J Pathol Transl Med.
2017 May;51(3):320-324. 10.4132/jptm.2016.09.07.
Unusual Histology of Eosinophilic Myenteric Ganglionitis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. jhjang@eulji.ac.kr
- KMID: 2392599
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.09.07
Abstract
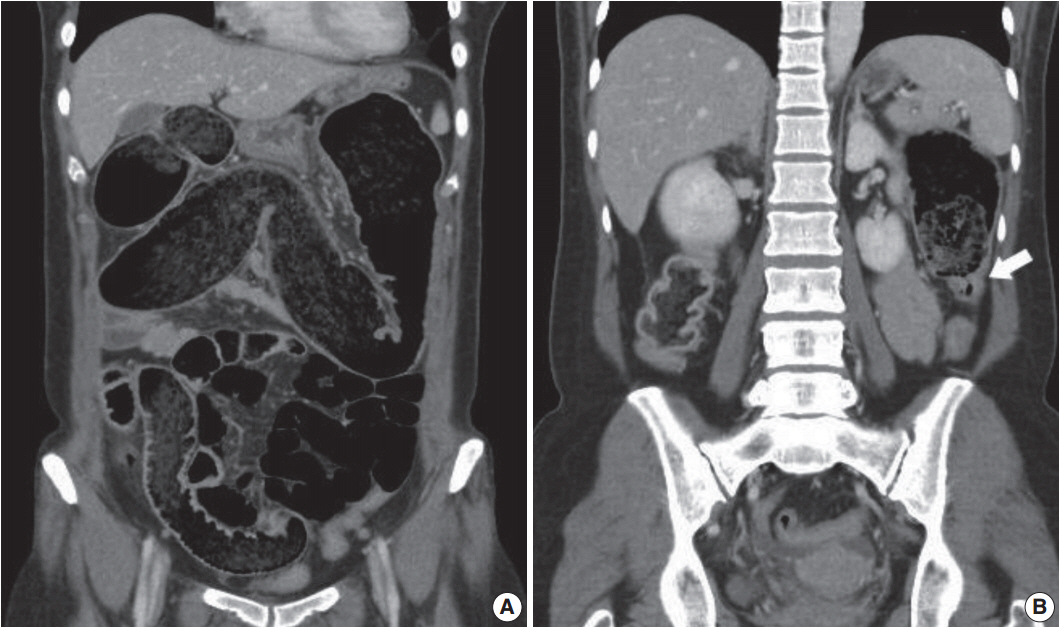
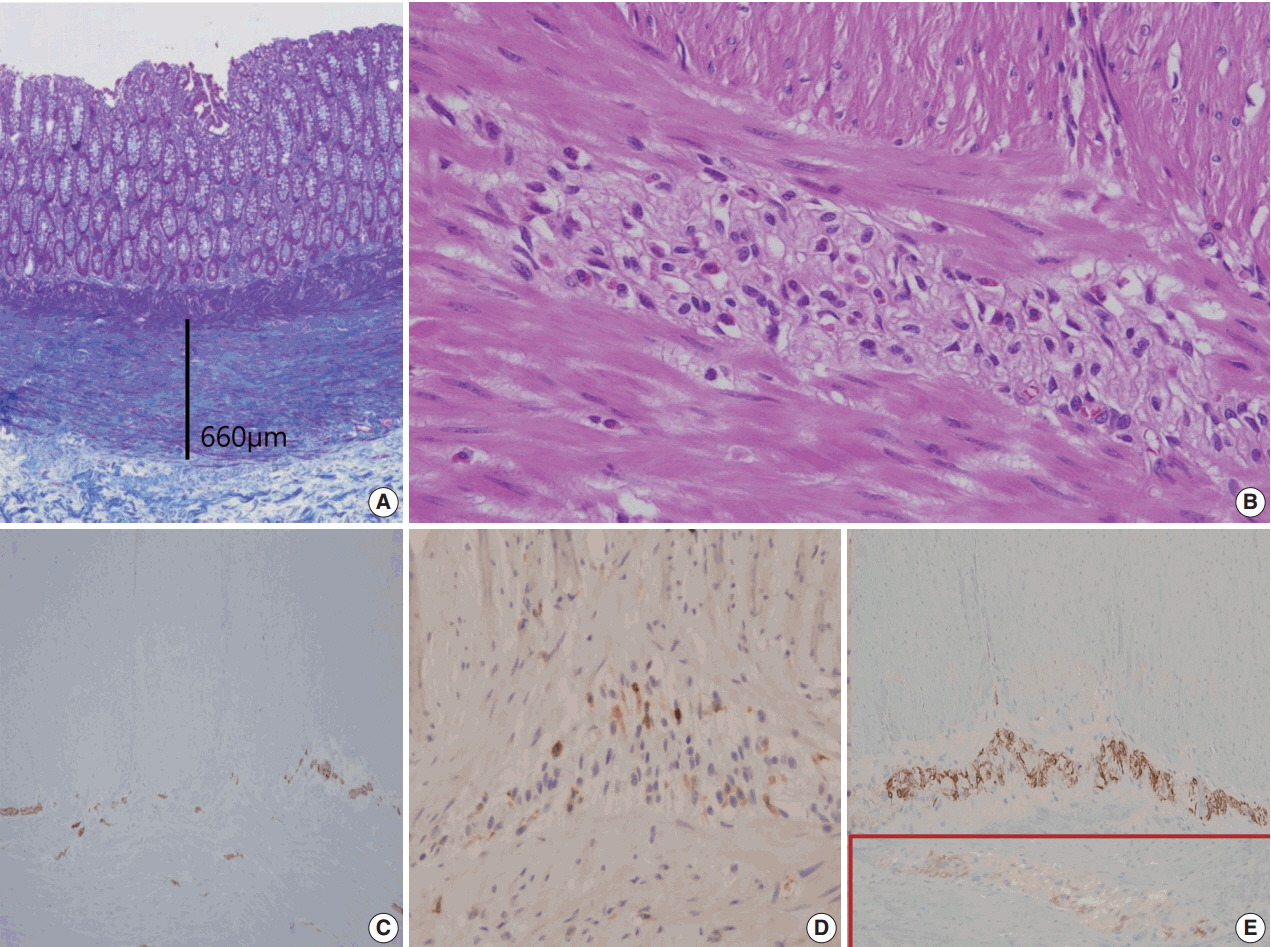
- Eosinophilic myenteric ganglionitis is a disorder characterized by infiltration of the Auerbach myenteric plexus by eosinophils. As a cause of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO), eosinophilic myenteric ganglionitis has been rarely reported and the majority of the reported cases in the literature were children. We experienced a case of eosinophilic myenteric ganglionitis associated with CIPO in a 53-year-old female patient. Histologic examination of the resected descending colon showed moderate eosinophilic infiltrates with hypogangliosis in the myenteric plexus. Immunohistochemical study revealed increased number of CD4-positive lymphocytes and stronger but scantier glial fibillary acid protein expression in the inflamed myenteric plexus.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. De Giorgio R, Sarnelli G, Corinaldesi R, Stanghellini V. Advances in our understanding of the pathology of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Gut. 2004; 53:1549–52.
Article2. Lee BH, Kim N, Kang SB, et al. Two cases of chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction with different clinical features. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010; 16:83–9.
Article3. Schäppi MG, Smith VV, Milla PJ, Lindley KJ. Eosinophilic myenteric ganglionitis is associated with functional intestinal obstruction. Gut. 2003; 52:752–5.4. Chander B, Fiedler P, Jain D. Eosinophilic myenteric ganglionitis: a case of intestinal pseudo-obstruction in a 93-year-old female. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011; 45:314–6.5. De Giorgio R, Camilleri M. Human enteric neuropathies: morphology and molecular pathology. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2004; 16:515–31.
Article6. De Giorgio R, Bovara M, Barbara G, et al. Anti-HuD-induced neuronal apoptosis underlying paraneoplastic gut dysmotility. Gastroenterology. 2003; 125:70–9.
Article7. Lakhan SE, Kirchgessner A. Neuroinflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2010; 7:37.
Article8. Rosenbaum C, Schick MA, Wollborn J, et al. Activation of myenteric glia during acute inflammation in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0151335.
Article9. De Giorgio R, Guerrini S, Barbara G, et al. Inflammatory neuropathies of the enteric nervous system. Gastroenterology. 2004; 126:1872–83.
Article10. De Winter BY, van den Wijngaard RM, de Jonge WJ. Intestinal mast cells in gut inflammation and motility disturbances. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012; 1822:66–73.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Four Cases of Unusual Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculits
- A Case of Eosinophilic Cholecystitis associated with Eosinophilic Cholangitis and Pancreatitis
- Enterobiliary Fistula as a Complication of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis: a Case Report
- Impact of Myenteric Plexus Alterations on Diabetes Related Gastrointestinal Dysmotility
- A case of subserosal type of eosinophilic gastroenteritis with ascites