Ann Dermatol.
2009 May;21(2):203-205. 10.5021/ad.2009.21.2.203.
Wheat-dependent, Exercise-induced Anaphylaxis: A Successful Case of Prevention with Ketotifen
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Seoul, Korea. dermap@paran.com
- KMID: 2219398
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2009.21.2.203
Abstract
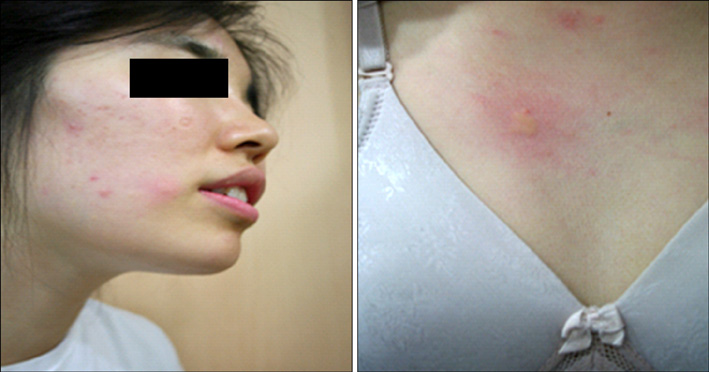
- Food-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis (FDEIA) is the triggering of anaphylaxis after ingestion of certain foods when followed by physical exercise. Symptoms vary from the typical generalized urticaria to severe allergic reactions. We report the case of a 20-year-old woman who had a 7-year history of recurrent wheals and dyspnea after ingesting several kinds of food (wheat, pork, and beef) along with physical exercise. Based on a provocation test, she was diagnosed with wheat-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis. She was instructed to take 2 mg of ketotifen 2 hours before ingestion of wheat to prevent the symptoms, and subsequently the provocation test did not elicit wheals. We therefore prescribed ketotifen (1 mg twice a day). She has not had recurrent wheals or dyspnea for 6 months. We herein report an interesting case of wheat-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis with successful prevention by ketotifen.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Overview of anaphylaxis in Korea: diagnosis and management
Gwang Cheon Jang, Yoon-Seok Chang, Sun Hee Choi, Woo-Jung Song, Soo-Young Lee, Hae-Sim Park, Hye-Ryun Kang, Yeong-Min Ye, Hyun-Jung Jin, Mi Yong Shin, Soo-Jin Lee, Hye One Kim, Jihyun Kim, Jae-Woo Jung, Hee-Bom Moon, Youngmin Ahn
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013;1(3):181-196. doi: 10.4168/aard.2013.1.3.181.Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Korea: a multicenter retrospective case study
Jae Hyoung Im, Hea Yoon Kwon, Young-Min Ye, Hae-Sim Park, Tae-Bum Kim, Gil-Soon Choi, Joo-Hee Kim, Gwang Cheon Jang, Mi Kyung Kim, Gyu-Young Hur, Young-Il Koh, Seong-Wook Sohn, Cheol-Woo Kim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013;1(3):203-210. doi: 10.4168/aard.2013.1.3.203.
Reference
-
1. Chong SU, Worm M, Zuberbier T. Role of adverse reactions to food in urticaria and exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002. 129:19–26.
Article2. Maulitz RM, Pratt DS, Schocket AL. Exercise-induced anaphylactic reaction to shellfish. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979. 63:433–434.
Article3. Aihara Y, Takahashi Y, Kotoyori T, Mitsuda T, Ito R, Aihara M, et al. Frequency of food-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Japanese junior-high-school students. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001. 108:1035–1039.
Article4. Shadick NA, Liang MH, Partridge AJ, Bingham C, Wright E, Fossel AH, et al. The natural history of exercise-induced anaphylaxis: survey results from a 10-year follow-up study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999. 104:123–127.
Article5. Morita E, Kunie K, Matsuo H. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Dermatol Sci. 2007. 47:109–117.
Article6. Harada S, Horikawa T, Ashida M, Kamo T, Nishioka E, Ichihashi M. Aspirin enhances the induction of type I allergic symptoms when combined with food and exercise in patients with food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Br J Dermatol. 2001. 145:336–339.
Article7. Aihara M, Miyazawa M, Osuna H, Tsubaki K, Ikebe T, Aihara Y, et al. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: influence of concurrent aspirin administration on skin testing and provocation. Br J Dermatol. 2002. 146:466–472.
Article8. Romano A, Di Fonso M, Giuffreda F, Papa G, Artesani MC, Viola M, et al. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: clinical and laboratory findings in 54 subjects. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001. 125:264–272.
Article9. Harada S, Horikawa T, Icihashi M. A study of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis by analyzing the Japanese cases reported in the literature. Arerugi. 2000. 49:1066–1073.10. Sheffer AL, Soter NA, McFadden ER Jr, Austen KF. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis: a distinct form of physical allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983. 71:311–316.
Article11. Sheffer AL, Tong AK, Murphy GF, Lewis RA, McFadden ER Jr, Austen KF. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis: a serious form of physical allergy associated with mast cell degranulation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985. 75:479–484.
Article12. Hanakawa Y, Tohyama M, Shirakata Y, Murakami S, Hashimoto K. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: a case related to the amount of food allergen ingested. Br J Dermatol. 1998. 138:898–900.
Article13. Palosuo K, Alenius H, Varjonen E, Koivuluhta M, Mikkola J, Keskinen H, et al. A novel wheat gliadin as a cause of exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999. 103:912–917.
Article14. Morita E, Matsuo H, Mihara S, Morimoto K, Savage AW, Tatham AS. Fast omega-gliadin is a major allergen in wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Dermatol Sci. 2003. 33:99–104.
Article15. Matsuo H, Kohno K, Morita E. Molecular cloning, recombinant expression and IgE-binding epitope of omega-5 gliadin, a major allergen in wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. FEBS J. 2005. 272:4431–4438.16. Petheram IS, Moxham J, Bierman CW, McAllen M, Spiro SG. Ketotifen in atopic asthma and exercise-induced asthma. Thorax. 1981. 36:308–312.
Article17. Berger G, Berger R, Goldberg A. Ketotifen induced inhibition of histamine release in a non-IgE model of middle ear effusion. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2006. 17:43–48.
Article18. Pichler WJ, Pichler CE, Helbing A. Exertion-induced anaphylaxis. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1987. 117:9–16.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Wheat-Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis
- Wheat - Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis Occurred With a Delayed Onset of 10 to 24 hours After Wheat Ingestion: A Case Report
- A case of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis developed only in winter
- Three Cases of Food-dependent Exercise-induced Anaphylaxis
- A case of wheat-induced anaphylaxis in an adult