Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2017 Mar;5(2):92-98. 10.4168/aard.2017.5.2.92.
Clinical characteristics of lower respiratory infections in preterm children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. joung756@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2392380
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2017.5.2.92
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We evaluated the clinical characteristics of lower respiratory infections of preterm children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) and compared them between those with and without lower respiratory infections that of preterm patients without BPD.
METHODS
This study enrolled preterm patients under 2 years old, who admitted with acute lower respiratory infection from March 2014 to May 2016. The patients were divided into 2 groups according to BPD, and we retrospectively reviewed their medical records.
RESULTS
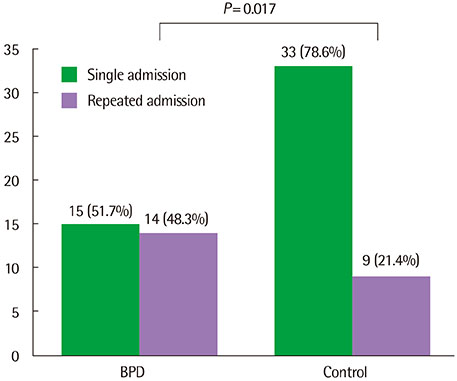
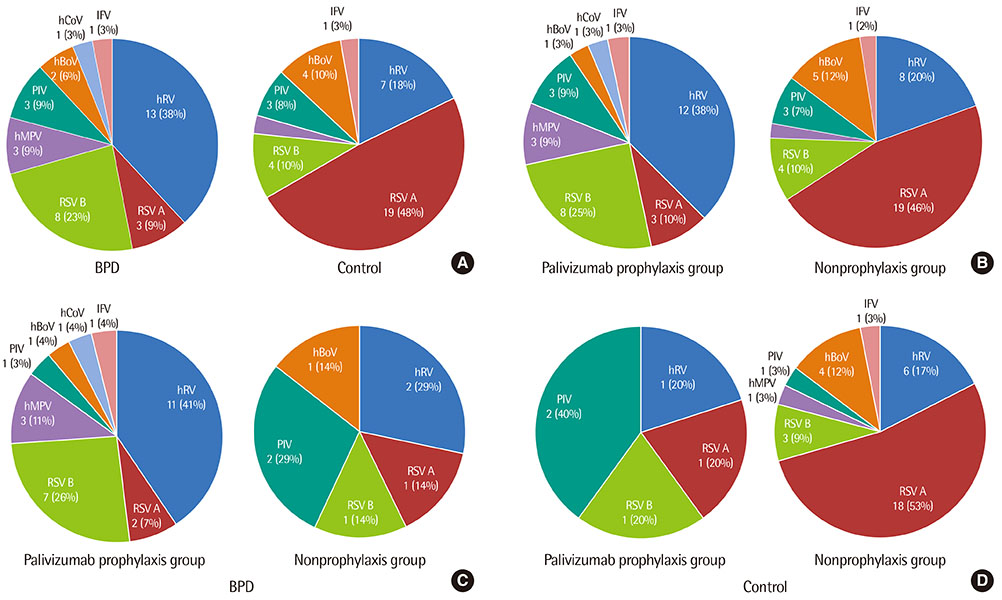
A total of 71 patients (106 cases) were enrolled; the BPD group consisited of 29 patients (54 cases) and the control group 42 patients (52 cases). Compared to the patients in the control group, those in the BPD group were older (P=0.001), had lower gestational age and birth weight (P<0.001), and showed more frequent readmission in hospital (P=0.017). The most common causative virus was human rhinovirus (hRV) in the BPD group, whereas respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in the control group. The patients in the BPD group showed a higher incidence of tachypnea, decreased aeration, and chest retraction (P<0.001, P=0.009, and P=0.026, respectively), a higher respiratory symptom score (P=0.011), a longer duration of cough and wheezy sounds (P=0.004 and P=0.009, respectively), and higher incidence and longer duration of treatment with oxygen, and mechanical ventilator support (P=0.016 and P=0.017, respectively) than those in the control group. In the BPD group, the patients with RSV showed a higher incidence of tachypnea and rales (P=0.033 and P=0.033, respectively) than those with hRV.
CONCLUSION
The preterm children with BPD may have more severe clinical manifestations than those without.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical characteristics of lower respiratory tract infection in low birth weight children
Yoonsun Yoon, Geehae Jung, Soohyun Ri, Ji Tae Choung, Young Yoo
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(4):211-218. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.4.211.
Reference
-
1. Northway WH Jr, Rosan RC, Porter DY. Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 1967; 276:357–368.
Article2. Coalson JJ. Pathology of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Perinatol. 2006; 30:179–184.
Article3. Choi CW, Kim BI, Kim EK, Song ES, Lee JJ. Incidence of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:914–921.
Article4. Kim JK, Chang YS, Sung S, Ahn SY, Yoo HS, Park WS. Trends in Survival and Incidence of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Extremely Preterm Infants at 23-26 Weeks Gestation. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:423–429.
Article5. Bhandari A, Panitch HB. Pulmonary outcomes in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Perinatol. 2006; 30:219–226.
Article6. Aujard Y, Fauroux B. Risk factors for severe respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants. Respir Med. 2002; 96:Suppl B. S9–S14.
Article7. Grimaldi M, Gouyon B, Michaut F, Huet F, Gouyon JB. Burgundy Perinatal Network. Severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis: epidemiologic variations associated with the initiation of palivizumab in severely premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004; 23:1081–1085.8. Morris SK, Dzolganovski B, Beyene J, Sung L. A meta-analysis of the effect of antibody therapy for the prevention of severe respiratory syncytial virus infection. BMC Infect Dis. 2009; 9:106.
Article9. Resch B, Pasnocht A, Gusenleitner W, Müller W. Rehospitalisations for respiratory disease and respiratory syncytial virus infection in preterm infants of 29-36 weeks gestational age. J Infect. 2005; 50:397–403.
Article10. García-Garcia ML, González-Carrasco E, Quevedo S, Muñoz C, Sánchez-Escudero V, Pozo F, et al. Clinical and virological characteristics of early and moderate preterm infants readmitted with viral respiratory infections. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015; 34:693–699.
Article11. Jobe AH, Bancalari E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 163:1723–1729.
Article12. Pavón D, Castro-Rodríguez JA, Rubilar L, Girardi G. Relation between pulse oximetry and clinical score in children with acute wheezing less than 24 months of age. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1999; 27:423–427.
Article13. Tal A, Bavilski C, Yohai D, Bearman JE, Gorodischer R, Moses SW. Dexamethasone and salbutamol in the treatment of acute wheezing in infants. Pediatrics. 1983; 71:13–18.
Article14. Furman L, Baley J, Borawski-Clark E, Aucott S, Hack M. Hospitalization as a measure of morbidity among very low birth weight infants with chronic lung disease. J Pediatr. 1996; 128:447–452.
Article15. Lee JH, Kim CS, Chang YS, Choi JH. Committee on Data Collection and Statistical Analysis of the Korean Society of Neonatology. Respiratory syncytial virus related readmission in preterm infants less than 34 weeks' gestation following discharge from a neonatal intensive care unit in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2015; 30:Suppl 1. S104–S110.
Article16. In : Lee HJ, editor. Immunoprophylaxis for respiratory syncytial virus. Korean Pediatric Society. Immunization guideline. 7th ed. Seoul: Korean Pediatric Society;2012. p. 231–233.17. Carbonell-Estrany X, Quero J, Bustos G, Cotero A, Doménech E, Figueras-Aloy J, et al. IRIS Study Group. Rehospitalization because of respiratory syncytial virus infection in premature infants younger than 33 weeks of gestation: a prospective study. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000; 19:592–597.
Article18. Park HW, Lee BS, Kim AR, Yoon HS, Kim BI, Song ES, et al. Epidemiology of respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants born at less than thirty-five weeks of gestational age. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012; 31:e99–e104.
Article19. The IMpact-RSV Study Group. Palivizumab, a humanized respiratory syncytial virus monoclonal antibody, reduces hospitalization from respiratory syncytial virus infection in high-risk infants. Pediatrics. 1998; 102(3 Pt 1):531–537.20. Pedraz C, Carbonell-Estrany X, Figueras-Aloy J, Quero J. IRIS Study Group. Effect of palivizumab prophylaxis in decreasing respiratory syncytial virus hospitalizations in premature infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003; 22:823–827.
Article21. Hervás D, Reina J, Yañez A, del Valle JM, Figuerola J, Hervás JA. Epidemiology of hospitalization for acute bronchiolitis in children: differences between RSV and non-RSV bronchiolitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012; 31:1975–1981.
Article22. Miller EK, Bugna J, Libster R, Shepherd BE, Scalzo PM, Acosta PL, et al. Human rhinoviruses in severe respiratory disease in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2012; 129:e60–e67.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Dexamethasone induced Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in Neonate with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
- Association of Positive Ureaplasma in Gastric Fluid with Clinical Features in Preterm Infants
- Recent progress in the understanding of clinical characteristics, epidemiology, and pathogenesis of new bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: how can we improve its outcomes?
- Epidemiology, Clinical Characteristics, and Pathophysiology of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia