J Pathol Transl Med.
2017 Sep;51(5):456-462. 10.4132/jptm.2017.07.19.
The Potential Roles of MELF-Pattern, Microvessel Density, and VEGF Expression in Survival of Patients with Endometrioid Endometrial Carcinoma: A Morphometrical and Immunohistochemical Analysis of 100 Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1University Research Laboratory, Gomel State Medical University, Gomel, Belarus. zinovkin2012@gmail.com
- 2University of Exeter Medical School, Institute of Biomedical and Clinical Science, Exeter, Devon, United Kingdom.
- 3Laboratory of Endocrinology and Biochemistry, Institute of Radiobiology National Academy of Sciences, Gomel, Belarus.
- 4Laboratory of Clinical Research, Republican Research Center for Radiation Medicine and Human Ecology, Gomel, Belarus.
- 5Department of Oncology, Gomel State Medical University, Gomel, Belarus.
- KMID: 2392564
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.07.19
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
In this study, we hypothesized that microcystic, elongated, fragmented (MELF)-pattern, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression by cancer cells and microvessel density of cancer stroma may be associated with progression of endometrioid adenocarcinoma.
METHODS
The study used data from the Belarus Cancer Registry and archival histological material of 100 patients with retrospectively known good (survival) and poor (disease progression and death) outcomes. All cases were immunohistochemically stained for CD34 and VEGF. Two independent samples were compared for the characteristics of signs, and obtained results were analyzed by receiver operating characteristic analysis, Mann-Whitney U test, χ² test (Yates correction), and Mantel-Cox test. Multivariate Cox hazard analysis and Spearman correlation test were used. A p-value of less than .05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
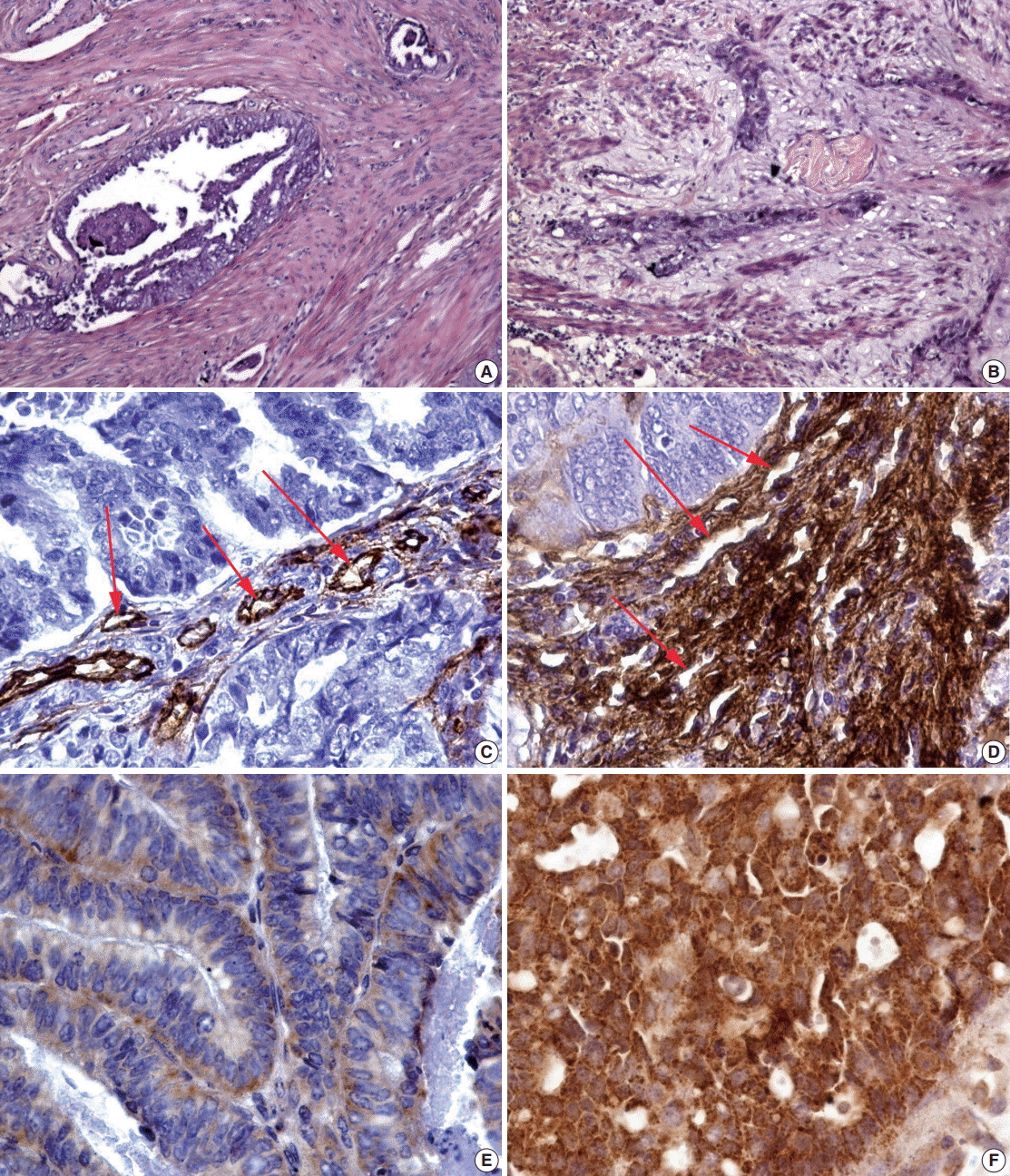
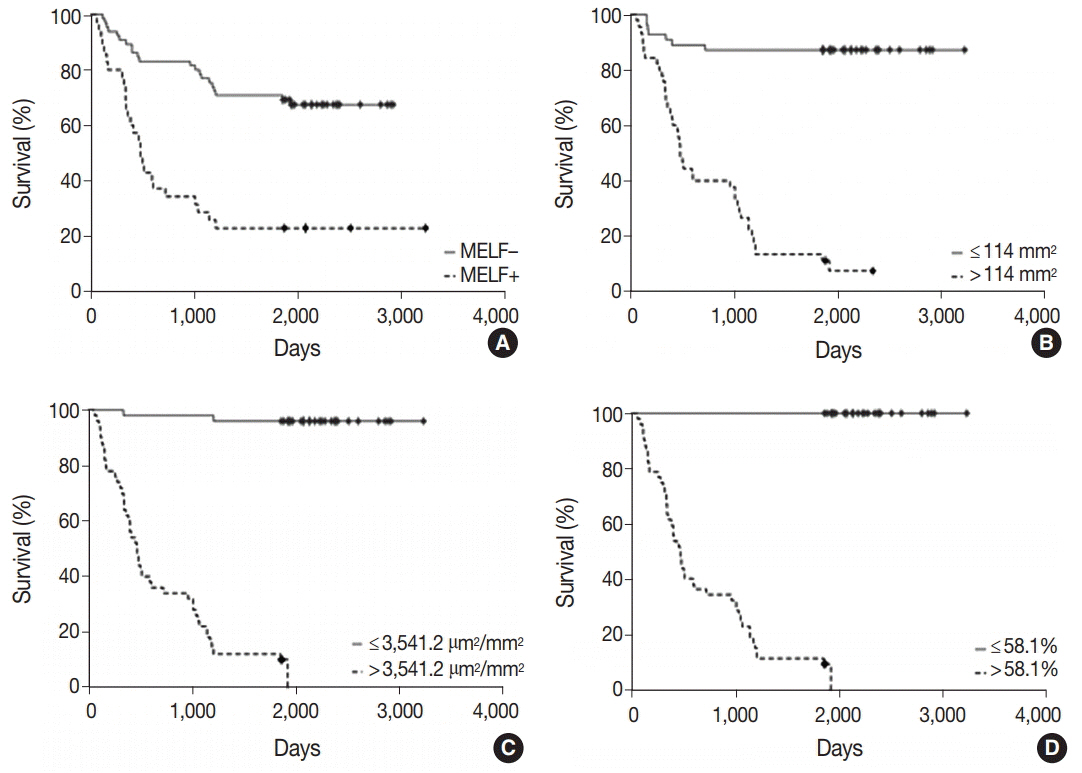
The observed survival rate of patients with endometrioid adenocarcinoma was significantly lower (p = .002) in MELF-pattern positive patients when compared with MELF-pattern negative patients. The overall survival rate of patients whose tumors had more than 114 vessels/mm² of tissue was significantly low (p < .001). Interestingly, a similar observation was found in patients with increased vessel area, evidenced by VEGF expression in the glandular tumor component.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study suggests, for the first time, that these criteria may be used as risk factors of endometrioid adenocarcinoma progression during 5 years after radical surgical treatment. However, a large independent cohort of samples should be considered in the future to validate our findings.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
High Expression of Galectin-1, VEGF and Increased Microvessel Density Are Associated with MELF Pattern in Stage I-III Endometrioid Endometrial Adenocarcinoma
Dmitry Aleksandrovich Zinovkin, Sergey Leonidovich Achinovich, Mikhail Grigoryevich Zubritskiy, Jacqueline Linda Whatmore, Md Zahidul Islam Pranjol
J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(5):280-288. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2019.05.13.
Reference
-
1. Gacche RN, Meshram RJ. Targeting tumor micro-environment for design and development of novel anti-angiogenic agents arresting tumor growth. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013; 113:333–54.2. Zigrino P, Löffek S, Mauch C. Tumor-stroma interactions: their role in the control of tumor cell invasion. Biochimie. 2005; 87:321–8.
Article3. Murray SK, Young RH, Scully RE. Unusual epithelial and stromal changes in myoinvasive endometrioid adenocarcinoma: a study of their frequency, associated diagnostic problems, and prognostic significance. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2003; 22:324–33.
Article4. Dogan Altunpulluk M, Kir G, Topal CS, Cetiner H, Gocmen A. The association of the microcystic, elongated and fragmented (MELF) invasion pattern in endometrial carcinomas with deep myometrial invasion, lymphovascular space invasion and lymph node metastasis. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2015; 35:397–402.
Article5. Kukreja I, Kapoor P, Deshmukh R, Kulkarni V. VEGF and CD 34: a correlation between tumor angiogenesis and microvessel density-an immunohistochemical study. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2013; 17:367–73.
Article6. Żyła MM, Kostrzewa M, Litwińska E, Szpakowski A, Wilczyński JR, Stetkiewicz T. The role of angiogenic factors in endometrial cancer. Prz Menopauzalny. 2014; 13:122–6.
Article7. Stefansson IM, Salvesen HB, Immervoll H, Akslen LA. Prognostic impact of histological grade and vascular invasion compared with tumour cell proliferation in endometrial carcinoma of endometrioid type. Histopathology. 2004; 44:472–9.
Article8. Stefansson IM, Salvesen HB, Akslen LA. Vascular proliferation is important for clinical progress of endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:3303–9.
Article9. Stewart CJ, Crook ML, Manso L. Fascin expression in low-grade uterine endometrioid adenocarcinoma: correlation with microcystic, elongated and fragmented (MELF)-type alteration at the deep invasive margin. Histopathology. 2011; 59:73–80.
Article10. Bajracharya D, Shrestha B, Kamath A, Menon A, Radhakrishnan R. Immunohistochemical correlation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-2 in tobacco associated epithelial dysplasia. Dis Markers. 2014; 2014:197813.
Article11. Zaino RJ. Unusual patterns of endometrial carcinoma including MELF and its relation to epithelial mesenchymal transition. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2014; 33:357–64.
Article12. Stewart CJ, Crook ML. Galectin-3 expression in uterine endometrioid adenocarcinoma: comparison of staining in conventional tumor glands and in areas of MELF pattern myometrial invasion. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2010; 29:555–61.13. Erdem O, Erdem M, Erdem A, Memis L, Akyol G. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and assessment of microvascular density with CD 34 and endoglin in proliferative endometrium, endometrial hyperplasia, and endometrial carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2007; 17:1327–32.
Article14. Aybatli A, Sayin C, Kaplan PB, Varol F, Altaner S, Süt N. The investigation of tumoral angiogenesis with HIF-1 alpha and microvessel density in women with endometrium cancer. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 2012; 13:37–44.
Article15. Haldorsen IS, Stefansson I, Grüner R, et al. Increased microvascular proliferation is negatively correlated to tumour blood flow and is associated with unfavourable outcome in endometrial carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 2014; 110:107–14.
Article16. Ozdemir O. Mast cell density, angiogenesis, and their significance in tumor development. Gynecol Oncol. 2006; 100:628–9.17. Simionescu C, Mărgăritescu C, Stepan A, Pirici D, Ciurea R, Cernea N. Tumor angiogenesis, macrophages and mast cell microdensities in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2013; 6:415–20.
Article18. Nunobiki O, Nakamura M, Taniguchi E, et al. Adrenomedullin, Bcl-2 and microvessel density in normal, hyperplastic and neoplastic endometrium. Pathol Int. 2009; 59:530–6.
Article19. Schmid BC, Oehler MK. Improvements in progression-free and overall survival due to the use of anti-angiogenic agents in gynecologic cancers. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2015; 16:318.
Article20. Saarelainen SK, Staff S, Peltonen N, et al. Endoglin, VEGF, and its receptors in predicting metastases in endometrial carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35:4651–7.
Article21. Wang J, Taylor A, Showeil R, et al. Expression profiling and significance of VEGF-A, VEGFR2, VEGFR3 and related proteins in endometrial carcinoma. Cytokine. 2014; 68:94–100.
Article22. Saito M, Sato Y, Watanabe J, Kuramoto H, Kaba S, Fukuda T. Angiogenic factors in normal endometrium and endometrial adenocarcinoma. Pathol Int. 2007; 57:140–7.
Article23. Matias-Guiu X, Davidson B. Prognostic biomarkers in endometrial and ovarian carcinoma. Virchows Arch. 2014; 464:315–31.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- High Expression of Galectin-1, VEGF and Increased Microvessel Density Are Associated with MELF Pattern in Stage I-III Endometrioid Endometrial Adenocarcinoma
- Microvessel Density and Expressions of bcl-2, p53, and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Endometrial Carcinoma
- Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Microvessel Density in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- VEGF Expression and Microvessel Density in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas
- Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in the Progression and Prognosis of Gastric Carcinomas