Healthc Inform Res.
2017 Jul;23(3):169-175. 10.4258/hir.2017.23.3.169.
Statistics and Deep Belief Network-Based Cardiovascular Risk Prediction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Computer and Information Engineering, Inha University, Incheon, Korea.
- 2IT Department, Gachon University, Seongnam, Korea. lyh@gachon.ac.kr
- KMID: 2403306
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2017.23.3.169
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Cardiovascular predictions are related to patients' quality of life and health. Therefore, a risk prediction model for cardiovascular conditions is needed.
METHODS
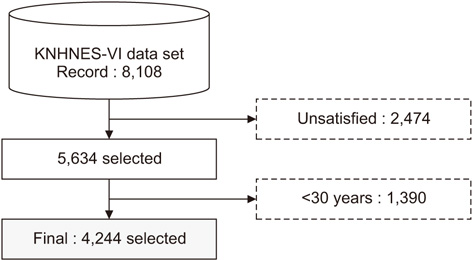
In this paper, we propose a cardiovascular disease prediction model using the sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES-VI) 2013 dataset to analyze cardiovascular-related health data. First, statistical analysis was performed to find variables related to cardiovascular disease using health data related to cardiovascular disease. Second, a model of cardiovascular risk prediction by learning based on the deep belief network (DBN) was developed.
RESULTS
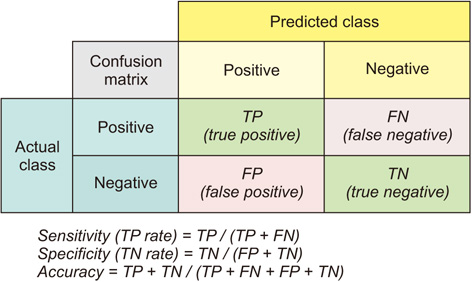
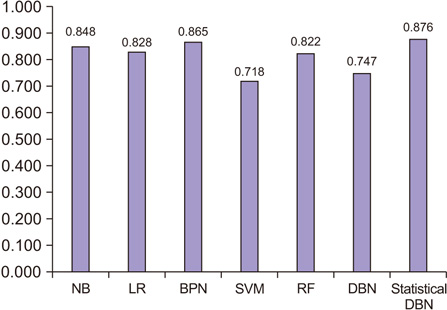
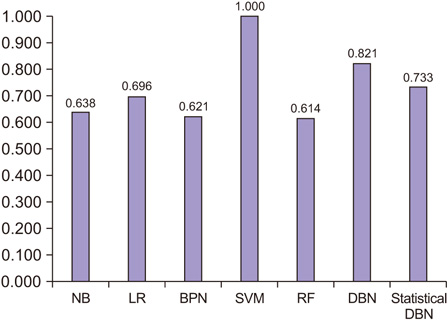
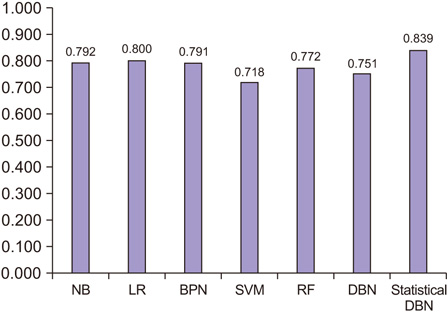
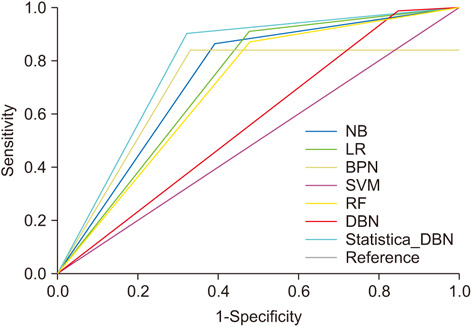
The proposed statistical DBN-based prediction model showed accuracy and an ROC curve of 83.9% and 0.790, respectively. Thus, the proposed statistical DBN performed better than other prediction algorithms.
CONCLUSIONS
The DBN proposed in this study appears to be effective in predicting cardiovascular risk and, in particular, is expected to be applicable to the prediction of cardiovascular disease in Koreans.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Austin PC, Tu JV, Ho JE, Levy D, Lee DS. Using methods from the data-mining and machine-learning literature for disease classification and prediction: a case study examining classification of heart failure subtypes. J Clin Epidemiol. 2013; 66(4):398–407.
Article2. Song MH, Kim SH, Park DK, Lee YH. A multi-classifier based guideline sentence classification system. Healthc Inform Res. 2011; 17(4):224–231.
Article3. Tomar D, Agarwal S. Feature selection based least square twin support vector machine for diagnosis of heart disease. Int J Biosci Biotechnol. 2014; 6(2):69–82.
Article4. Kim JK, Rho MJ, Lee JS, Park YH, Lee JY, Choi IY. Improved prediction of the pathologic stage of patient with prostate cancer using the CART-PSO optimization analysis in the Korean population. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2016; 12. 16. [Epub] http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1533034616681396.
Article5. Khatibi V, Montazer GA. A fuzzy-evidential hybrid inference engine for coronary heart disease risk assessment. Expert Syst Appl. 2010; 37(12):8536–8542.
Article6. Krishnaiah V, Narsimha G, Chandra NS. Heart disease prediction system using data mining technique by fuzzy K-NN approach. In : Satapathy S, Govardhan A, Raju K, Mandal J, editors. Emerging ICT for Bridging the Future-Proceedings of the 49th Annual Convention of the Computer Society of India (CSI) Volume 1. Cham: Springer International Publishing;2015. p. 371–384.7. Lee DY, Rhee EJ, Choi ES, Kim JH, Won JC, Park CY, et al. Comparison of the predictability of cardiovascular disease risk according to different metabolic syndrome criteria of American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and International Diabetes Federation in Korean men. Korean Diabetes J. 2008; 32(4):317–327.
Article8. Kim JK, Lee JS, Park DK, Lim YS, Lee YH, Jung EY. Adaptive mining prediction model for content recommendation to coronary heart disease patients. Clust Comput. 2014; 17(3):881–891.
Article9. Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, Setio AA, Ciompi F, Ghafoorian M, et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Ithaca (NY): arXiv.org;c2017. cited at 2017 Jul 1. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1702.05747.10. Hinton GE, Osindero S, Teh YW. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 2006; 18(7):1527–1554.
Article11. Dahl GE, Yu D, Deng L, Acero A. Context-dependent pre-trained deep neural networks for large-vocabulary speech recognition. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process. 2012; 20(1):30–42.
Article12. Abdel-Zaher AM, Eldeib AM. Breast cancer classification using deep belief networks. Expert Syst Appl. 2016; 46:139–144.
Article13. Tamilselvan P, Wang P. Failure diagnosis using deep belief learning based health state classification. Reliab Eng Syst Saf. 2013; 115:124–135.
Article14. Fakoor R, Ladhak F, Nazi A, Huber M. Using deep learning to enhance cancer diagnosis and classification. In : Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning; 2013 Jun 17-19; Atlanta, GA.15. Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention. The sixth Korea National Health & Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES-VI) 2013 [Internet]. Cheongju: Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention;c2017. cited at 2017 Jul 1. Available: http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/.16. Ankle Brachial Index Collaboration. Fowkes FG, Murray GD, Butcher I, Heald CL, Lee RJ, et al. Ankle brachial index combined with Framingham Risk Score to predict cardiovascular events and mortality: a metaanalysis. JAMA. 2008; 300(2):197–208.
Article17. Palm RB. DeepLearnToolbox: a MATLAB toolbox for deep learning [Internet]. San Francisco (CA): GitHub Inc.;c2017. cited at 2017 Jul 1. Available:https://github.com/rasmusbergpalm/DeepLearnToolbox.18. Hinton GE. A practical guide to training restricted Boltzmann machines. Toronto: University of Toronto;2010.19. Hinton GE, Salakhutdinov RR. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science. 2006; 313(5786):504–507.
Article20. Salama MA, Hassanien AE, Fahmy AA. Deep belief network for clustering and classification of a continuous data. In : Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT); 2010 Dec 15-18; Luxor, Egypt. p. 473–477.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development and Application of a Performance Prediction Model for Home Care Nursing Based on a Balanced Scorecard using the Bayesian Belief Network
- Deep Neural Network-Based Prediction of the Risk of Advanced Colorectal Neoplasia
- Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Based Diabetes Prediction System Using a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort
- Review on Cardiovascular Disease Prediction Model in Diabetes Patients
- Development of a Stress Classification Model Using Deep Belief Networks for Stress Monitoring