, Gonen M, et al. Surrogate imaging biomarkers of response of colorectal liver metastases after salvage radioembolization using 90Y-loaded resin microspheres. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016; 207:661–670.
Article39. Bester L, Hobbins PG, Wang SC, Salem R. Imaging characteristics following 90yttrium microsphere treatment for unresectable liver cancer. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2011; 55:111–118.
Article40. Jiang T, Zhu AX, Sahani DV. Established and novel imaging biomarkers for assessing response to therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2013; 58:169–177.
Article41. Taouli B, Koh DM. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the liver. Radiology. 2010; 254:47–66.
Article42. Kokabi N, Camacho JC, Xing M, Qiu D, Kitajima H, Mittal PK, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient quantification as an early imaging biomarker of response and predictor of survival following yttrium-90 radioembolization for unresectable infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis. Abdom Imaging. 2014; 39:969–978.
Article43. Schmeel FC, Simon B, Sabet A, Luetkens JA, Träber F, Schmeel LC, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging predicts survival in patients with liver-predominant metastatic colorectal cancer shortly after selective internal radiation therapy. Eur Radiol. 2017; 27:966–975.
Article44. Joo I, Lee JM, Han JK, Choi BI. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging for monitoring the therapeutic efficacy of the vascular disrupting agent CKD-516 in rabbit VX2 liver tumors. Radiology. 2014; 272:417–426.
Article45. Koh DM, Collins DJ, Orton MR. Intravoxel incoherent motion in body diffusion-weighted MRI: reality and challenges. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 196:1351–1361.
Article46. Yang SH, Lin J, Lu F, Han ZH, Fu CX, Lv P, et al. Evaluation of antiangiogenic and antiproliferative effects of sorafenib by sequential histology and intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging in an orthotopic hepatocellular carcinoma xenograft model. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017; 45:270–280.
Article47. Pieper CC, Meyer C, Sprinkart AM, Block W, Ahmadzadehfar H, Schild HH, et al. The value of intravoxel incoherent motion model-based diffusion-weighted imaging for outcome prediction in resin-based radioembolization of breast cancer liver metastases. Onco Targets Ther. 2016; 9:4089–4098.
Article48. Pieper CC, Sprinkart AM, Meyer C, König R, Schild HH, Kukuk GM, et al. Evaluation of a simplified intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) analysis of diffusion-weighted imaging for prediction of tumor size changes and imaging response in breast cancer liver metastases undergoing radioembolization: a retrospective single center analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e327.49. Memon K, Kulik L, Lewandowski RJ, Wang E, Ryu RK, Riaz A, et al. Alpha-fetoprotein response correlates with EASL response and survival in solitary hepatocellular carcinoma treated with transarterial therapies: a subgroup analysis. J Hepatol. 2012; 56:1112–1120.
Article50. Hipps D, Ausania F, Manas DM, Rose JD, French JJ. Selective interarterial radiation therapy (SIRT) in colorectal liver metastases: how Do we monitor response? HPB Surg. 2013; 2013:570808.
Article51. Kallini JR, Miller FH, Gabr A, Salem R, Lewandowski RJ. Hepatic imaging following intra-arterial embolotherapy. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2016; 41:600–661.
Article52. Ibrahim SM, Nikolaidis P, Miller FH, Lewandowski RJ, Ryu RK, Sato KT, et al. Radiologic findings following Y90 radioembolization for primary liver malignancies. Abdom Imaging. 2009; 34:566–581.
Article53. Bhangoo MS, Karnani DR, Hein PN, Giap H, Knowles H, Issa C, et al. Radioembolization with Yttrium-90 microspheres for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2015; 6:469–478.54. Park MJ, Kim SY, Yoon SM, Kim JH, Park SH, Lee SS, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy-induced arterial hypervascularity of non-tumorous hepatic parenchyma in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: potential pitfalls in tumor response evaluation on multiphase computed tomography. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e90327.
Article55. Lock M, Malayeri AA, Mian OY, Mayr NA, Herman JM, Lo SS. Computed tomography imaging assessment of postexternal beam radiation changes of the liver. Future Oncol. 2016; 12:2729–2739.
Article56. Herfarth KK, Hof H, Bahner ML, Lohr F, Höss A, van Kaick G, et al. Assessment of focal liver reaction by multiphasic CT after stereotactic single-dose radiotherapy of liver tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003; 57:444–451.
Article57. Marin D, Cappabianca S, Serra N, Sica A, Lassandro F, D’Angelo R, et al. CT appearance of hepatocellular carcinoma after locoregional treatments: a comprehensive review. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015; 2015:670965.
Article58. Kulik LM, Atassi B, van Holsbeeck L, Souman T, Lewandowski RJ, Mulcahy MF, et al. Yttrium-90 microspheres (TheraSphere) treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: downstaging to resection, RFA and bridge to transplantation. J Surg Oncol. 2006; 94:572–586.
Article59. Braat AJ, Huijbregts JE, Molenaar IQ, Borel Rinkes IH, van den Bosch MA, Lam MG. Hepatic radioembolization as a bridge to liver surgery. Front Oncol. 2014; 4:199.
Article60. Prince JF, van den Hoven AF, van den Bosch MA, Elschot M, de Jong HW, Lam MG. Radiation-induced cholecystitis after hepatic radioembolization: do we need to take precautionary measures. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014; 25:1717–1723.
Article61. Yu MH, Kim YJ, Park HS, Jung SI, Jeon HJ. Imaging patterns of intratumoral calcification in the abdominopelvic cavity. Korean J Radiol. 2017; 18:323–335.
Article62. Sharma RA, Van Hazel GA, Morgan B, Berry DP, Blanshard K, Price D, et al. Radioembolization of liver metastases from colorectal cancer using yttrium-90 microspheres with concomitant systemic oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:1099–1106.
Article63. Riaz A, Awais R, Salem R. Side effects of yttrium-90 radioembolization. Front Oncol. 2014; 4:198.
Article64. Gil-Alzugaray B, Chopitea A, Iñarrairaegui M, Bilbao JI, Rodriguez-Fraile M, Rodriguez J, et al. Prognostic factors and prevention of radioembolization-induced liver disease. Hepatology. 2013; 57:1078–1087.
Article65. Hamoui N, Ryu RK. Hepatic radioembolization complicated by fulminant hepatic failure. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2011; 28:246–251.
Article66. Kuo JC, Tazbirkova A, Allen R, Kosmider S, Gibbs P, Yip D. Serious hepatic complications of selective internal radiation therapy with yttrium-90 microsphere radioembolization for unresectable liver tumors. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2014; 10:266–272.
Article67. Wright CL, Werner JD, Tran JM, Gates VL, Rikabi AA, Shah MH, et al. Radiation pneumonitis following yttrium-90 radioembolization: case report and literature review. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012; 23:669–674.
Article68. Padia SA, Lewandowski RJ, Johnson GE, Sze DY, Ward TJ, Gaba RC, et al. Radioembolization of hepatic malignancies: background, quality improvement guidelines, and future directions. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017; 28:1–15.
Article69. Parakh S, Gananadha S, Allen R, Yip D. Cholecystitis after yttrium-90 resin microsphere radioembolization treatment: clinical and pathologic findings. Asian J Surg. 2016; 39:144–148.
Article70. Sag AA, Savin MA, Lal NR, Mehta RR. Yttrium-90 radioembolization of malignant tumors of the liver: gallbladder effects. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014; 202:1130–1135.
Article71. Hickey R, Lewandowski RJ. Hepatic radioembolization complicated by radiation cholecystitis. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2011; 28:230–233.
Article72. Choi JW, Yoo MY, Kim HC, Paeng JC, Kim YJ, Chung JW. Prophylactic temporary occlusion of the cystic artery using a fibered detachable coil during 90y radioembolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2017; 40:1624–1630.
Article73. South CD, Meyer MM, Meis G, Kim EY, Thomas FB, Rikabi AA, et al. Yttrium-90 microsphere induced gastrointestinal tract ulceration. World J Surg Oncol. 2008; 6:93.
Article74. Kallini JR, Gabr A, Thorlund K, Balijepalli C, Ayres D, Kanters S. Comparison of the adverse event profile of TheraSphere® with SIR-Spheres® for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2017; 40:1033–1043.
Article75. Sun B, Lapetino SR, Diffalha SA, Yong S, Gaba RC, Bui JT, et al. Microvascular injury in persistent gastric ulcers after yttrium-90 microsphere radioembolization for liver malignancies. Hum Pathol. 2016; 50:11–14.
Article76. Veloso N, Brandäo C, Gonçalves B, Costa L, Coimbra N, Jacome M, et al. Gastroduodenal ulceration following liver radioembolization with yttrium-90. Endoscopy. 2013; 45:Suppl 2 UCTN. E108–E109.
Article77. Naymagon S, Warner RR, Patel K, Harpaz N, Machac J, Weintraub JL, et al. Gastroduodenal ulceration associated with radioembolization for the treatment of hepatic tumors: an institutional experience and review of the literature. Dig Dis Sci. 2010; 55:2450–2458.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radioembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Radioembolization for the Treatment of Primary and Metastatic Liver Cancers
- Diagnosis of Osteomyelitis by the Sequential Use of â¹â¹mTc - Methylene Diphosphonate and â¶â·Ga Imaging
- Effect of ME Collimator Characteristic, Energy Window Width, and Reconstruction Algorithm Selection on Imaging Performance of Yttrium-90: Simulation Study
- Radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: what clinicians need to know