J Vet Sci.
2010 Sep;11(3):213-220. 10.4142/jvs.2010.11.3.213.
Inhibitory effects of interleukin-10 plasmid DNA on the development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 500-757, Korea. bjlee@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 1093495
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2010.11.3.213
Abstract
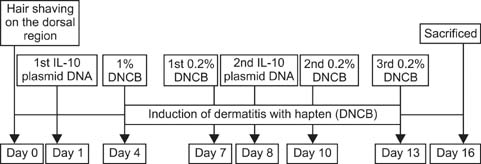
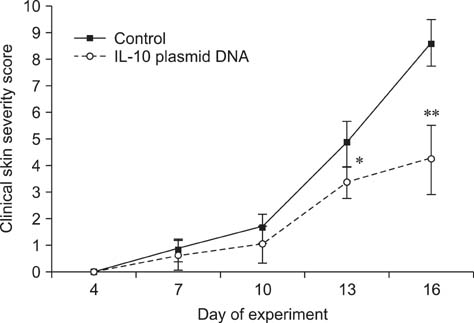
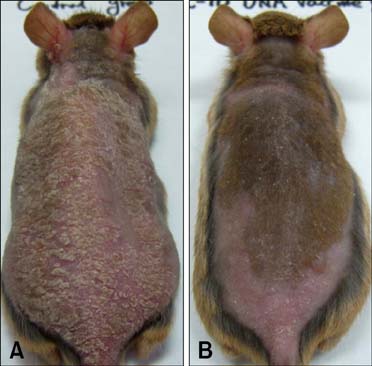
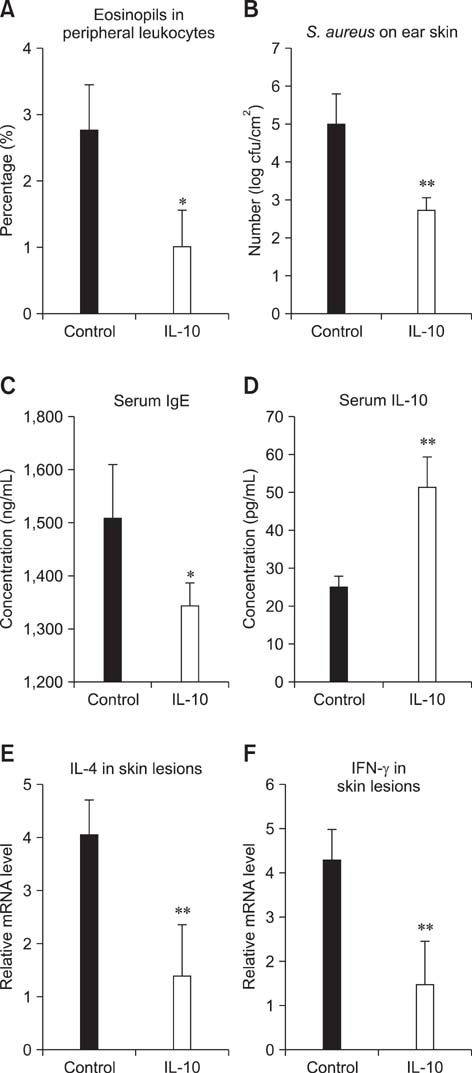
- Interleukin (IL)-10 exerts potent anti-inflammatory effects by suppression of both T-help (Th) 1 and Th2 cells. Previous studies have reported that IL-10 can ameliorate various inflammatory disorders. The present study was performed to examine whether IL-10 plasmid DNA could suppress development of atopic dermatitis (AD)-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice, as an initial step towards the development of an appliance for use in dogs with AD. Intradermal injection of IL-10 plasmid DNA markedly inhibited the development of AD-like skin lesions, as evidenced by a marked decrease in skin symptoms and reduced inflammation within the skin lesions. Efficacy was confirmed by significant decreases in eosinophil ratio and serum IgE concentration, and a reduction in the number of Staphylococcus aureus recovered from the ear. Moreover, relative mRNA expression levels of IL-4 and interferon-gamma in the skin lesions of mice injected with IL-10 plasmid DNA were also decreased compared with those of control mice. Of note, higher serum IL-10 levels in mice injected with IL-10 plasmid DNA were maintained compared with those in control mice. Taken together, the results indicate that IL-10 plasmid DNA can suppress the development of AD-like skin lesions by suppressing both Th1 and Th2 cell responses. Beneficial effects of IL-10 plasmid DNA may be expected in dogs with AD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Case-Control Studies
DNA Primers/genetics
Dermatitis, Atopic/immunology/*prevention & control
Disease Models, Animal
Dogs
Female
Interleukin-10/genetics/*immunology/*therapeutic use
Mice
Mice, Mutant Strains
Plasmids/genetics/*therapeutic use
Staphylococcus aureus/isolation & purification
Statistics, Nonparametric
T-Lymphocytes, Helper-Inducer/*immunology
Figure
Reference
-
1. Asadullah K, Sterry W, Stephanek K, Jasulaitis D, Leupold M, Audring H, Volk HD, Döcke WD. IL-10 is a key cytokine in psoriasis. Proof of principle by IL-10 therapy: a new therapeutic approach. J Clin Invest. 1998. 101:783–794.
Article2. Barnes PJ, Chung KF, Page CP. Inflammatory mediators of asthma: an update. Pharmacol Rev. 1998. 50:515–596.3. Chernoff AE, Granowitz EV, Shapiro L, Vannier E, Lonnemann G, Angel JB, Kennedy JS, Rabson AR, Wolff SM, Dinarello CA. A randomized, controlled trial of IL-10 in humans. Inhibition of inflammatory cytokine production and immune responses. J Immunol. 1995. 154:5492–5499.4. Fazakerley J, Nuttall T, Sales D, Schmidt V, Carter SD, Hart CA, McEwan NA. Staphylococcal colonization of mucosal and lesional skin sites in atopic and healthy dogs. Vet Dermatol. 2009. 20:179–184.
Article5. Fiorentino DF, Bond MW, Mosmann TR. Two types of mouse T helper cell. IV. Th2 clones secrete a factor that inhibits cytokine production by Th1 clones. J Exp Med. 1989. 170:2081–2095.
Article6. Griffin CE, DeBoer DJ. The ACVD task force on canine atopic dermatitis (XIV): clinical manifestations of canine atopic dermatitis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2001. 81:255–269.
Article7. Hashimoto Y, Kaneda Y, Akashi T, Arai I, Nakaike S. Persistence of Staphylococcus aureus colonization on the skin of NC/Nga mice. J Dermatol Sci. 2004. 35:143–150.
Article8. Hayashi A, Kimura M, Nakamura Y, Yasui H. Anti-atopic dermatitis effects and the mechanism of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Mongolian fermented milk. J Dairy Res. 2009. 76:158–164.
Article9. Hayashiya S, Tani K, Morimoto M, Hayashi T, Hayasaki M, Nomura T, Une S, Nakaichi M, Taura Y. Expression of T helper 1 and T helper 2 cytokine mRNAs in freshly isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from dogs with atopic dermatitis. J Vet Med A Physiol Pathol Clin Med. 2002. 49:27–31.
Article10. Hengge UR, Chan EF, Foster RA, Walker PS, Vogel JC. Cytokine gene expression in epidermis with biological effects following injection of naked DNA. Nat Genet. 1995. 10:161–166.
Article11. Hill PB, Lo A, Eden CA, Huntley S, Morey V, Ramsey S, Richardson C, Smith DJ, Sutton C, Taylor MD, Thorpe E, Tidmarsh R, Williams V. Survey of the prevalence, diagnosis and treatment of dermatological conditions in small animals in general practice. Vet Rec. 2006. 158:533–539.
Article12. Kang JS, Yoon WK, Han MH, Lee H, Lee CW, Lee KH, Han SB, Lee K, Yang KH, Park SK, Kim HM. Inhibition of atopic dermatitis by topical application of silymarin in NC/Nga mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2008. 8:1475–1480.
Article13. Kishimoto T, Hirano T. Molecular regulation of B lymphocyte response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988. 6:485–512.
Article14. Kokura S, Yoshida N, Ishikawa T, Higashihara H, Sakamoto N, Takagi T, Uchiyama K, Naito Y, Mazda O, Okanoue T, Yoshikawa T. Interleukin-10 plasmid DNA inhibits subcutaneous tumor growth of Colon 26 adenocarcinoma in mice. Cancer Lett. 2005. 218:171–179.
Article15. Lee HS, Kim SK, Han JB, Choi HM, Park JH, Kim EC, Choi MS, An HJ, Um JY, Kim HM, Min BI. Inhibitory effects of Rumex japonicus Houtt. on the development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. Br J Dermatol. 2006. 155:33–38.
Article16. Leung DY, Bieber T. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet. 2003. 361:151–160.
Article17. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001. 25:402–408.
Article18. Lund EM, Armstrong PJ, Kirk CA, Kolar LM, Klausner JS. Health status and population characteristics of dogs and cats examined at private veterinary practices in the United States. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1999. 214:1336–1341.19. Marsella R, Olivry T. Animal models of atopic dermatitis. Clin Dermatol. 2003. 21:122–133.
Article20. Moore KW, O'Garra A, de Waal Malefyt R, Vieira P, Mosmann TR. Interleukin-10. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993. 11:165–190.
Article21. Nuttall TJ, Knight PA, McAleese SM, Lamb JR, Hill PB. Expression of Th1, Th2 and immunosuppressive cytokine gene transcripts in canine atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002. 32:789–795.
Article22. Okada M, Hirasawa Y, Yoshijima K, Imaeda T, Fujimura T, Nagase T, Kimura H, Kyuki K. Effects of clobetasol propionate, a corticosteroid on hapten-induced dermatitis in SPF NC/Nga mice. Pharmacometrics. 2000. 59:135–139.23. Olivry T, Dean GA, Tompkins MB, Dow JL, Moore PF. Toward a canine model of atopic dermatitis: amplification of cytokine-gene transcripts in the skin of atopic dogs. Exp Dermatol. 1999. 8:204–211.
Article24. Olivry T, DeBoer DJ, Griffin CE, Halliwell RE, Hill PB, Hillier A, Marsella R, Sousa CA. The ACVD task force on canine atopic dermatitis: forewords and lexicon. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2001. 81:143–146.
Article25. Overbergh L, Valckx D, Waer M, Mathieu C. Quantification of murine cytokine mRNAs using real time quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR. Cytokine. 1999. 11:305–312.
Article26. Pokharel YR, Lim SC, Kim SC, Heo TH, Choi HK, Kang KW. Sopungyangjae-Tang Inhibits Development of Dermatitis in Nc/Nga Mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2008. 5:173–180.
Article27. Pretolani M, Goldman M. IL-10: a potential therapy for allergic inflammation? Immunol Today. 1997. 18:277–280.
Article28. Sakamoto T, Miyazaki E, Aramaki Y, Arima H, Takahashi M, Kato Y, Koga M, Tsuchiya S. Improvement of dermatitis by iontophoretically delivered antisense oligonucleotides for interleukin-10 in NC/Nga mice. Gene Ther. 2004. 11:317–324.
Article29. Sawada J, Morita H, Tanaka A, Salminen S, He F, Matsuda H. Ingestion of heat-treated Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG prevents development of atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007. 37:296–303.
Article30. Schandené L, Alonso-Vega C, Willems F, Gérard C, Delvaux A, Velu T, Devos R, de Boer M, Goldman M. B7/CD28-dependent IL-5 production by human resting T cells is inhibited by IL-10. J Immunol. 1994. 152:4368–4374.31. Segawa S, Hayashi A, Nakakita Y, Kaneda H, Watari J, Yasui H. Oral administration of heat-killed Lactobacillus brevis SBC8803 ameliorates the development of dermatitis and inhibits immunoglobulin E production in atopic dermatitis model NC/Nga mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008. 31:884–889.
Article32. Shiohara T, Hayakawa J, Mizukawa Y. Animal models for atopic dermatitis: are they relevant to human disease? J Dermatol Sci. 2004. 36:1–9.
Article33. Sinke JD, Rutten VP, Willemse T. Immune dysregulation in atopic dermatitis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002. 87:351–356.
Article34. van Deventer SJ, Elson CO, Fedorak RN. Crohn's Disease Study Group. Multiple doses of intravenous interleukin 10 in steroid-refractory Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1997. 113:383–389.
Article35. Watanabe M, Fenton RG, Wigginton JM, McCormick KL, Volker KM, Fogler WE, Roessler PG, Wiltrout RH. Intradermal delivery of IL-12 naked DNA induces systemic NK cell activation and Th1 response in vivo that is independent of endogenous IL-12 production. J Immunol. 1999. 163:1943–1950.36. Wolff JA, Ludtke JJ, Acsadi G, Williams P, Jani A. Long-term persistence of plasmid DNA and foreign gene expression in mouse muscle. Hum Mol Genet. 1992. 1:363–369.
Article37. Wolff JA, Malone RW, Williams P, Chong W, Acsadi G, Jani A, Felgner PL. Direct gene transfer into mouse muscle in vivo. Science. 1990. 247:1465–1468.38. Yoshidome H, Kato A, Edwards MJ, Lentsch AB. Interleukin-10 suppresses hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice: implications of a central role for nuclear factor κB. Hepatology. 1999. 30:203–208.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Developing an Atopic Dermatitis Model and the Effects of Actinidia Extract on Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice
- Topical Application of Eupatilin Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin Lesions in NC/Nga Mice
- A Study on Tests of Skin Safety and Inhibition of Atopic Dermatitis Using a StoneTouch(R) Infrared Scanner in a Mouse Model
- Therapeutic Effects of Light Emitting Diode on Atopic Dermatitis-Like Lesions in NC/Nga Mice
- Inhibitory Effect of Luteolin Liposome Solution by Animal Model for Atopic Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice