Asia Pac Allergy.
2012 Apr;2(2):161-164. 10.5415/apallergy.2012.2.2.161.
Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis occurred only in a warm but not in a cold environment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-799, Korea. addchang@snu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul 110-799, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam 463-802, Korea.
- KMID: 2397370
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2012.2.2.161
Abstract
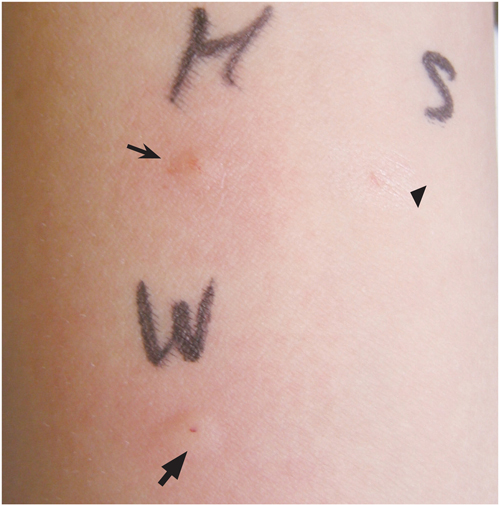
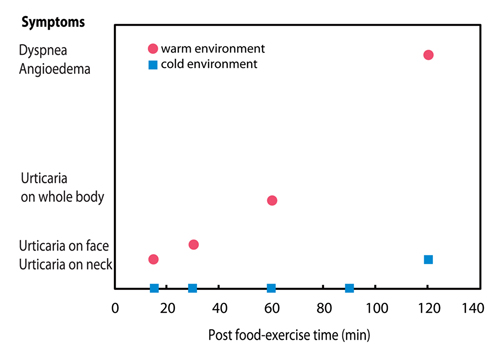
- Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis (FDEIA) is a type of exercise-induced anaphylaxis associated with postprandial exercise. We describe a 19-year-old man with FDEIA. Our patient complained of urticaria, angioedema, dizziness and hypotension associated with exercise after ingestion of walnut-containing foods in a warm environment. Skin prick test and prick to prick test were positive for walnut antigen. The attack didn't occur by free running outside for 10 min 2 h after taking walnuts, and the temperature was about -2℃. Food-exercise test was done again in a warm environment based on prior history. Anaphylaxis was developed after exercise for 10 min in a warm environment after taking walnuts. Some environmental factors such as high temperature and high humidity or cold temperature may influence exercise-induced anaphylaxis. In our case, the cofactor was a warm environment: the challenge test done in a cold environment was negative, but positive in a warm environment. Physicians should be aware that the challenge test of FDEIA can show different results depending on temperature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Korean children: a single-center retrospective case study
Eun Lee, Min-Ju Kim, Song-I Yang, Jinho Yu, Soo-Jong Hong
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(3):194-199. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.3.194.Wheat-Induced Anaphylaxis in Korean Adults: A Report of 6 Cases
Seung-Eun Lee, Suh-Young Lee, Eun-Jung Jo, Mi-Young Kim, Sae-Hoon Kim, Yoon-Seok Chang
Clin Nutr Res. 2013;2(1):76-79. doi: 10.7762/cnr.2013.2.1.76.Asia Pacific Allergy: a successful first year and the future
Yoon-Seok Chang
Asia Pac Allergy. 2012;2(2):91-92. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2012.2.2.91.
Reference
-
1. Johansson SG, Hourihane JO, Bousquet J, Bruijnzeel-Koomen C, Dreborg S, Haahtela T, Kowalski ML, Mygind N, Ring J, van Cauwenberge P, van Hage-Hamsten M, Wüthrich B. A revised nomenclature for allergy. An EAACI position statement from the EAACI nomenclature task force. Allergy. 2001; 56:813–824.
Article2. Lieberman P, Camargo CA Jr, Bohlke K, Jick H, Miller RL, Sheikh A, Simons FE. Epidemiology of anaphylaxis: findings of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Epidemiology of Anaphylaxis Working Group. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006; 97:596–602.
Article3. Yang MS, Lee SH, Kim TW, Kwon JW, Lee SM, Kim SH, Kwon HS, Park CH, Park HW, Kim SS, Cho SH, Min KU, Kim YY, Chang YS. Epidemiologic and clinical features of anaphylaxis in Korea. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 100:31–36.
Article4. Simons FE. Anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:S161–S181.
Article5. Wong CG, Mace SR. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: a case related to chickpea ingestion and review. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2007; 3:134–137.
Article6. Wolańczyk-Medrala A, Barg W, Radlińska A, Panaszek B, Medrala W. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis-sequence of causative factors might be reversed. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2010; 17:315–317.7. Maulitz RM, Pratt DS, Schocket AL. Exercise-induced anaphylactic reaction to shellfish. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979; 63:433–434.
Article8. Kidd JM 3rd, Cohen SH, Sosman AJ, Fink JN. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983; 71:407–411.9. Aihara Y, Takahashi Y, Kotoyori T, Mitsuda T, Ito R, Aihara M, Ikezawa Z, Yokota S. Frequency of food-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Japanese junior-high-school students. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:1035–1039.
Article10. Kurowski K, Boxer RW. Food allergies: detection and management. Am Fam Physician. 2008; 77:1678–1686.11. Yang MS, Lee SH, Kim KM, Kwon HS, Kim DI, Park CH, Son SW, Park HW, Chang YS, Kim SS, Cho SH, Min KU, Kim YY. A case report of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis to apples. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 26:242–245.12. Robson-Ansley P, Toit GD. Pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 10:312–317.
Article13. Sheffer AL, Tong AK, Murphy GF, Lewis RA, McFadden ER Jr, Austen KF. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis: a serious form of physical allergy associated with mast cell degranulation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985; 75:479–484.
Article14. de Oliveira EP, Burini RC. Food-dependent, exercise-induced gastrointestinal distress. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2011; 8:12.
Article15. Palosuo K, Varjonen E, Nurkkala J, Kalkkinen N, Harvima R, Reunala T, Alenius H. Transglutaminase-mediated cross-linking of a peptic fraction of omega-5 gliadin enhances IgE reactivity in wheat-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111:1386–1392.16. Barg W, Medrala W, Wolanczyk-Medrala A. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis: an update on diagnosis and treatment. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011; 11:45–51.
Article17. Welle M. Development, significance, and heterogeneity of mast cells with particular regard to the mast cell-specific proteases chymase and tryptase. J Leukoc Biol. 1997; 61:233–245.
Article18. Shimizu T, Furumoto H, Kinoshita E, Ogasawara Y, Nakamura C, Hashimoto Y, Nagai K, Muto M. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis occurring only in winter. Dermatology. 2000; 200:279.
Article19. Miller CW, Guha B, Krishnaswamy G. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis: a serious but preventable disorder. Phys Sportsmed. 2008; 36:87–94.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis developed only in winter
- A Case of Wheat-Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis
- Food allergies and food-induced anaphylaxis: role of cofactors
- A Case of Cold Urticaria with Exercise- and Cold-Induced Anaphylaxis
- Wheat-dependent, Exercise-induced Anaphylaxis: A Successful Case of Prevention with Ketotifen