Korean J Ophthalmol.
2018 Feb;32(1):1-7. 10.3341/kjo.2017.0030.
Long-term Efficacy of Botulinum Neurotoxin-A Treatment for Essential Blepharospasm
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea. eye@cha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2402713
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.0030
Abstract
- PURPOSE
In the present study, we investigated the treatment efficacy and clinical outcomes of botulinum neurotoxin-A (BoNT-A) administered for longer than 5 years to patients with essential blepharospasm.
METHODS
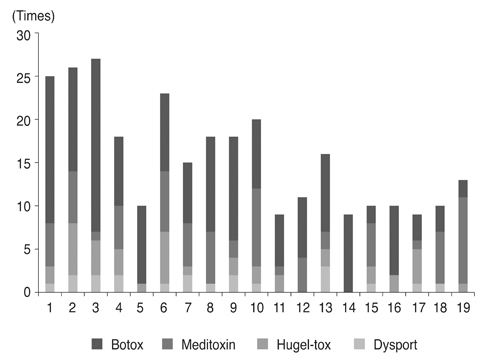
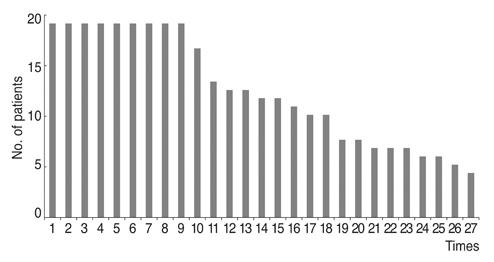
We retrospectively reviewed 19 patients (male : female = 8 : 11) diagnosed with essential blepharospasm between March 2006 and July 2016 who underwent BoNT-A injections for over 5 years and were followed. Efficacy of 297 injections of Botox (n = 162), Meditoxin (n = 75), Hugel-tox (n = 40), or Dysport (n = 20) was based on the symptom improvement score at the final injection (−1, worse; 0, same; 1, better). Injection dose (botox unit), duration of efficacy (months), and adverse events were also investigated.
RESULTS
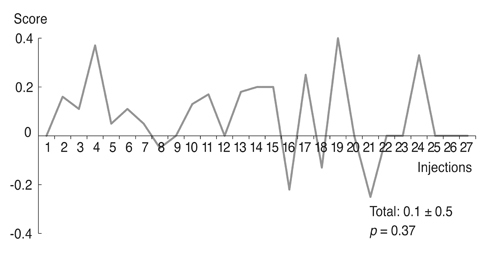
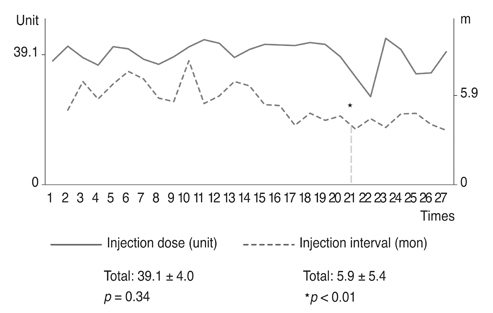
Based on product type, significant differences in patient age (59.3 ± 9.8 years), disease period (5.0 ± 5.4 years), number of botulinum neurotoxin injections before visiting our clinic (1.6 ± 2.6), and follow-up period (7.2 ± 1.6 years) were not observed. Treatment efficacy score and injection dose of repetitive injections were 0.1 ± 0.5 and 39.1 ± 4.0 units, respectively, and did not show significant differences with repeated injections. Duration of response was 5.9 ± 5.4 months, but this significantly decreased as the injections were repeated (p < 0.01). Among the 297 injections, adverse events occurred 12 times (4.0%) with no severe sequelae.
CONCLUSIONS
In this study, we showed that repetitive, long-term BoNT-A injections are considered a stable and effective treatment for essential blepharospasm in terms of consistent injection dose and maintenance of treatment efficacy. However, the duration of long-term efficacy could be decreased in patients injected repetitively.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kenney C, Jankovic J. Botulinum toxin in the treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2008; 115:585–591.
Article2. Naumann M, Albanese A, Heinen F, et al. Safety and efficacy of botulinum toxin type A following long-term use. Eur J Neurol. 2006; 13:Suppl 4. 35–40.
Article3. Sung Y, Nam SM, Lew H. Clinical outcomes of individualized botulinum neurotoxin type A injection techniques in patients with essential blepharospasm. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2015; 29:115–120.
Article4. Scott AB, Kennedy RA, Stubbs HA. Botulinum A toxin injection as a treatment for blepharospasm. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985; 103:347–350.
Article5. Dutton JJ, Fowler AM. Botulinum toxin in ophthalmology. Surv Ophthalmol. 2007; 52:13–31.
Article6. Sampaio C, Ferreira JJ, Simoes F, et al. DYSBOT: a single-blind, randomized parallel study to determine whether any differences can be detected in the efficacy and tolerability of two formulations of botulinum toxin type A (Dysport a nd Botox) a ssuming a ratio o f 4:1. Mov Disord. 1997; 12:1013–1018.7. Rieder CR, Schestatsky P, Socal MP, et al. A double-blind, randomized, crossover study of prosigne versus botox in patients with blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2007; 30:39–42.
Article8. Pagan FL, Harrison A. A guide to dosing in the treatment of cervical dystonia and blepharospasm with Xeomin: a new botulinum neurotoxin A. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012; 18:441–445.
Article9. Shin JH, Jeon C, Woo KI, Kim YD. Clinical comparability of dysport and botox in essential blepharospasm. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:331–335.
Article10. Yoon JS, Kim JC, Lee SY. Double-blind, randomized, comparative study of Meditoxin versus Botox in the treatment of essential blepharospasm. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2009; 23:137–141.
Article11. Ababneh OH, Cetinkaya A, Kulwin DR. Long-term efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin A injections to treat blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014; 42:254–261.
Article12. Ramirez-Castaneda J, Jankovic J. Long-term efficacy, safety, and side effect profile of botulinum toxin in dystonia: a 20-year follow-up. Toxicon. 2014; 90:344–348.
Article13. Czyz CN, Burns JA, Petrie TP, et al. Long-term botulinum toxin treatment of benign essential blepharospasm, hemifacial spasm, and Meige syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013; 156:173–177.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of blepharospasm with botulinum A toxin
- Clinical Comparability of Dysport and Botox in Essential Blepharospasm
- Clinical Effect of Limited Myectomy for the Treatment of Essential Blepharospasm
- Management of Essential Blepharospasm: Botulinum Toxin A Treatment and Orbicularis Myectomy Operation
- Botulinum-Induced Changes in Orbicularis Oculi Muscle