Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2017 Sep;5(5):256-261. 10.4168/aard.2017.5.5.256.
Effect of atopic dermatitis on the natural course of food allergy in infants and young children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea. kimjhmd@inha.ac.kr
- 2The Environmental Health Center for Allergic Rhinitis, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Research Institute for Healthcare Policy, Korean Medical Association, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2392400
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2017.5.5.256
Abstract
- PURPOSE
There have been studies showing that food allergy plays a role in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. However, there have been few studies about the effect of atopic dermatitis on remission of food allergy. Thus, this study aimed to evaluate the difference in remission according to the presence of atopic dermatitis in infants and young children with milk or egg allergy.
METHODS
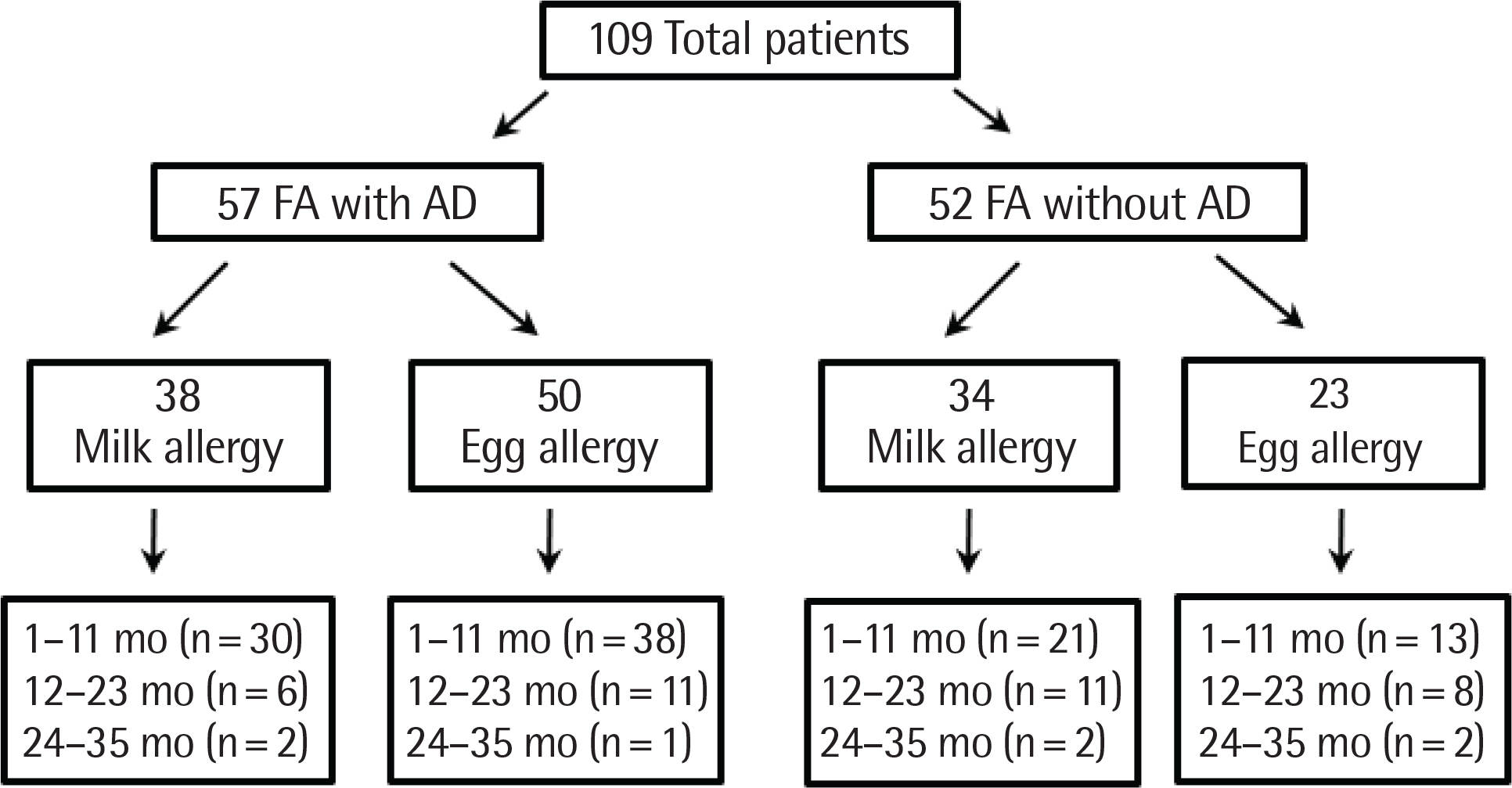
A retrospective study was performed on 109 infants and young children with IgE-mediated food allergy in a tertiary hospital. They divided into food allergy with atopic dermatitis (FA with AD) and without atopic dermatitis (FA without AD).
RESULTS
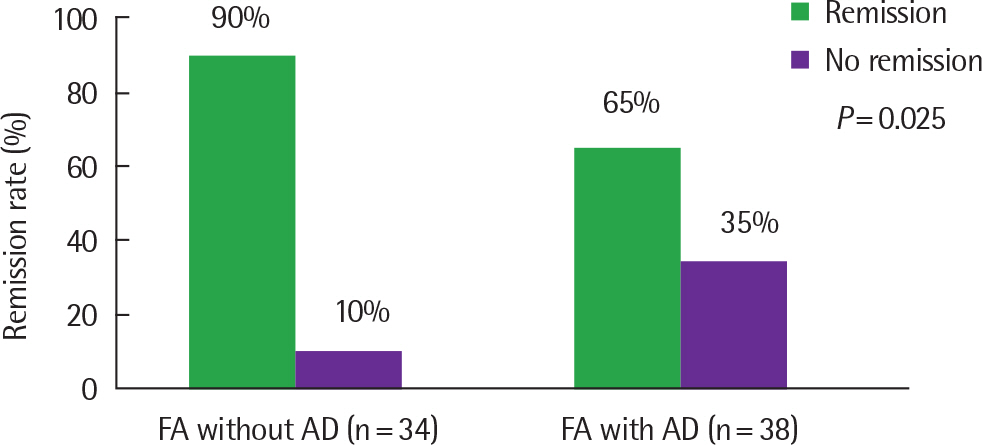
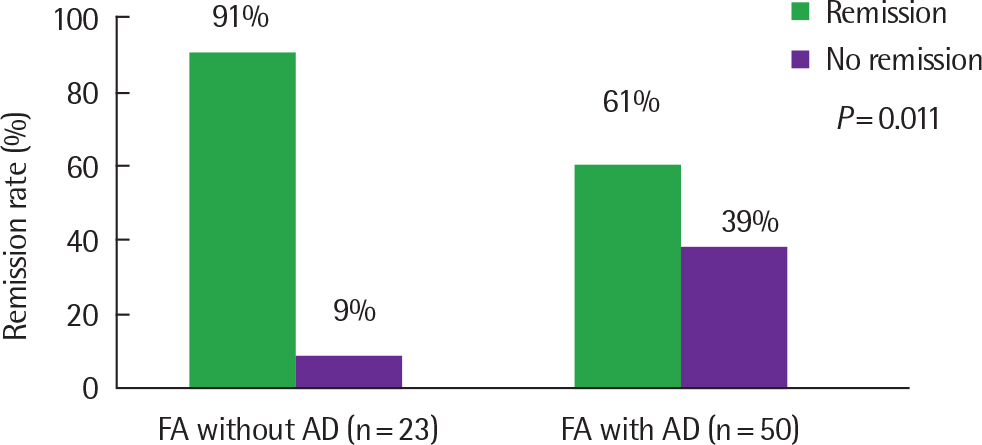
In the milk allergy group, initial milk-specific IgE levels were 21.16±27.98 kU(A)/L and 11.36±22.88 kU(A)/L, respectively, in FA with AD and FA without AD under 12 months of age. The remission rates of milk allergy at 36 months of age were 64.9% and 90.0%, respectively, in FA with AD and FA without AD. In the egg allergy groups, initial egg-specific IgE levels were 34.48±36.72 kU(A)/L and 15.66±28.60 kU(A)/L, respectively, in FA with AD and FA without AD under 12 months of age. The remission rates of egg allergy at 36 months of age were 61.2% and 90.0% in children with FA with AD and FA without AD.
CONCLUSION
Atopic dermatitis may play an important role in the natural history of food allergy in infants. Different strategies are needed for the management of food allergy in young children with atopic dermatitis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Clinical and Laboratory Predictors of Egg Allergy Resolution in Children
Jeong Hee Kim
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11(4):446-449. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.4.446.Factors related with the natural course of food allergy
So-Yeon Lee
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017;5(5):237-238. doi: 10.4168/aard.2017.5.5.237.
Reference
-
1. Leung DY, Sicherer SH. Atopic dermatitis (atopic eczema). Kliegman R, Stanton B, St Geme J, Schor N, editors. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 20th ed.Philadelphia: Elsevier;2015. p. 1116–21.
Article2. Schloss OM. Allergy to common foods. Trans Am Pediatr Soc. 1915; 27:62–8.3. Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Food hypersensitivity and atopic dermatitis: pathophysiology, epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 104(3 Pt 2):S114–22.
Article4. Burks AW, James JM, Hiegel A, Wilson G, Wheeler JG, Jones SM, et al. Atopic dermatitis and food hypersensitivity reactions. J Pediatr. 1998; 132:132–6.
Article5. Kelleher MM, Dunn-Galvin A, Gray C, Murray DM, Kiely M, Kenny L, et al. Skin barrier impairment at birth predicts food allergy at 2 years of age. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 137:1111–6.e8.6. Dunkin D, Berin MC, Mayer L. Allergic sensitization can be induced via multiple physiologic routes in an adjuvant-dependent manner. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128:1251–8.e2.
Article7. Wood RA. The natural history of food allergy. Pediatrics. 2003; 111(6 Pt 3):1631–7.
Article8. Hanifin JM, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic eczema. Acta Dermatol Venereol Suppl (Stockh). 1980; 92:44–7.9. Flohr C, Perkin M, Logan K, Marrs T, Radulovic S, Campbell LE, et al. Atopic dermatitis and disease severity are the main risk factors for food sensitization in exclusively breastfed infants. J Invest Dermatol. 2014; 134:345–50.
Article10. Du Toit G, Roberts G, Sayre PH, Plaut M, Bahnson HT, Mitchell H, et al. Identifying infants at high risk of peanut allergy: the Learning Early About Peanut Allergy (LEAP) screening study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:135–43.e1-12.
Article11. Tsakok T, Marrs T, Mohsin M, Baron S, du Toit G, Till S, et al. Does atopic dermatitis cause food allergy? A systematic review. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 137:1071–8.
Article12. Hill DJ, Hosking CS. Food allergy and atopic dermatitis in infancy: an epidemiologic study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004; 15:421–7.
Article13. Pourpak Z, Farhoudi A, Mahmoudi M, Movahedi M, Ghargozlou M, Kazemnejad A, et al. The role of cow milk allergy in increasing the severity of atopic dermatitis. Immunol Invest. 2004; 33:69–79.
Article14. Pourpak M, et al. The study of egg allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. World Allergy Organ J. 2009; 2:123–7.15. Spergel JM, Boguniewicz M, Schneider L, Hanifin JM, Paller AS, Eichen-field LF. Food allergy in infants with atopic dermatitis: limitations of food-specific IgE measurements. Pediatrics. 2015; 136:e1530–8.
Article16. Novak N, Bieber T, Leung DY. Immune mechanisms leading to atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 112(6 Suppl):S128–39.
Article17. Fartasch M. Epidermal barrier in disorders of the skin. Microsc Res Tech. 1997; 38:361–72.
Article18. Wood RA, Sicherer SH, Vickery BP, Jones SM, Liu AH, Fleischer DM, et al. The natural history of milk allergy in an observational cohort. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:805–12.
Article19. Sicherer SH, Wood RA, Vickery BP, Jones SM, Liu AH, Fleischer DM, et al. The natural history of egg allergy in an observational cohort. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014; 133:492–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Natural History and Risk Factors of Atopic Dermatitis in Children
- A Study on the Use of Complementary Alternative Medicine in Children with Atopic Dermatitis
- The Effect of Antigen Sensitization and Development of Respiratory Allergy Disease on Severity of Atopic Dermatitis
- Study on Persistence of Egg Allergy and Its Risk Factors in Infants and Young Children with Atopic Dermatitis
- Risk Factors of Atopic Dermatitis in Young Children