Asia Pac Allergy.
2015 Jul;5(3):170-176. 10.5415/apallergy.2015.5.3.170.
Repeat oral food challenges in peanut and tree nut allergic children with a history of mild/moderate reactions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Sydney Children's Hospital, Sydney, NSW 2031, Australia. brynn.wainstein@sesiahs.health.nsw.gov.au
- 2School of Women's and Children's Health, University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia.
- KMID: 2397047
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2015.5.3.170
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
In peanut and tree nut allergic children a history of anaphylaxis is associated with subsequent severe reactions.
OBJECTIVE
We aimed to prospectively rechallenge peanut and tree nut allergic children with a history of mild/moderate reactions to assess their allergy over time.
METHODS
In this cohort study peanut and tree nut allergic children with a history of mild/moderate reactions during a controlled oral challenge were invited to have a follow-up oral challenge to the same food at least 1 year later.
RESULTS
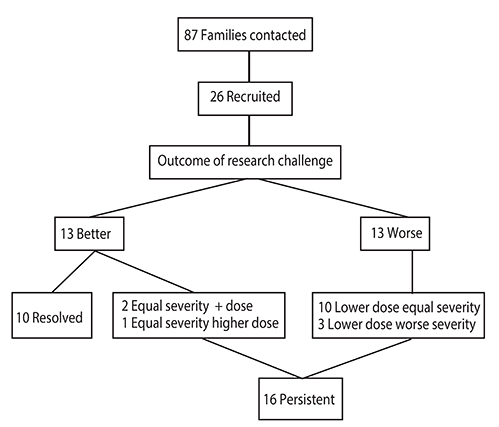
Twenty-six children participated in the study. The mean time interval between the first and second challenge for all participants was 35.5 months. Peanut or tree nut allergy resolved in 38.5% of participants. Those with persistent peanut or tree nut allergy showed a decrease in their reaction threshold and/or increased severity in 81% of cases. There were no demographic features or skin test results that were predictive of changes in severity over time.
CONCLUSION
Peanut and tree nut allergic children with a history of mild/moderate reactions who remained allergic demonstrated a high rate of more severe reactions and/or reduced thresholds upon rechallenge over a year later, however, the rate of resolution of allergy in this group may be higher than previously reported.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bock SA, Munoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA. Fatalities due to anaphylactic reactions to foods. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107:191–193.
Article2. Macdougall CF, Cant AJ, Colver AF. How dangerous is food allergy in childhood? The incidence of severe and fatal allergic reactions across the UK and Ireland. Arch Dis Child. 2002; 86:236–239.
Article3. Pumphrey RS. Lessons for management of anaphylaxis from a study of fatal reactions. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000; 30:1144–1150.
Article4. Liew WK, Williamson E, Tang ML. Anaphylaxis fatalities and admissions in Australia. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:434–442.
Article5. Avery NJ, King RM, Knight S, Hourihane JO. Assessment of quality of life in children with peanut allergy. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2003; 14:378–382.
Article6. Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Peanut allergy: emerging concepts and approaches for an apparent epidemic. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:491–503.
Article7. Vander Leek TK, Liu AH, Stefanski K, Blacker B, Bock SA. The natural history of peanut allergy in young children and its association with serum peanut-specific IgE. J Pediatr. 2000; 137:749–755.
Article8. Wainstein BK, Studdert J, Ziegler M, Ziegler JB. Prediction of anaphylaxis during peanut food challenge: usefulness of the peanut skin prick test (SPT) and specific IgE level. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010; 21(4 Pt 1):603–611.
Article9. Sicherer SH, Furlong TJ, Munoz-Furlong A, Burks AW, Sampson HA. A voluntary registry for peanut and tree nut allergy: characteristics of the first 5149 registrants. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:128–132.
Article10. Simons FE, Clark S, Camargo CA Jr. Anaphylaxis in the community: learning from the survivors. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:301–306.
Article11. Fleischer DM, Conover-Walker MK, Christie L, Burks AW, Wood RA. The natural progression of peanut allergy: Resolution and the possibility of recurrence. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 112:183–189.
Article12. Hourihane JO, Grimshaw KE, Lewis SA, Briggs RA, Trewin JB, King RM, Kilburn SA, Warner JO. Does severity of low-dose, double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenges reflect severity of allergic reactions to peanut in the community? Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:1227–1233.
Article13. Neuman-Sunshine DL, Eckman JA, Keet CA, Matsui EC, Peng RD, Lenehan PJ, Wood RA. The natural history of persistent peanut allergy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012; 108:326–331.e3.
Article14. Skolnick HS, Conover-Walker MK, Koerner CB, Sampson HA, Burks W, Wood RA. The natural history of peanut allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107:367–374.
Article15. Spergel JM, Beausoleil JL, Fiedler JM, Ginsberg J, Wagner K, Pawlowski NA. Correlation of initial food reactions to observed reactions on challenges. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004; 92:217–224.
Article16. Spergel JM, Beausoleil JL, Pawlowski NA. Resolution of childhood peanut allergy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2000; 85(6 Pt 1):473–476.
Article17. Fleischer DM, Conover-Walker MK, Matsui EC, Wood RA. The natural history of tree nut allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 116:1087–1093.
Article18. ASCIA Guidelines for adrenaline autoinjector prescription [Internet]. Balgowlah (AU): Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy;c2015. cited 2014 Nov 5. Available from: http://www.allergy.org.au/health-professionals/anaphylaxis-resources/adrenaline-autoinjector-prescription.19. Sampson HA. Anaphylaxis and emergency treatment. Pediatrics. 2003; 111(6 Pt 3):1601–1608.
Article20. Fleischer DM, Conover-Walker MK, Christie L, Burks AW, Wood RA. Peanut allergy: recurrence and its management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 114:1195–1201.
Article21. Hill DJ, Hosking CS, Reyes-Benito LV. Reducing the need for food allergen challenges in young children: a comparison of in vitro with in vivo tests. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001; 31:1031–1035.
Article22. Sampson HA. Utility of food-specific IgE concentrations in predicting symptomatic food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107:891–896.
Article23. Wainstein BK, Yee A, Jelley D, Ziegler M, Ziegler JB. Combining skin prick, immediate skin application and specific-IgE testing in the diagnosis of peanut allergy in children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2007; 18:231–239.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A 5-year retrospective review of children with peanut allergy in the largest paediatric hospital in Singapore
- Cashew nut allergy in Singaporean children
- Food Allergy
- Clinical Significance of Component Allergens in Fagales Pollen-Sensitized Peanut Allergy in Korea
- IgE mediated food allergy in Korean children: focused on plant food allergy