Asia Pac Allergy.
2016 Jan;6(1):70-73. 10.5415/apallergy.2016.6.1.70.
Ibuprofen induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome - toxic epidermal necrolysis in Nepal
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, Chitwan Medical College, Bharatpur 44200, Nepal.
- 2Department of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology, Universal College of Medical Sciences and Teaching Hospital, Siddharthanagar 32900, Nepal. dr.abhishekkarn@gmail.com
- KMID: 2396973
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2016.6.1.70
Abstract
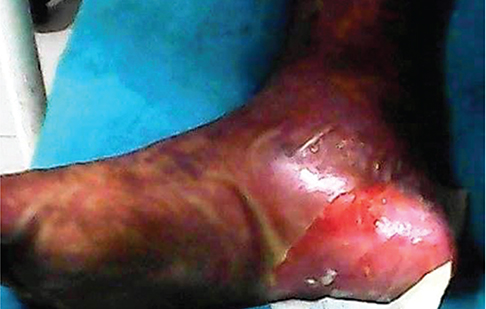
- Despite the fact that any drug can be an impending cause of hypersensitivity reactions, Ibuprofen, an over-the-counter drug used extensively as an analgesic and antipyretic in Asia, is considered to be relatively safe. But herein we report a rare extremely 'rapid onset' occurrence of a severe case of Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) in a 22-year-old male, induced by 3 doses of 400 mg of Ibuprofen taken at 8-hour interval for eye pain, probably the first case report of rapid onset of TEN by nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs in Nepal. SJS and TEN are idiosyncratic, delayed hypersensitivity inflammatory adverse drug reactions that are severe adverse cutaneous drug reactions which predominantly involve the skin and mucous membranes and are linked with high morbidity and mortality. Nevertheless, removal of ibuprofen and its metabolites with plasma exchange and treatment with antibiotics and intravenous corticosteroids along with supportive therapy improved the course of the disorder. This rare case report addresses the fact that severe hypersensitivity reactions can occur with Ibuprofen, which can be potentially dangerous and life threatening. It is thus important for the clinicians to be alert to such severe hypersensitivity reactions even with drugs which are deemed to be probably safe.
MeSH Terms
-
Adrenal Cortex Hormones
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Asia
Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Eye Pain
Humans
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity, Delayed
Ibuprofen*
Immune System Diseases
Male
Mortality
Mucous Membrane
Nepal*
Plasma Exchange
Skin
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome*
Young Adult
Adrenal Cortex Hormones
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Ibuprofen
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Asia Pacific Allergy: it's been five years!
Yoon-Seok Chang
Asia Pac Allergy. 2016;6(1):1-2. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2016.6.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Nanau RM, Neuman MG. Ibuprofen-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Transl Res. 2010; 155:275–293.
Article2. Auquier-Dunant A, Mockenhaupt M, Naldi L, Correia O, Schröder W, Roujeau JC. SCAR Study Group. Severe cutaneous adverse reactions. Correlations between clinical patterns and causes of erythema multiforme majus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis: results of an international prospective study. Arch Dermatol. 2002; 138:1019–1024.
Article3. Bastuji-Garin S, Rzany B, Stern RS, Shear NH, Naldi L, Roujeau JC. Clinical classification of cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and erythema multiforme. Arch Dermatol. 1993; 129:92–96.
Article4. Balint B, Stepic N, Todorovic M, Zolotarevski L, Ostojic G, Vucetic D, Pavlovic M, Novakovic M. Ibuprofen-induced extensive toxic epidermal necrolysis: a multidisciplinary therapeutic approach in a single case. Blood Transfus. 2014; 12:438–439.5. Thong BY. Stevens-Johnson syndrome / toxic epidermal necrolysis: an Asia-Pacific perspective. Asia Pac Allergy. 2013; 3:215–223.
Article6. Mockenhaupt M. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: clinical patterns, diagnostic considerations, etiology, and therapeutic management. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2014; 33:10–16.7. Kim EJ, Lim H, Park SY, Kim S, Yoon SY, Bae YJ, Kwon HS, Cho YS, Moon HB, Kim TB. Rapid onset of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis after ingestion of acetaminophen. Asia Pac Allergy. 2014; 4:68–72.
Article8. Yalcin AD, Karakas AA, Soykam G, Gorczynski RM, Sezer C, Bisgin A, Strauss LG. A case of toxic epidermal necrolysis with diverse etiologies: successful treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin and pulse prednisolone and effects on sTRAIL and sCD200 levels. Clin Lab. 2013; 59:681–685.
Article9. Aires DJ, Fraga G, Korentager R, Richie CP, Aggarwal S, Wick J, Liu DY. Early treatment with nonsucrose intravenous immunoglobulin in a burn unit reduces toxic epidermal necrolysis mortality. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013; 12:679–684.10. Lee HY, Chung WH. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: the year in review. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 13:330–336.11. Aguiar D, Pazo R, Duran I, Terrasa J, Arrivi A, Manzano H, Martín J, Rifa J. Toxic epidermal necrolysis in patients receiving anticonvulsants and cranial irradiation: a risk to consider. J Neurooncol. 2004; 66:345–350.
Article12. Aydin F, Cokluk C, Senturk N, Aydin K, Canturk MT, Turanli AY. Stevens-Johnson syndrome in two patients treated with cranial irradiation and phenytoin. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006; 20:588–590.
Article13. Harr T, French LE. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010; 5:39.
Article14. Lebargy F, Wolkenstein P, Gisselbrecht M, Lange F, Fleury-Feith J, Delclaux C, Roupie E, Revuz J, Roujeau JC. Pulmonary complications in toxic epidermal necrolysis: a prospective clinical study. Intensive Care Med. 1997; 23:1237–1244.
Article15. Litt JZ. Litt's drug eruptions and reactions manual. 16th ed. London: Informa Healthcare;2010.16. Momin SB. Review of intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of stevens-johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2009; 2:51–58.17. Kardaun SH, Jonkman MF. Dexamethasone pulse therapy for Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007; 87:144–148.
Article18. Jagadeesan S, Sobhanakumari K, Sadanandan SM, Ravindran S, Divakaran MV, Skaria L, Kurien G. Low dose intravenous immunoglobulins and steroids in toxic epidermal necrolysis: a prospective comparative open-labelled study of 36 cases. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013; 79:506–511.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- T Cell Mediated Drug Hypersensitivity: Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
- Ibuprofen Associated Acute Vanishing Bile Duct Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in an Infant
- A Case of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
- A comparative clinical study of toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Two Cases of HLA-B59(+) Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS)-Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) Associated with Methazolamide Treatment