Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2018 Jan;6(1):26-33. 10.4168/aard.2018.6.1.26.
Outcomes of drug provocation tests in Korean children with suspected drug hypersensitivity reaction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Childhood Asthma Atopy Center, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sjhong@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Environmental Health Center, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2403182
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2018.6.1.26
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Drug provocation tests (DPT) are the gold standard for confirming the diagnosis of drug hypersensitivity reactions (DHRs). However, there are little studies of DPT in children. The purpose of this study was to evaluate DPT results and safety as diagnostic methods of DHR in Korean children.
METHODS
We reviewed the medical records of 39 children under 18 years of age with a suspected DHR and performed DPT between January 2010 and May 2016 at Asan Medical Center.
RESULTS
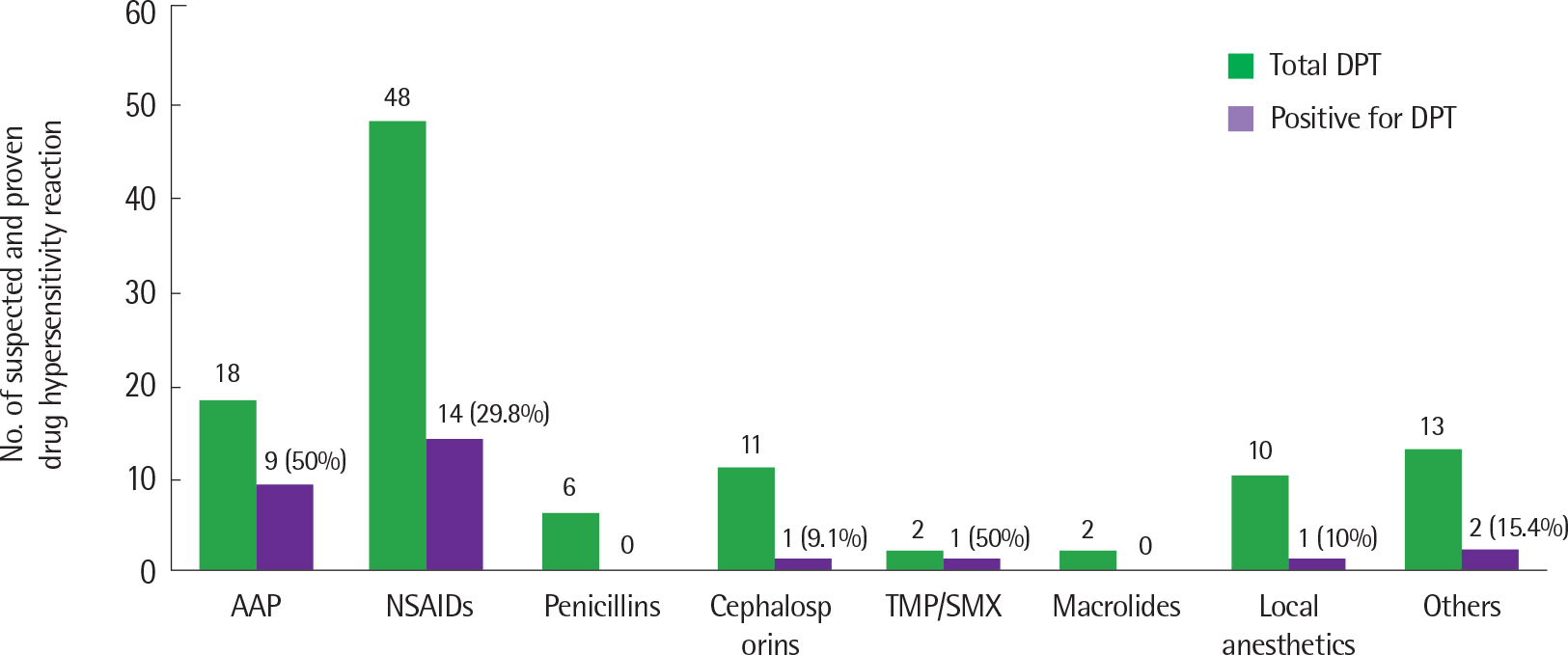
Total 110 DPT were performed in 39 children (20 boys and 19 girls) with a history of DHR. Clinical presentation of DHR included skin rash (n=7), pruritus (n=3), urticaria (n=18), angioedema (n=19), dyspnea (n=5), hoarseness (n=1), hypothermia (n=1), and anaphylaxis (n=5). The median age at the time of DPT was 9 years. Positive DPT were observed in 21 of 39 children (53.8%) and 28 of 110 cases (25.5%). Drugs causing positive reactions were acetaminophen in 50% (9 of 18), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in 29.2% (14 of 48), cephalosporin in 9.1% (1 of 11), trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole in 50% (1 of 2), local anesthetics in 10% (1 of 10), and others (levodropropizine and idursulfase) in 15.4% (2 of 13). There was no statistical difference between children who had positive and negative results in sex, age, personal and parental history of allergic disease, eosinophil count, or total IgE level. Children with positive DPT did not develop anaphylaxis during the DPT procedure.
CONCLUSION
Drug provocation test is safe, and it can be considered in children with suspected DHRs.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Johansson SG, Bieber T, Dahl R, Friedmann PS, Lanier BQ, Lockey RF, et al. Revised nomenclature for allergy for global use: Report of the Nomenclature Review Committee of the World Allergy Organization, October 2003. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:832–6.
Article2. Khan DA, Solensky R. Drug allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125(2 Suppl 2):S126–37.
Article3. Aberer W, Bircher A, Romano A, Blanca M, Campi P, Fernandez J, et al. Drug provocation testing in the diagnosis of drug hypersensitivity reactions: general considerations. Allergy. 2003; 58:854–63.
Article4. Demoly P, Bousquet J. Epidemiology of drug allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 1:305–10.
Article5. Seitz CS, Bröcker EB, Trautmann A. Diagnosis of drug hypersensitivity in children and adolescents: discrepancy between physician-based assessment and results of testing. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2011; 22:405–10.
Article6. Vezir E, Erkocoglu M, Civelek E, Kaya A, Azkur D, Akan A, et al. The evaluation of drug provocation tests in pediatric allergy clinic: a single center experience. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2014; 35:156–62.
Article7. Aun MV, Bisaccioni C, Garro LS, Rodrigues AT, Tanno LK, Ensina LF, et al. Outcomes and safety of drug provocation tests. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2011; 32:301–6.
Article8. Messaad D, Sahla H, Benahmed S, Godard P, Bousquet J, Demoly P. Drug provocation tests in patients with a history suggesting an immediate drug hypersensitivity reaction. Ann Intern Med. 2004; 140:1001–6.
Article9. Na HR, Lee JM, Jung JW, Lee SY. Usefulness of drug provocation tests in children with a history of adverse drug reaction. Korean J Pediatr. 2011; 54:304–9.
Article10. Choi J, Lee JY, Kim KH, Choi J, Ahn K, Kim J. Evaluation of drug provocation tests in Korean children: a single center experience. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2016; 34:130–6.
Article11. Simons FE, Ardusso LR, Dimov V, Ebisawa M, El-Gamal YM, Lockey RF, et al. World Allergy Organization Anaphylaxis Guidelines: 2013 update of the evidence base. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013; 162:193–204.
Article12. Simons FE, Ardusso LR, Bilò MB, Cardona V, Ebisawa M, El-Gamal YM, et al. International consensus on (ICON) anaphylaxis. World Allergy Organ J. 2014; 7:9.
Article13. Mirakian R, Ewan PW, Durham SR, Youlten LJ, Dugué P, Friedmann PS, et al. BSACI guidelines for the management of drug allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009; 39:43–61.
Article14. Rubio M, Bousquet PJ, Gomes E, Romano A, Demoly P. Results of drug hypersensitivity evaluations in a large group of children and adults. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012; 42:123–30.
Article15. Indradat S, Veskitkul J, Pacharn P, Jirapongsananuruk O, Visitsunthorn N. Provocation proven drug allergy in Thai children with adverse drug reactions. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2016; 34:59–64.
Article16. Park GM, Han HW, Kim JW, Hwang KH, Lee E, Yang SI, et al. Delayed urticaria caused by lidocaine in a child. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2014; 2:298–301.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Drug Allergy in Children: What Should We Know?
- Usefulness of drug provocation tests in children with a history of adverse drug reaction
- An Overview of Multiple Drug Hypersensitivity Syndrome
- Recent Updates on Diagnosis and Prevention of Hypersensitivity Reactions to Iodinated Contrast Media
- Update on the diagnosis of drug allergy