J Adv Prosthodont.
2017 Dec;9(6):409-415. 10.4047/jap.2017.9.6.409.
A standardization model based on image recognition for performance evaluation of an oral scanner
- Affiliations
-
- 1A3DI, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea. kblee@knu.ac.kr
- 2Myeong Moon Dental Co., LTD, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
- 3Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2398044
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2017.9.6.409
Abstract
- PURPOSE
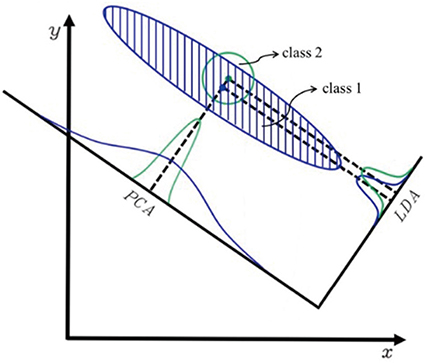
Accurate information is essential in dentistry. The image information of missing teeth is used in optically based medical equipment in prosthodontic treatment. To evaluate oral scanners, the standardized model was examined from cases of image recognition errors of linear discriminant analysis (LDA), and a model that combines the variables with reference to ISO 12836:2015 was designed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
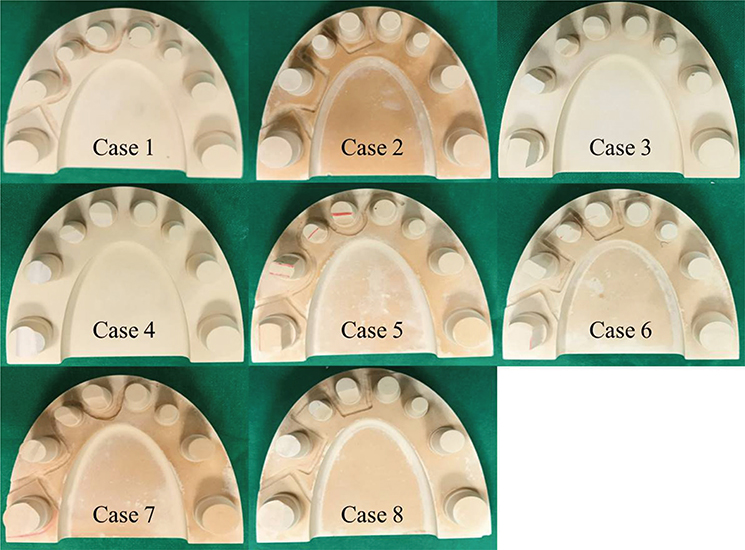
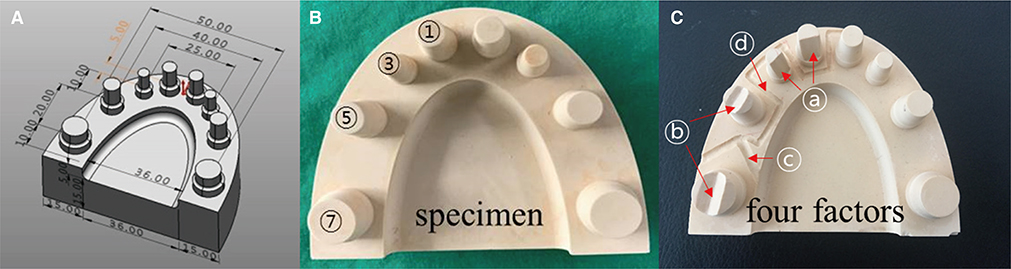
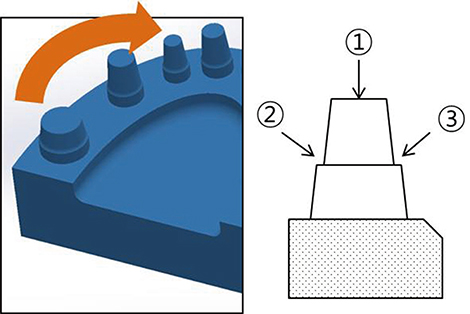
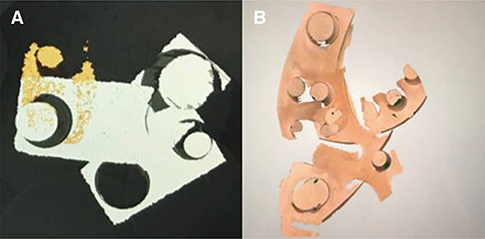
The basic model was fabricated by applying 4 factors to the tooth profile (chamfer, groove, curve, and square) and the bottom surface. Photo-type and video-type scanners were used to analyze 3D images after image capture. The scans were performed several times according to the prescribed sequence to distinguish the model from the one that did not form, and the results confirmed it to be the best.
RESULTS
In the case of the initial basic model, a 3D shape could not be obtained by scanning even if several shots were taken. Subsequently, the recognition rate of the image was improved with every variable factor, and the difference depends on the tooth profile and the pattern of the floor surface.
CONCLUSION
Based on the recognition error of the LDA, the recognition rate decreases when the model has a similar pattern. Therefore, to obtain the accurate 3D data, the difference of each class needs to be provided when developing a standardized model.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Syrek A, Reich G, Ranftl D, Klein C, Cerny B, Brodesser J. Clinical evaluation of all-ceramic crowns fabricated from intraoral digital impressions based on the principle of active wavefront sampling. J Dent. 2010; 38:553–559.2. Thalji G, Bryington M, De Kok IJ, Cooper LF. Prosthodontic management of implant therapy. Dent Clin North Am. 2014; 58:207–225.3. Moghaddam B, Pentland A. Probabilistic visual learning for object representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 1997; 19:696–710.4. Kang SK, Lee JH. Improve the performance of people detection using fisher linear discriminant analysis in surveillance. J Digit Converg. 2013; 11:295–302.5. Sung KK, Poggio S. Learning a distribution-based face model for human face detection. In Neural Networks for Signal Processing [1995] V. In : Proceedings of The 1995 IEEE Workshop; IEEE;1995.6. Moura DC, Barbosa JG. Real-scale 3D models of the scoliotic spine from biplanar radiography without calibration objects. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2014; 38:580–585.7. Wang J, Suenaga H, Liao H, Hoshi K, Yang L, Kobayashi E, Sakuma I. Real-time computer-generated integral imaging and 3D image calibration for augmented reality surgical navigation. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2015; 40:147–159.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparative study on quality of scanned images from varying materials and surface conditions of standardized model for dental scanner evaluation
- Relationship between job competency, core self-evaluation, and job performance in dental hygienists
- Protected Health Information Recognition by Fine-Tuning a Pre-training Transformer Model
- Applications of Optical Imaging System in Dentistry
- The development of food image detection and recognition model of Korean food for mobile dietary management