J Korean Acad Oral Health.
2017 Sep;41(3):188-193. 10.11149/jkaoh.2017.41.3.188.
In vitro antimicrobial activity of different mouthwashes available in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral Microbiology, College of Dentistry, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Korea.
- 2Department of Preventive and Public Health Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Korea. mads@gwnu.ac.kr
- 3Research Institute of Oral Science, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Korea.
- KMID: 2392437
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11149/jkaoh.2017.41.3.188
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to compare the oral antimicrobial effects of seven different mouthwashes available in Korea.
METHODS
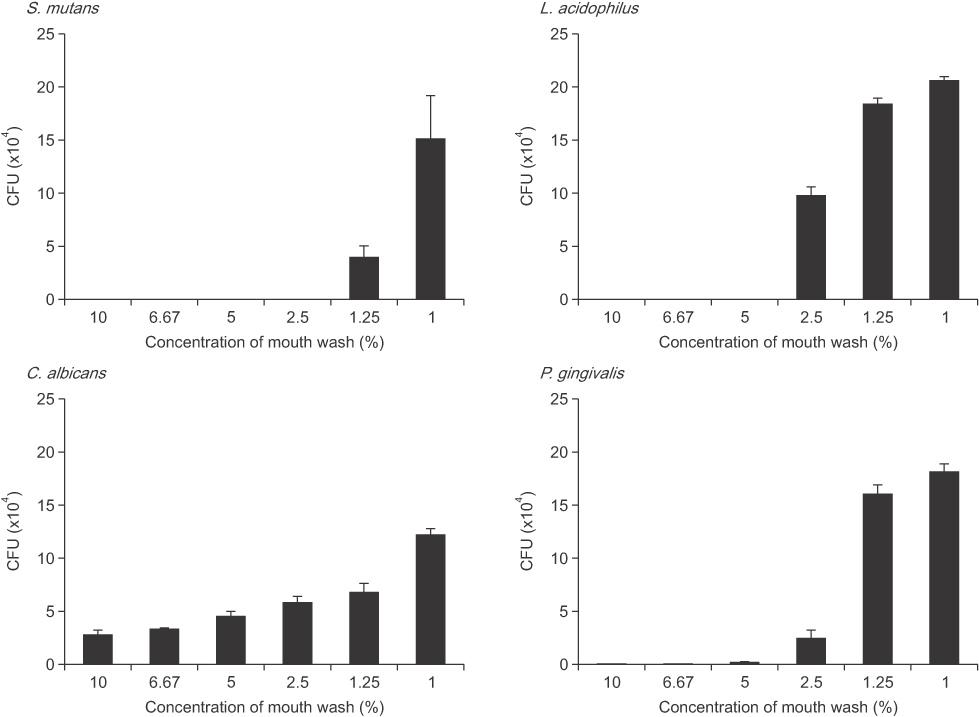
To examine the antimicrobial effects of the seven mouthwashes, their minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) were determined using broth microdilution methods. Streptococcus mutans ATCC 25175, Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4355, Candida albicans KCTC 7270, and Porphyromonas gingivalis ATCC 33277 were used in this experiment. S. mutans and P. gingivalis were examined using a scanning electron microscope (SEM), after treatment with the mouthwashes containing cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC).
RESULTS
Mouthwashes containing CPC had lower MIC and MBC values against the four microorganisms. Their bactericidal effects were concentration-dependent. S. mutans and C. albicans were highly sensitive to the concentration of CPC in the mouthwashes. According to the SEM observation, the treatment of bacteria with mouthwashes containing CPC, changed the cell surface texture of S. mutans and P. gingivalis.
CONCLUSIONS
Mouthwashes containing CPC showed relatively lower MIC and MBC values under the same conditions against the four microorganisms used in this study.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. ten Cate JM. Biofilms, a new approach to the microbiology of dental plaque. Odontology. 2006; 94:1–9.
Article2. Wu CD, Savitt ED. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of over-the-counter oral hygiene products for the reduction and control of plaque and gingivitis. Periodontol 2000. 2002; 28:91–105.
Article3. Council on Dental Therapeutics accepts Listerine. J Am Dent Assoc. 1988; 117:515–516.4. Allen DR, Davies R, Bradshaw B, Ellwood R, Simone AJ, Robinson R, et al. Efficacy of a mouthrinse containing 0.05% cetylpyridinium chloride for the control of plaque and gingivitis: A 6-month clinical study in adults. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 1998; 19:Suppl 2. 20–26.5. Mandel ID. Chemotherapeutic agents for controlling plaque and gingivitis. J Clin Periodontol. 1988; 15:488–498.
Article6. Renton-Harper P, Addy M, Moran J, Doherty FM, Newcombe RG. A comparison of chlorhexidine, cetylpyridinium chloride, triclosan, and C31G mouthrinse products for plaque inhibition. J Periodontol. 1996; 67:486–489.
Article7. James P, Worthington HV, Parnell C, Harding M, Lamont T, et al. Chlorhexidine mouthrinse as an adjunctive treatment for gingival health. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017; 31(3):CD008676.
Article8. Gunsolley JC. Clinical efficacy of antimicrobial mouthrinses. J Dent. 2010; 38:Suppl 1. S6–S10.
Article9. Barnett ML. The role of therapeutic antimicrobial mouthrinses in clinical practice: Control of supragingival plaque and gingivitis. J Am Dent Assoc. 2003; 134:699–704.10. Baker PJ, Coburn RA, Genco RJ, Evans RT. The in vitro inhibition of microbial growth and plaque formation by surfactant drugs. J Periodontal Res. 1978; 13:474–485.
Article11. Gjermo P, Baastad KL, Rolla G. The plaque-inhibiting capacity of 11 antibacterial compounds. J Periodontal Res. 1970; 5:102–109.
Article12. Emilson CG. Susceptibility of various microorganisms to chlorhexidine. Scand J Dent Res. 1977; 85:255–265.
Article13. Roberts WR, Addy M. Comparison of the in vivo and in vitro antibacterial properties of antiseptic mouthrinses containing chlorhexidine, alexidine, cetyl pyridinium chloride and hexetidine. relevance to mode of action. J Clin Periodontol. 1981; 8:295–310.
Article14. Emilson CG. Potential efficacy of chlorhexidine against mutans streptococci and human dental caries. J Dent Res. 1994; 73:682–691.
Article15. Jenkins S, Addy M, Newcombe RG. A comparison of cetylpyridinium chloride, triclosan and chlorhexidine mouthrinse formulations for effects on plaque regrowth. J Clin Periodontol. 1994; 21:441–444.
Article16. Araujo MW, Charles CA, Weinstein RB, McGuire JA, Parikh-Das AM, Du Q, et al. Meta-analysis of the effect of an essential oil-containing mouthrinse on gingivitis and plaque. J Am Dent Assoc. 2015; 146:610–622.
Article17. Haps S, Slot DE, Berchier CE, Van der Weijden GA. The effect of cetylpyridinium chloride-containing mouth rinses as adjuncts to toothbrushing on plaque and parameters of gingival inflammation: a systematic review. Int J Dent Hyg. 2008; 6:290–303.
Article18. Kwon YR, Lee YS, Jeon JG, Han SK, Ahn JH, Chang KW. Preventive dentisty : Effect on biofilm formation of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus by some mouth rinsing solution sold in Korea. J Korean Acad Dent Health. 2008; 32:1–9.19. Song JH, Ban SH, Kim JB, Ahn JH, Kim JC, Ha WH, et al. Antibacterial effect of some mouth rinsing solution in Korea. J Korean Acad Dent Health. 2007; 31:482–488.20. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests: M02-A10, vol.29, no.1. Pennsylvania: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2009. p. 1.21. Thomas JG, Nakaishi LA. Managing the complexity of a dynamic biofilm. J Am Dent Assoc. 2006; 137:Suppl. S10–S15.
Article22. ten Cate JM. Contemporary perspective on the use of fluoride products in caries prevention. Br Dent J. 2013; 214:161–167.
Article23. Bradshaw DJ, Marsh PD, Hodgson RJ, Visser JM. Effects of glucose and fluoride on competition and metabolism within in vitro dental bacterial communities and biofilms. Caries Res. 2002; 36:81–86.
Article24. Latimer J, Munday JL, Buzza KM, Forbes S, Sreenivasan PK, McBain AJ. Antibacterial and anti-biofilm activity of mouthrinses containing cetylpyridinium chloride and sodium fluoride. BMC Microbiol. 2015; 15:169.
Article25. Moran J, Addy M. The pattern of adsorption of cationic antiseptics to polymethylmethacrylate. J Oral Rehabil. 1985; 12:81–90.
Article26. Bonesvoll P, Gjermo P. A comparision between chlorhexidine and some quaternary ammonium compounds with regard to retention, salivary concentration and plaque-inhibiting effect in the human mouth after mouth rinses. Arch Oral Biol. 1978; 23:289–294.
Article27. Addy M, Roberts WR. The use of polymethylmethacrylate to compare the adsorption and staining reactions of some cationic antiseptics. J Periodontol. 1981; 52:380–385.
Article28. Llewelyn J. A double-blind crossover trial on the effect of cetylpyridinium chloride 0.05 per cent (merocet) on plaque accumulation. Br Dent J. 1980; 148:103–104.
Article29. Pan PC, Harper S, Ricci-Nittel D, Lux R, Shi W. In-vitro evidence for efficacy of antimicrobial mouthrinses. J Dent. 2010; 38:Suppl 1. S16–S20.
Article30. Elias-Boneta AR, Toro MJ, Noboa J, Romeu FL, Mateo LR, Ahmed R, Chaknis P, et al. Efficacy of CPC and essential oils mouthwashes compared to a negative control mouthwash in controlling established dental plaque and gingivitis: A 6-week, randomized clinical trial. Am J Dent. 2015; 28 Spec No A:21A–26A.31. Nyvad B, Crielaard W, Mira A, Takahashi N, Beighton D. Dental caries from a molecular microbiological perspective. Caries Res. 2013; 47:89–102.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antimicrobial effect of slightly acidic electrolyzed water on oral microorganisms
- A new in vitro method for evaluating the antimicrobial activity of toothpaste
- Antimicrobial activity of candidate probiotic Streptococcus salivarius against Gram-positive bacteria in oral cavity
- Influence of Some Commercially Available Mouthwashes on Teeth
- Effectiveness of mentha extracts against oral microorganisms: an in vitro study