Ann Dermatol.
2017 Dec;29(6):796-799. 10.5021/ad.2017.29.6.796.
Therapeutic Effects of a Light Emitting Diode at a Variety of Wavelengths on Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin Lesions in NC/Nga Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. yymmpark6301@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2395193
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.6.796
Abstract
- No abstract available.
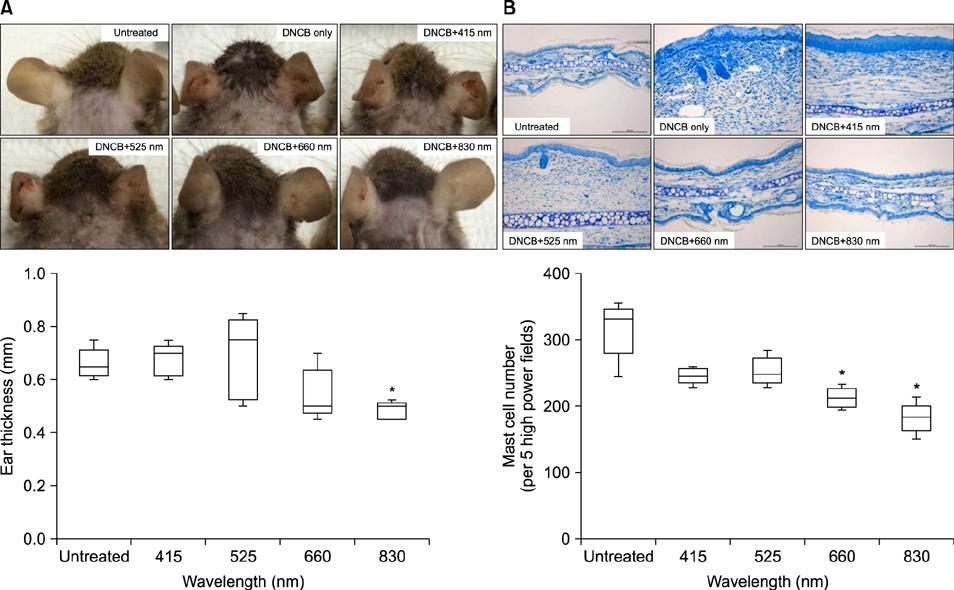
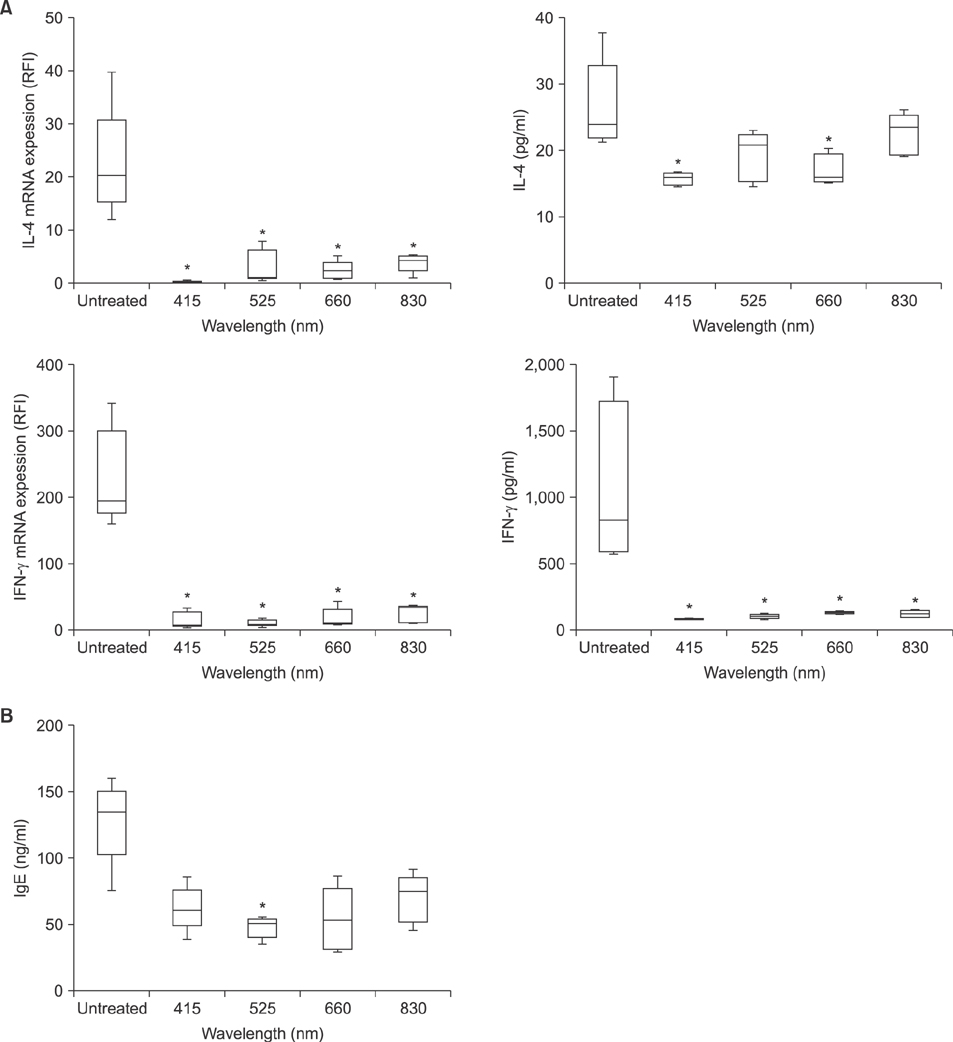
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cui HS, Ahn IS, Byun YS, Yang YS, Kim JH, Chung BY, et al. Dietary pattern and nutrient intake of korean children with atopic dermatitis. Ann Dermatol. 2014; 26:570–575.
Article2. Schmitt J, von Kobyletzki L, Svensson A, Apfelbacher C. Efficacy and tolerability of proactive treatment with topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors for atopic eczema: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Br J Dermatol. 2011; 164:415–428.
Article3. von Kobyletzki G, Pieck C, Hoffmann K, Freitag M, Altmeyer P. Medium-dose UVA1 cold-light phototherapy in the treatment of severe atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999; 41:931–937.
Article4. Gambichler T, Othlinghaus N, Tomi NS, Holland-Letz T, Boms S, Skrygan M, et al. Medium-dose ultraviolet (UV) A1 vs. narrowband UVB phototherapy in atopic eczema: a randomized crossover study. Br J Dermatol. 2009; 160:652–658.
Article5. Pavlovsky M, Baum S, Shpiro D, Pavlovsky L, Pavlotsky F. Narrow band UVB: is it effective and safe for paediatric psoriasis and atopic dermatitis? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011; 25:727–729.
Article6. Barolet D. Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) in dermatology. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2008; 27:227–238.
Article7. Yeh NG, Wu CH, Cheng TC. Light-emitting diodes-Their potential in biomedical applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2010; 14:2161–2166.
Article8. Morita H, Kohno J, Tanaka S, Kitano Y, Sagami S. Clinical application of GaAlAs 830 nm diode laser for atopic dermatitis. Laser Ther. 1993; 5:75–78.
Article9. Cheong KA, Kim CH, Choi Y, Park CD, Lee AY. Irradiation of light emitting diode at 850nm inhibits T cell-induced cytokine expression. J Dermatol Sci. 2012; 65:27–37.
Article10. Jung KE, Lee YJ, Ryu YH, Kim JE, Kim HS, Kim BJ, et al. Effects of topically applied rapamycin and mycophenolic acid on TNCB-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015; 26:432–438.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Therapeutic Effects of Light Emitting Diode on Atopic Dermatitis-Like Lesions in NC/Nga Mice
- Topical Application of Eupatilin Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin Lesions in NC/Nga Mice
- Developing an Atopic Dermatitis Model and the Effects of Actinidia Extract on Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice
- A Study on Tests of Skin Safety and Inhibition of Atopic Dermatitis Using a StoneTouch(R) Infrared Scanner in a Mouse Model
- Inhibitory effects of interleukin-10 plasmid DNA on the development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice