Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2017 Nov;5(6):320-325. 10.4168/aard.2017.5.6.320.
Prevalence of respiratory virus infection with regard to age, sex, and seasonality factors: A single center experience against children hospitalized during the 10 years
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Bundang CHA Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. drmesh@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pediatrics, CHA Gangnam Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, CHA Gumi Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Gumi, Korea.
- KMID: 2396672
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2017.5.6.320
Abstract
- PURPOSE
It is well known that respiratory viral infection has epidemiological characteristics, including season. This study aimed to investigate the patterns of the prevalence of common respiratory viruses during a period of 10 years with regard to age, sex, and season in Korean children.
METHODS
From June 2006 to November 2016, we obtained 11,798 specimens from patients aged less than 18 years who were admitted with lower respiratory infections. Ten respiratory viruses were detected using multiplex reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
RESULTS
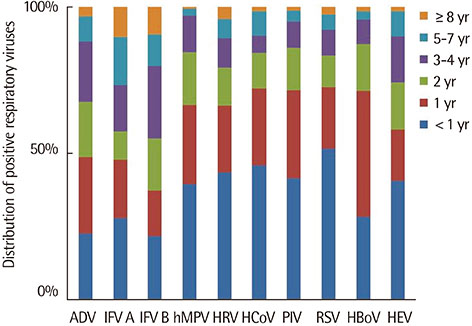
Of 11,798 specimens, at least 1 virus was detected in 4,845 (41.1%). Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV, 18.9%) was the most common virus detected, followed by human rhinovirus (HRV, 14.8%), adenovirus (9.5%), and human bocavirus (HBoV, 7.4%). The detection rate of HRV was higher in male subjects (male 60.0% vs. female 40.0%, P=0.004), but the other viruses had no significant differences with regard to sex. The subjects who were positive for RSV test were youngest (median, 10.5 months; interquartile range, 3.0-25.0 months), followed by human coronavirus (median, 13.0 months), HRV (median, 14 months), and parainfluenza (median, 14 months). HBoV was most commonly detected in spring (29.3%), enterovirus in summer (25.8%), HRV in fall (22.6%), and RSV in October and winter (22.6%).
CONCLUSION
We found that the prevalence of respiratory viruses in Korean children during a period of 10 years was associated with age, sex, and season when the infection occurred. Further nationwide data is warranted to infer clinical implication of our results.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Seasonality and etiology of croup in pediatric patients hospitalized with lower respiratory tract infections: A long-term study between 2009 and 2017
Kyung Jin Oh, Dong Hwa Yang, Hyeong Rok Shin, Eun Jin Kim, Yong Han Sun, Eell Ryoo, Hye Kyung Cho, Hye Jung Cho
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2019;7(1):28-36. doi: 10.4168/aard.2019.7.1.28.Reemergence of Parainfluenza Virus Type 3 and Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Kuenyoul Park, Heungsup Sung, Mi-Na Kim
Ann Lab Med. 2023;43(1):114-116. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.114.
Reference
-
1. Kim MR, Lee HR, Lee GM. Epidemiology of acute viral respiratory tract infections in Korean children. J Infect. 2000; 41:152–158.
Article2. Park JS. Acute viral lower respiratory tract infections in children. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:269–276.
Article3. van den Bergh MR, Biesbroek G, Rossen JW, de Steenhuijsen Piters WA, Bosch AA, van Gils EJ, et al. Associations between pathogens in the upper respiratory tract of young children: interplay between viruses and bacteria. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e47711.
Article4. Victora CG, Fuchs SC, Flores JA, Fonseca W, Kirkwood B. Risk factors for pneumonia among children in a Brazilian metropolitan area. Pediatrics. 1994; 93(6 Pt 1):977–985.
Article5. Pillet S, Lardeux M, Dina J, Grattard F, Verhoeven P, Le Goff J, et al. Comparative evaluation of six commercialized multiplex PCR kits for the diagnosis of respiratory infections. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e72174.
Article6. Krause JC, Panning M, Hengel H, Henneke P. The role of multiplex PCR in respiratory tract infections in children. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2014; 111:639–645.
Article7. Allander T, Tammi MT, Eriksson M, Bjerkner A, Tiveljung-Lindell A, Andersson B. Cloning of a human parvovirus by molecular screening of respiratory tract samples. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:12891–12896.
Article8. Choi EH, Lee HJ, Kim SJ, Eun BW, Kim NH, Lee JA, et al. The association of newly identified respiratory viruses with lower respiratory tract infections in Korean children, 2000-2005. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 43:585–592.
Article9. van den Hoogen BG, de Jong JC, Groen J, Kuiken T, de Groot R, Fouchier RA, et al. A newly discovered human pneumovirus isolated from young children with respiratory tract disease. Nat Med. 2001; 7:719–724.
Article10. Williams JV, Harris PA, Tollefson SJ, Halburnt-Rush LL, Pingsterhaus JM, Edwards KM, et al. Human metapneumovirus and lower respiratory tract disease in otherwise healthy infants and children. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:443–450.
Article11. Khetsuriani N, Kazerouni NN, Erdman DD, Lu X, Redd SC, Anderson LJ, et al. Prevalence of viral respiratory tract infections in children with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:314–321.
Article12. Jartti T, Lehtinen P, Vuorinen T, Koskenvuo M, Ruuskanen O. Persistence of rhinovirus and enterovirus RNA after acute respiratory illness in children. J Med Virol. 2004; 72:695–699.
Article13. Shaw Stewart PD. Seasonality and selective trends in viral acute respiratory tract infections. Med Hypotheses. 2016; 86:104–119.
Article14. Jartti T, van den Hoogen B, Garofalo RP, Osterhaus AD, Ruuskanen O. Metapneumovirus and acute wheezing in children. Lancet. 2002; 360:1393–1394.
Article15. Kim YK, Kim JW, Wee YS, Yoo EG, Han MY. Clinical features of human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus infection in hospitalized children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2009; 19:12–19.16. Weigl JA, Puppe W, Schmitt HJ. Seasonality of respiratory syncytial virus-positive hospitalizations in children in Kiel, Germany, over a 7-year period. Infection. 2002; 30:186–192.
Article17. Jeong JW, Hwang YH, Cho KS, Jung MJ, Min SK, Kim SJ, et al. Viral etiology and epidemiology of outpatients with acute respiratory illnesses in Busan: 2007-2008. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2010; 17:130–136.
Article18. Monto AS. Epidemiology of viral respiratory infections. Disease-a-Month. 2003; 49:160–174.
Article19. Fisman D. Seasonality of viral infections: mechanisms and unknowns. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012; 18:946–954.
Article20. Mäkinen TM, Juvonen R, Jokelainen J, Harju TH, Peitso A, Bloigu A, et al. Cold temperature and low humidity are associated with increased occurrence of respiratory tract infections. Respir Med. 2009; 103:456–462.
Article21. Lowen AC, Mubareka S, Steel J, Palese P. Influenza virus transmission is dependent on relative humidity and temperature. PLoS Pathog. 2007; 3:1470–1476.
Article22. Shaman J, Pitzer VE, Viboud C, Grenfell BT, Lipsitch M. Absolute humidity and the seasonal onset of influenza in the continental United States. PLoS Biol. 2010; 8:e1000316.
Article23. Xatzipsalti M, Kyrana S, Tsolia M, Psarras S, Bossios A, Laza-Stanca V, et al. Rhinovirus viremia in children with respiratory infections. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 172:1037–1040.
Article24. Hendley JO, Gwaltney JM Jr. Mechanisms of transmission of rhinovirus infections. Epidemiol Rev. 1988; 10:243–258.
Article25. Dushoff J, Plotkin JB, Levin SA, Earn DJ. Dynamical resonance can account for seasonality of influenza epidemics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101:16915–16916.
Article26. Dowell SF. Seasonal variation in host susceptibility and cycles of certain infectious diseases. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001; 7:369–374.
Article27. Bi P, Zhang Y, Parton KA. Weather variables and Japanese encephalitis in the metropolitan area of Jinan city, China. J Infect. 2007; 55:551–556.
Article28. Shay DK, Holman RC, Newman RD, Liu LL, Stout JW, Anderson LJ. Bronchiolitis-associated hospitalizations among US children, 1980-1996. JAMA. 1999; 282:1440–1446.
Article29. Carroll ML, Yerkovich ST, Pritchard AL, Davies JM, Upham JW. Adaptive immunity to rhinoviruses: sex and age matter. Respir Res. 2010; 11:184.
Article30. Tse SM, Rifas-Shiman SL, Coull BA, Litonjua AA, Oken E, Gold DR. Sex-specific risk factors for childhood wheeze and longitudinal phenotypes of wheeze. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 138:1561–1568.e6.
Article31. Hacimustafaoglu M, Celebi S, Aynaci E, Sinirtas M, Koksal N, Kucukerdogan A, et al. The progression of maternal RSV antibodies in the offspring. Arch Dis Child. 2004; 89:52–53.
Article32. Meddens MJ, Herbrink P, Lindeman J, van Dijk WC. Serodiagnosis of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection in children as measured by detection of RSV-specific immunoglobulins G, M, and A with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1990; 28:152–155.
Article33. Singleton RJ, Bulkow LR, Miernyk K, DeByle C, Pruitt L, Hummel KB, et al. Viral respiratory infections in hospitalized and community control children in Alaska. J Med Virol. 2010; 82:1282–1290.
Article34. Blomqvist S. Epidemiology of human rhinoviruses. Helsinki (Finland): University of Helsinki;2004. p. 26–33.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Seasonality and etiology of croup in pediatric patients hospitalized with lower respiratory tract infections: A long-term study between 2009 and 2017
- Seasonality of asthma exacerbation in children caused by respiratory virus infection and allergen sensitization
- Prevalence of Respiratory Viral Infection Using Multiplex Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Clinical features of respiratory adenovirus infections in pediatric inpatients in a single medical center
- The Seasonal Changes of Influenza Virus and Rotavirus in Children