Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2017 Dec;10(4):321-324. 10.21053/ceo.2017.00129.
Substance P and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide in the Glands of External Auditory Canal Skin
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology, Chonbuk National University Medical School and Research Institute of Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
- 2Department of Otolaryngology, Wonkwang University Hospital, Iksan, Korea. sverige80@naver.com
- KMID: 2396786
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2017.00129
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The earwax (cerumen) that covers external auditory canal (EAC) skin contains a mixture of ceruminous and sebaceous gland substances, such as lipids, peptides, and proteins. The components secreted from the ceruminous gland that is a modified sweat gland form cerumen and contain several antimicrobial factors. Since substance P (SP) and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), known as a secretagogue, have been found in sweat glands, our purpose was to determine the expression of SP and CGRP in the glands of EAC skin.
METHODS
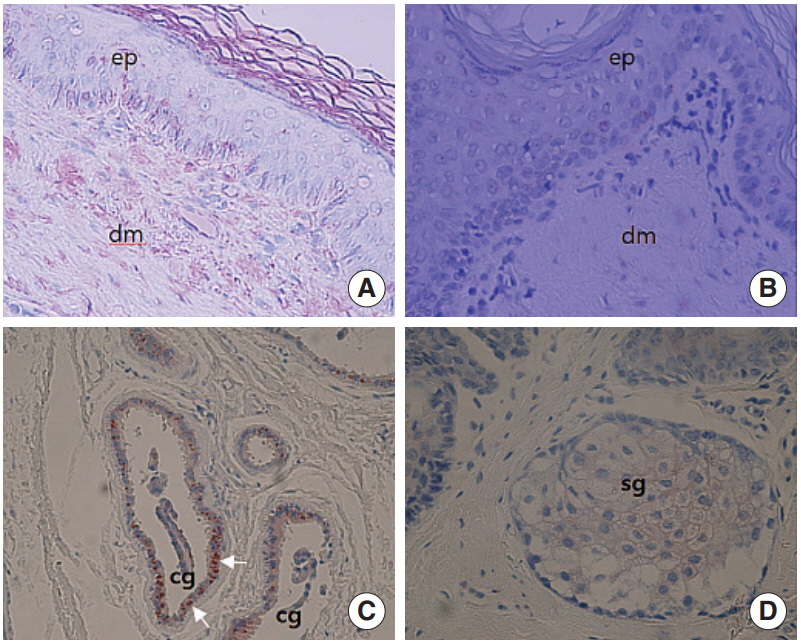
Sections of normal human EAC skins were immunostained for the presence of SP and CGRP using polyclonal antibodies. Immunoreactivity was detected using an avidin-biotin peroxidase complex method.
RESULTS
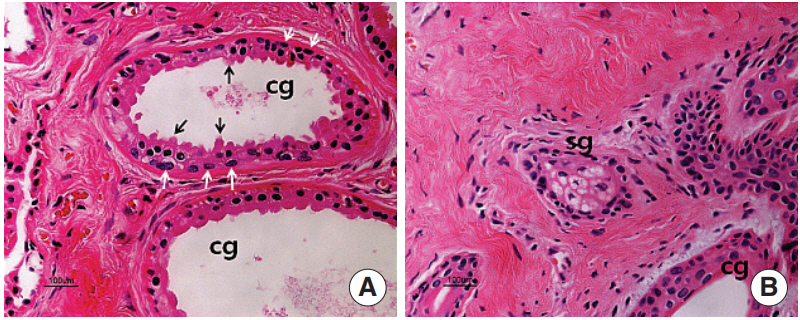
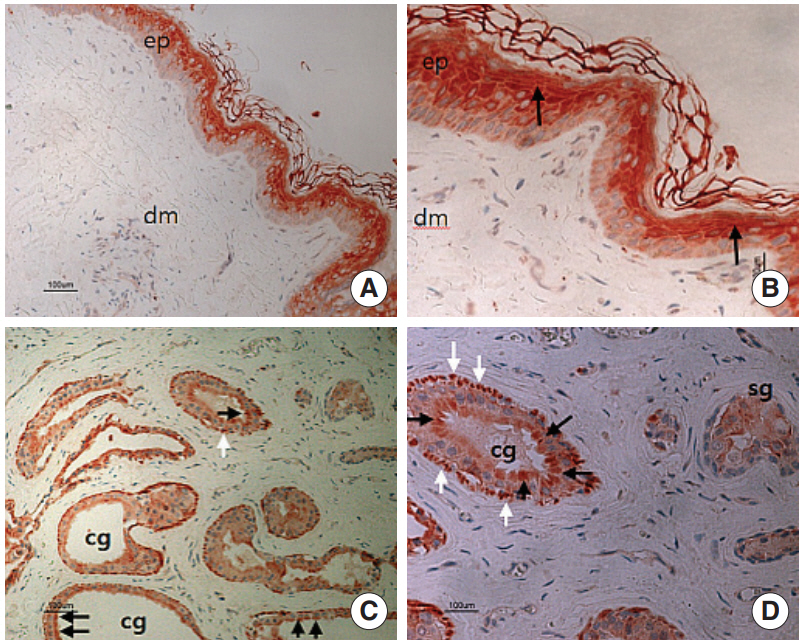
SP staining was found in ceruminous gland acini and myoepithelial cells. But the SP staining was not found in the sebaceous glands and epidermal region. CGRP was strongly stained in the ceruminous gland and weakly in the sebaceous gland cells. Interestingly, most prominent staining of SP and CGRP was noted in the myoepithelial cells of the ceruminous gland.
CONCLUSION
The findings in this study suggest that SP and CGRP are expressed in the glands of the EAC skin and secreted in the process of ceruminous gland secretion.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Main T, Lim D. The human external auditory canal, secretory system: an ultrastructural study. Laryngoscope. 1976; Aug. 86(8):1164–76.2. Ogawa H. Immunocytological localization of lysozyme in human skin. J Dermatol. 1975; Mar. 2(1):45–50.
Article3. Harder J, Bartels J, Christophers E, Schroder JM. A peptide antibiotic from human skin. Nature. 1997; Jun. 387(6636):861.
Article4. Ali RS, Falconer A, Ikram M, Bissett CE, Cerio R, Quinn AG. Expression of the peptide antibiotics human beta defensin-1 and human beta defensin-2 in normal human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2001; Jul. 117(1):106–11.5. Yoon YJ, Park JW, Lee EJ. Presence of hBD-1 and hBD-2 in human cerumen and external auditory canal skin. Acta Otolaryngol. 2008; Aug. 128(8):871–5.6. Yoon YJ, Lee EJ. Spatial distribution of antimicrobial peptides and mast cells in the skin of the external auditory canal. J Laryngol Otol. 2011; Nov. 125(11):e6.
Article7. Jankowski A, Kapusta E, Nowacka B. On the bacteriostatic or bactericidal function of ceruminous glands secretion. Otolaryngol Pol. 1992; 46(6):557–60.8. Church MK, Lowman MA, Robinson C, Holgate ST, Benyon RC. Interaction of neuropeptides with human mast cells. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989; 88(1-2):70–8.
Article9. Ansel JC, Brown JR, Payan DG, Brown MA. Substance P selectively activates TNF-alpha gene expression in murine mast cells. J Immunol. 1993; May. 150(10):4478–85.10. Tandler B, Phillips CJ. Structure of serous cells in salivary glands. Microsc Res Tech. 1993; Sep. 26(1):32–48.
Article11. Jeffery PK. Morphologic features of airway surface epithelial cells and glands. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983; Aug. 128(2 Pt 2):S14–20.12. Haxhiu MA, Haxhiu-Poskurica B, Moracic V, Carlo WA, Martin RJ. Reflex and chemical responses of tracheal submucosal glands in piglets. Respir Physiol. 1990; Dec. 82(3):267–77.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Antiandrogen on Calcitonin Gene-related Peptide mRNA Expression ofthe Rat Cremaster Nucleus
- Expression of Neuropeptides and Their Receptors in Psoriatic Lesions
- A immunohistochemical study of localization of calcitonin gene related peptide in the rats cochlear nucleus and superior olivary complex
- Expression of Neuropeptides and Their Receptors in Melasma
- The Effect of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide on Hair Growth in Vitro