Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital Bandung, Indonesia from 2009-2013
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Allergy-Immunology, Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Padjadjaran - Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital, Bandung 40161, Indonesia. wulan_yoewita@yahoo.com
- KMID: 2396969
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2016.6.1.43
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) are severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR) with high mortality and have a significant public health impact because of high mortality and morbidity.
OBJECTIVE
To describe data the epidemiological features, etiology, and treatment of retrospectively reviewed data of all patients with SJS and TEN.
METHODS
Retrospective study was conducted in patients with SJS and TEN treated from January 1, 2009 to December 31, 2013 in Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital Bandung, Indonesia.
RESULTS
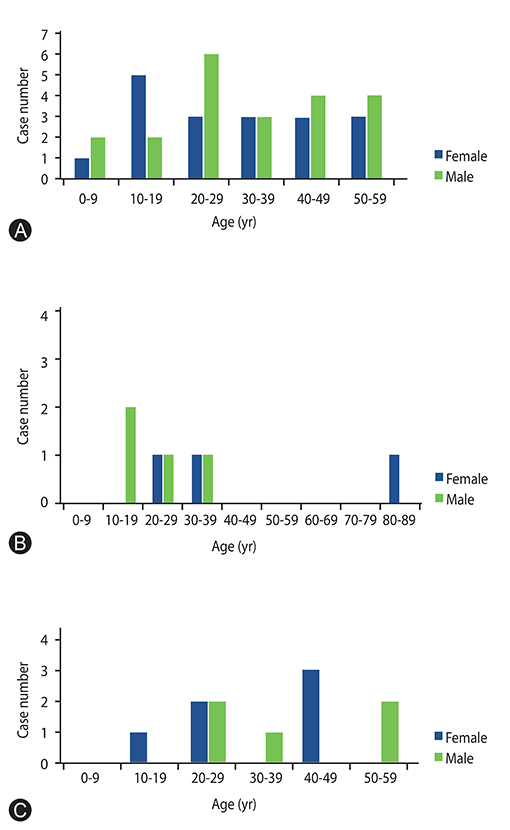
A total of 57 patients were enrolled in the study. Thirty-nine cases of SJS (21 males and 18 females), 7 cases of SJS overlapping TEN (4 males and 3 females), and 11 cases of TEN (5 males and 6 females) were reported. All cases of SJS and TEN were caused by drugs, such as paracetamol (16.56%), carbamazepine (7%), amoxicillin (5.73%), ibuprofen (4.46%), rifampicin (3.18%), and trihexyphenidyl (3.18%). All cases were treated systemically with corticosteroid alone (100%). Seven from 57 patients (12,28%) died; 5 cases developed sepsis and 2 cases developed respiratory failure. The mortality rate was 7.69% in SJS, 0% in SJS/TEN overlap, and 36.36% in TEN.
CONCLUSION
The role of systemic corticosteroids in SJS and TEN are still controversial, but with a prompt and earlier treatment reduces mortality and improves outcomes of SJS and TEN patients.
MeSH Terms
-
Acetaminophen
Adrenal Cortex Hormones
Amoxicillin
Carbamazepine
Hospitals, General*
Humans
Ibuprofen
Indonesia*
Male
Mortality
Public Health
Respiratory Insufficiency
Retrospective Studies
Rifampin
Sepsis
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome*
Trihexyphenidyl
Acetaminophen
Adrenal Cortex Hormones
Amoxicillin
Carbamazepine
Ibuprofen
Rifampin
Trihexyphenidyl
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Asia Pacific Allergy: it's been five years!
Yoon-Seok Chang
Asia Pac Allergy. 2016;6(1):1-2. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2016.6.1.1.Drug hypersensitivity reactions in Asia: regional issues and challenges
Bernard Yu-Hor Thong, Michaela Lucas, Hye-Ryun Kang, Yoon-Seok Chang, Philip Hei Li, Min Moon Tang, James Yun, Jie Shen Fok, Byung-Keun Kim, Mizuho Nagao, Iris Rengganis, Yi-Giien Tsai, Wen-Hung Chung, Masao Yamaguchi, Ticha Rerkpattanapipat, Wasu Kamchaisatian, Ting Fan Leung, Ho Joo Yoon, Luo Zhang, Amir Hamzah Abdul Latiff, Takao Fujisawa, Francis Thien, Mariana C. Castells, Pascal Demoly, Jiu-Yao Wang, Ruby Pawankar
Asia Pac Allergy. 2020;10(1):e8. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2020.10.e8.Drug hypersensitivity reactions in Asia: regional issues and challenges
Bernard Yu-Hor Thong, Michaela Lucas, Hye-Ryun Kang, Yoon-Seok Chang, Philip Hei Li, Min Moon Tang, James Yun, Jie Shen Fok, Byung-Keun Kim, Mizuho Nagao, Iris Rengganis, Yi-Giien Tsai, Wen-Hung Chung, Masao Yamaguchi, Ticha Rerkpattanapipat, Wasu Kamchaisatian, Ting Fan Leung, Ho Joo Yoon, Luo Zhang, Amir Hamzah Abdul Latiff, Takao Fujisawa, Francis Thien, Mariana C. Castells, Pascal Demoly, Jiu-Yao Wang, Ruby Pawankar
Asia Pac Allergy. 2020;10(1):. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2020.10.e8.
Reference
-
1. Chung WH, Hung SI. Genetic markers and danger signals in stevens-johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Allergol Int. 2010; 59:325–332.
Article2. French LE. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens Johnson syndrome: our current understanding. Allergol Int. 2006; 55:9–16.
Article3. Valeyrie-Allanore L, Roujeau JC. Epidermal necrolysis (stevens-johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis). In : Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell D, Wolff K, editors. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 8th ed. New York: McGraw Hill;2012. p. 439–448.4. Yamane Y, Aihara M, Ikezawa Z. Analysis of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Japan from 2000 to 2006. Allergol Int. 2007; 56:419–425.
Article5. Guegan S, Bastuji-Garin S, Poszepczynska-Guigne E, Roujeau JC, Revuz J. Performance of the SCORTEN during the first five days of hospitalization to predict the prognosis of epidermal necrolysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2006; 126:272–276.6. Verma R, Vasudevan B, Pragasam V. Severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions. Med J Armed Forces India. 2013; 69:375–383.
Article7. Wolkenstein PE, Roujeau JC, Revuz J. Drug-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis. Clin Dermatol. 1998; 16:399–408.
Article8. Roongpisuthipong W, Prompongsa S, Klangjareonchai T. Retrospective analysis of corticosteroid treatment in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and/or toxic epidermal necrolysis over a period of 10 years in Vajira Hospital, Navamindradhiraj University, Bangkok. Dermatol Res Pract. 2014; 2014:237821.
Article9. Harr T, French LE. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010; 5:39.
Article10. Azfar NA, Zia MA, Malik LM, Khan AR, Jahangir M. Role of systemic steroids in the outcome of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Pak Assoc Dermatol. 2010; 20:158–162.11. Martin T, Li H. Severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions: a review on epidemiology, etiology, clinical manifestation and pathogenesis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2008; 121:756–761.12. Kardaun SH, Jonkman MF. Dexamethasone pulse therapy for Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007; 87:144–148.
Article13. Tripathi A, Ditto AM, Grammer LC, Greenberger PA, McGrath KG, Zeiss CR, Patterson R. Corticosteroid therapy in an additional 13 cases of Stevens-Johnson syndrome: a total series of 67 cases. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2000; 21:101–105.
Article14. Rijal A, Agrawal S. Outcome of Stevens Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis treated with corticosteroids. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009; 75:613–614.
Article15. Kim HI, Kim SW, Park GY, Kwon EG, Kim HH, Jeong JY, Chang HH, Lee JM, Kim NS. Causes and treatment outcomes of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in 82 adult patients. Korean J Intern Med. 2012; 27:203–210.
Article16. Chantaphakul H, Sanon T, Klaewsongkram J. Clinical characteristics and treatment outcome of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Exp Ther Med. 2015; 10:519–524.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- T Cell Mediated Drug Hypersensitivity: Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
- The detection of Howell-Jolly body-like inclusions in a case of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19)
- A Case of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
- A comparative clinical study of toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Caused by Topical Ophthalmic Use of Dorzolamide