Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2018 Jan;20(1):36-40. 10.14253/acn.2018.20.1.36.
Lennox-Gastaut syndrome associated with dysgenesis of corpus callosum
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Center for Neurology, Fairfax, VI, USA.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, King Faisal Specialist Hospital, Hail University, Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. dr.legend@hotmail.com
- 3Dow Medical College, Karachi, Pakistan.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, King Khaled Hospital, Hail, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
- 5Department of Pediatrics, King Khaled Hospital, Hail, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
- 6Center for Rehabilitation, King Khaled Hospital, Hail, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
- 7Speclaist in Autism and Behavioral Disorder at King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center, Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
- KMID: 2403220
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2018.20.1.36
Abstract
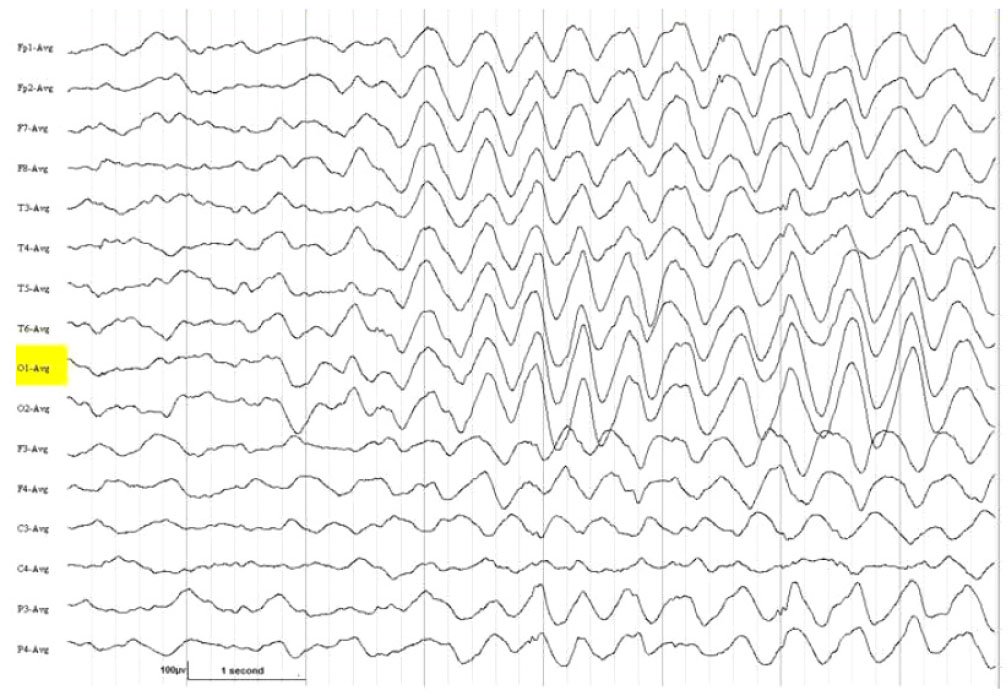
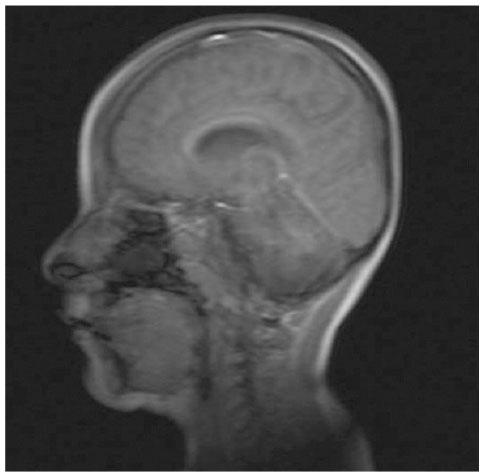
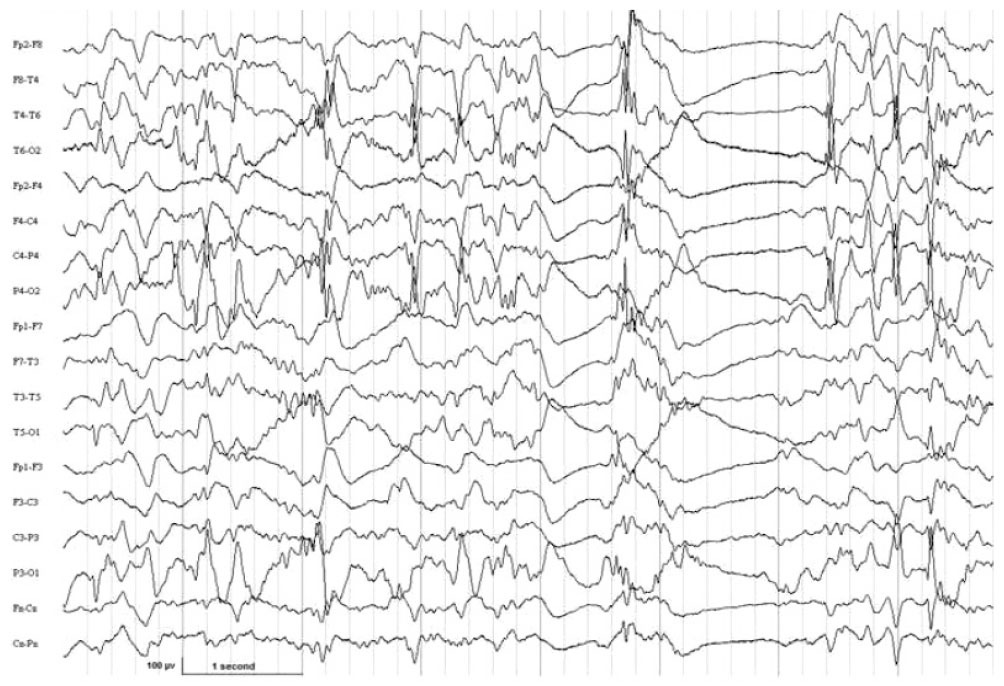
- Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) is an electro-clinical syndrome composed of the triad of mental retardation, multiple seizure types, and the characteristic generalized slow spike-wave complexes in the electroencephalogram. In this article, we report on two patients with LGS whose brain magnetic resonance imaging showed dysgenesis of corpus callosum (CC). We discuss the role of CC in the genesis of secondary bilateral synchrony.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gastaut H, Broughton RJ. Clinical and electrographic features, diagnosis and treatment. Springfield: Charles C Thomas;1972. p. 176–182.2. Blume WT. Pathogenesis of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome: considerations and hypothesis. Epileptic Disord. 2001; 3:183–196.3. Lombroso CT. A prospective study of infantile spasms: clinical and therapeutic correlations. Epilepsia. 1983; 24:135–158.
Article4. Aicardi J, Lefebvre J, Lerique-Koechlin A. A new syndrome: Spasm in flexion, callosal agenesis, ocular abnormalities. Electroencephal Clin Neurophysiol. 1965; 19:609–610.5. Hrachovy RA, Frost JD Jr. The EEG in selected generalized seizures. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2006; 23:312–332.
Article6. Intusoma U, Abbott DF, Masterton RA, Stagnitti MR, Newton MR, Jackson GD, et al. Tonic seizures of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome: periictal single-photon emission computed tomography suggests a corticopontine network. Epilepsia. 2013; 54:2151–2157.
Article7. Niedermeyer E, da Silva FL. Electroencephalography: basic principles, clinical applications, and related fields. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins;2005; 412–456.8. Tinuper P, Cerullo A, Marini C, Avoni P, Rosati A, Riva R, et al. Epileptic drop attacks in partial epilepsy: clinical features, evolution, and prognosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988; 64:231–237.
Article9. Janati A. Aberrant EEG rhythms and epilepsy. J Clin Neuophysiol. 2011; 28:533. author reply 533.
Article10. Alghasab N, Janati AB, Khan A. Partial agenesis of corpus callosum in Sanjad-Sakati syndrome(p-ACC). Can J Neurol Sci. 2012; 39:39.