J Bacteriol Virol.
2017 Sep;47(3):132-138. 10.4167/jbv.2017.47.3.132.
The Effects of Staphylococci on the Degranulation of Human Mast Cell-1
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology and Cancer Research Institute, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. jekpark@cnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Medical Science, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2392961
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2017.47.3.132
Abstract
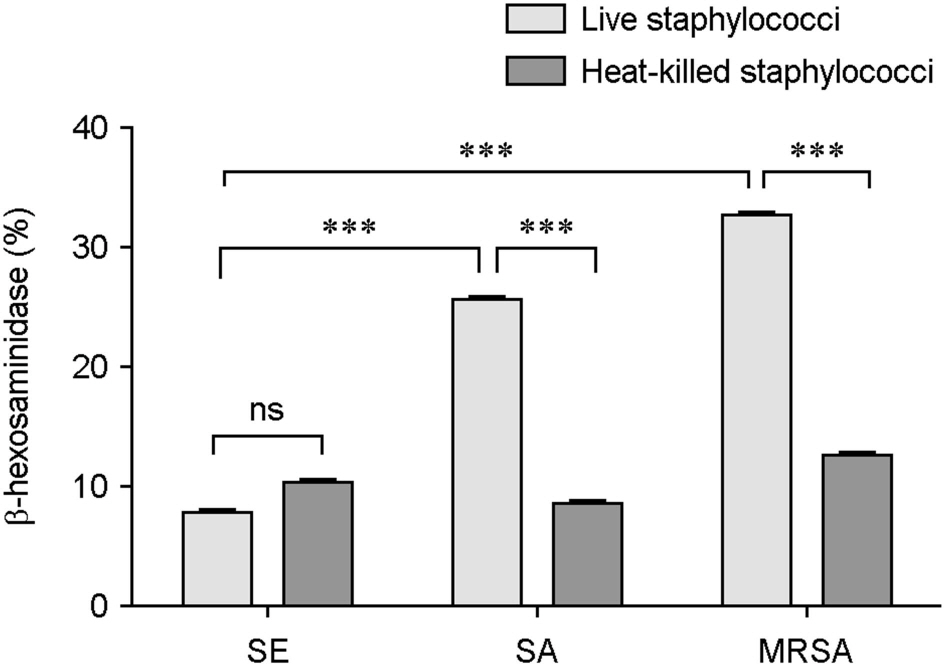
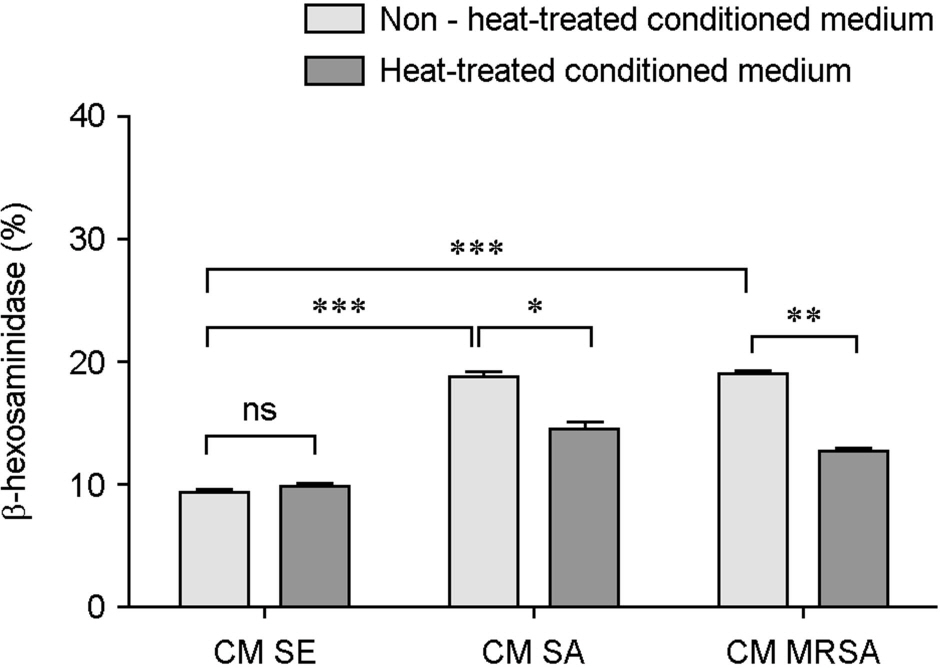
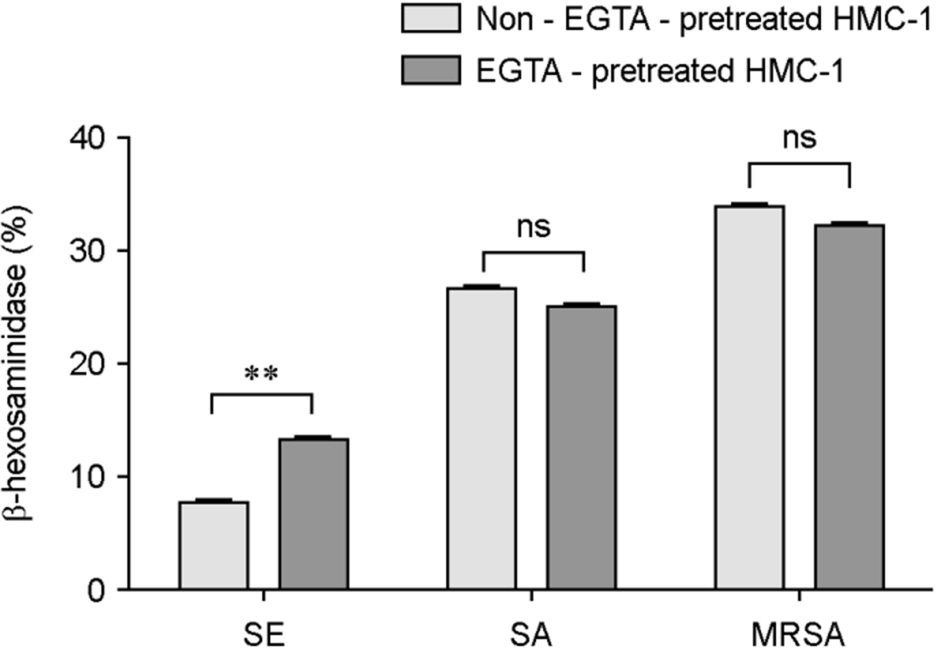
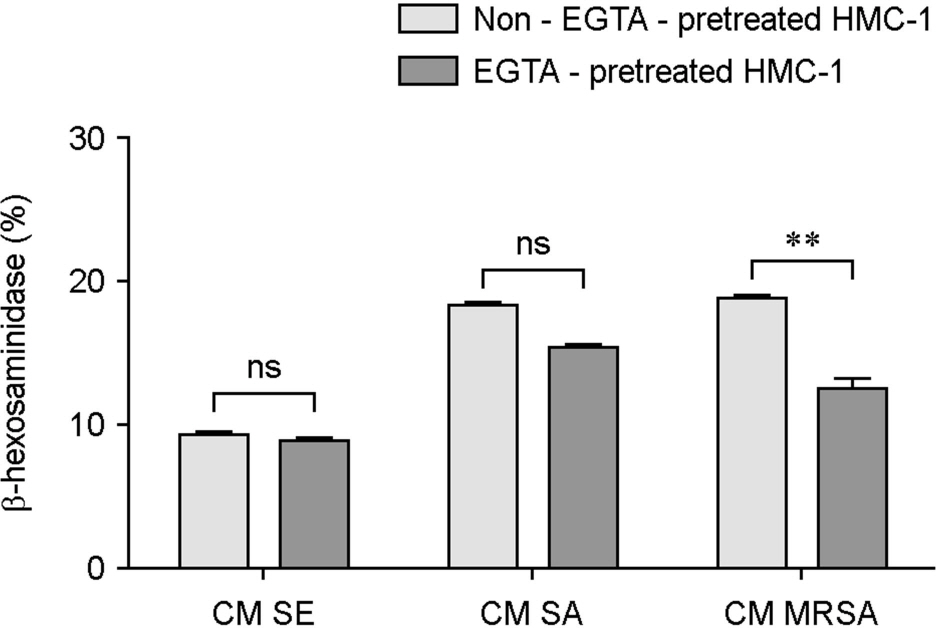
- Atopic dermatitis (AD) is characterized by disturbances in epidermal barrier functions and the hyperactive immune response. Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) can be cultured from 90% of AD skin lesions and can exacerbate or contribute to the persistent skin inflammation in AD by secreting toxins with superantigenic properties. Superantigens can induce mast cell (MC) degranulation after penetrating the epidermal barrier. The role of MCs in AD is suggested by the increase in the MC number and MC activation. MCs are activated for degranulation and mediator release by allergens that cross-link IgE molecules or by microbial products. Therefore, MCs may be critically involved in the pathogenesis of AD. However, the understanding mechanisms of MC degranulation by S. aureus in relation to AD have still not been fully elucidated. In this study, we found that live S. aureus or methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) but not heat-killed bacteria induced MC degranulation. The heat-treatment partially inhibited MC degranulation by conditioned media (CM) of S. aureus or MRSA. The calcium chelator ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid (EGTA) did not block MC degranulation induced by live S. aureus or MRSA, but EGTA-treatment partially inhibited MC degranulation by CM from S. aureus or MRSA. These results suggest that live S. aureus and MRSA can degranulate MCs via direct interaction which may be important role in AD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Allergens
Bacteria
Calcium
Culture Media, Conditioned
Dermatitis, Atopic
Egtazic Acid
Humans*
Immunoglobulin E
Inflammation
Mast Cells
Methicillin Resistance
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Skin
Staphylococcus aureus
Superantigens
Allergens
Calcium
Culture Media, Conditioned
Egtazic Acid
Immunoglobulin E
Superantigens
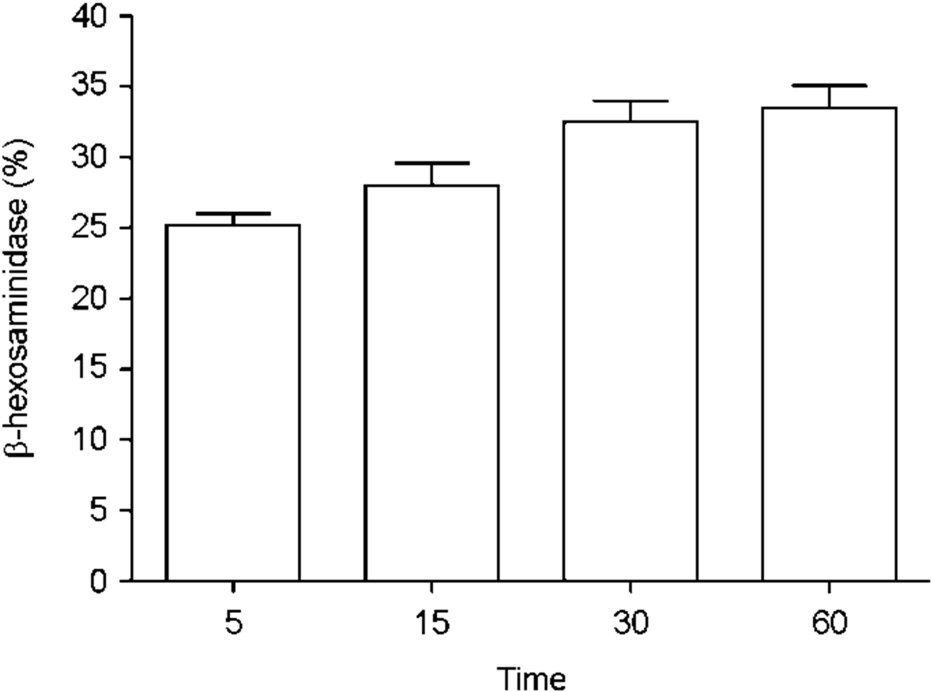
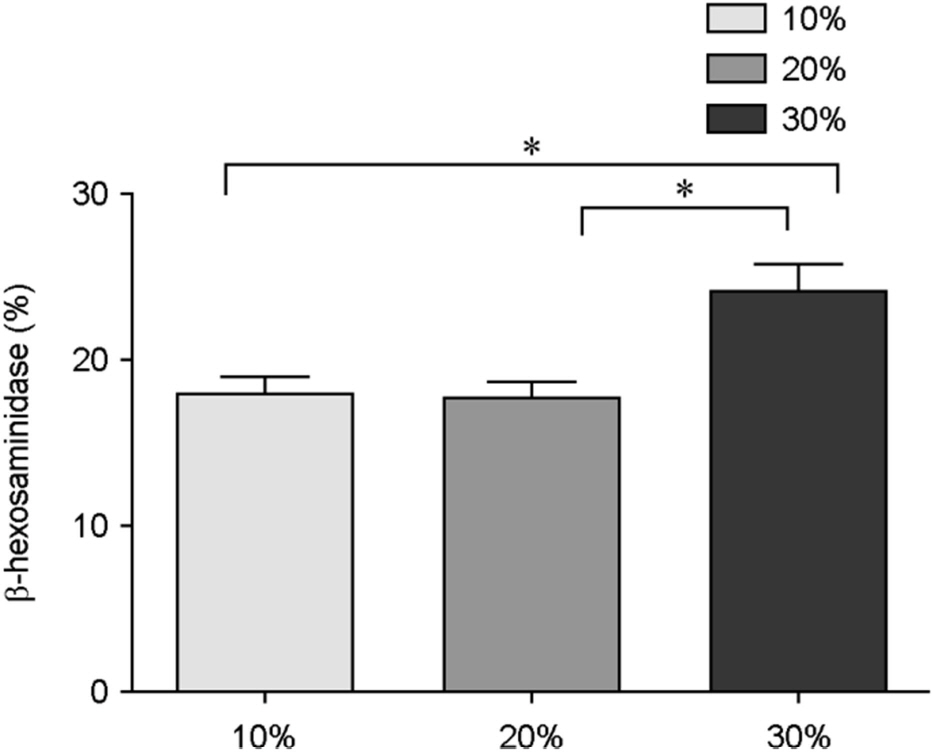
Figure
Reference
-
1). Nutten S. Atopic dermatitis: global epidemiology and risk factors. Ann Nutr Metab. 2015; 66:8–16.
Article2). Wollina U. Microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017; 10:51–6.
Article3). St John AL, Abraham SN. Innate immunity and its regulation by mast cells. J Immunol. 2013; 190:4458–63.4). Flannagan RS, Cosío G, Grinstein S. Antimicrobial mechanisms of phagocytes and bacterial evasion strategies. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009; 7:355–66.
Article5). Wesolowski J, Paumet F. The impact of bacterial infection on mast cell degranulation. Immunol Res. 2011; 51:215–26.
Article6). Park KD, Pak SC, Park KK. The Pathogenetic Effect of Natural and Bacterial Toxins on Atopic Dermatitis. Toxins (Basel). 2016; 9:1–19.
Article7). Nakamura Y, Oscherwitz J, Cease KB, Chan SM, Muñoz-Planillo R, Hasegawa M, et al. Staphylococcus δ-toxin induces allergic skin disease by activating mast cells. Nature. 2013; 503:397–401.
Article8). Sun D, Ong PY. Infectious Complications in Atopic Dermatitis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2017; 37:75–93.
Article9). Naik S, Bouladoux N, Linehan JL, Han SJ, Harrison OJ, Wilhelm C, et al. Commensal-dendritic-cell interaction specifies a unique protective skin immune signature. Nature. 2015; 520:104–8.
Article10). Higaki S, Morohashi M, Yamagishi T, Hasegawa Y. Comparative study of staphylococci from the skin of atopic dermatitis patients and from healthy subjects. Int J Dermatol. 1999; 38:265–9.
Article11). Kojima R, Ohno T, Iikura M, Niki T, Hirashima M, Iwaya K, et al. Galectin-9 enhances cytokine secretion, but suppresses survival and degranulation, in human mast cell line. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e86106.
Article12). Johnzon CF, Rönnberg E, Guss B, Pejler G. Live Staphylococcus aureus Induces Expression and Release of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Terminally Differentiated Mouse Mast Cells. Front Immunol. 2016; 7:247.
Article13). Swindle EJ, Brown JM, Rådinger M, DeLeo FR, Metcalfe DD. Interferon-γ enhances both the anti-bacterial and the pro-inflammatory response of human mast cells to Staphylococcus aureus. Immunology. 2015; 146:470–85.14). Tsai CC, Kuo TY, Hong ZW, Yeh YC, Shih KS, Du SY, et al. Helicobacter pylori neutrophil-activating protein induces release of histamine and interleukin-6 through G protein-mediated MAPKs and PI3K/Akt pathways in HMC-1 cells. Virulence. 2015; 6:755–65.15). Joly F, Vigrain I, Bossant MJ, Bessou G, Benveniste J, Ninio E. Biosynthesis of paf-acether. Activators of protein kinase C stimulate cultured mast cell acetyltransferase without stimulating paf-acether synthesis. Biochem J. 1990; 271:501–7.
Article16). Yang M, Jang IT, Kim HJ, Park JK. Bacillus spp. or Bacillus spp.-derived membrane vesicles induce the intrinsic pathways of apoptosis of human colon cancer cell lines. J Bacteriol Virol. 2016; 46:84–92.17). Wesolowski J, Paumet F. The impact of bacterial infection on mast cell degranulation. Immunol Res. 2011; 51:215–26.
Article18). Yamada N, Matsushima H, Tagaya Y, Shimada S, Katz SI. Generation of a large number of connective tissue type mast cells by culture of murine fetal skin cells. J Invest Dermatol. 2003; 121:1425–32.
Article19). Wollina U. Microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017; 10:51–6.
Article20). Laouini D, Kawamoto S, Yalcindag A, Bryce P, Mizoguchi E, Oettgen H, et al. Epicutaneous sensitization with superantigen induces allergic skin inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 112:981–7.
Article21). Sun D, Ong PY. Infectious Complications in Atopic Dermatitis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2017; 37:75–93.
Article22). Williams JV, Vowels BR, Honig PJ, Leyden JJ. S. aureus isolation from the lesions, the hands, and the anterior nares of patients with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 1998; 15:194–8.
Article23). Grice EA, Segre JA. The skin microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011; 9:244–53.
Article24). Goldmann O, Tuchscherr L, Rohde M, Medina E. α-Hemolysin enhances Staphylococcus aureus internalization and survival within mast cells by modulating the expression of β1 integrin. Cell Microbiol. 2016; 18:807–19.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- On the Degranulation of Mesenteric Mast Cells Caused by Morphine and Meperidine Hydrochloride in White Rats
- Mast Cell Degranulation with Special Reference to the Effect of Lipid Administration upon the Mesenteric Mast Cell of Albino Rats
- Inhibitory Effect of Disosium Cromoglycate and Ketotifen on Human Seminal Plasma-Induced Mast Cell Activation
- Mast Cell Degranulation with Special Reference to the Effect of a Saponin Extract of Ginseng upon the Mesenteric Mast Cell of Albino Rats
- On the Effect of Morphine Hydrochloride on the Mesenteric Mast cells of Albino Rats