Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2016 Sep;4(5):340-345. 10.4168/aard.2016.4.5.340.
Clinical outcomes after recovery from severe asthma exacerbation: the third report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. ischoi@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2391923
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2016.4.5.340
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Up to 10% of the mortality rate of asthmatics within a year from the near-fatal attacks has been reported. We previously reported that not a few patients with acute severe asthma died after discharge from the hospital. This study investigated whether our efforts to improve clinical outcomes of patients after recovery from severe asthma exacerbation did work or not.
METHODS
Follow-up data from asthmatic patients who had been hospitalized due to severe exacerbation between 2007 and 2014 (present) were compared with that the previous one (1998-2006) (previous).
RESULTS
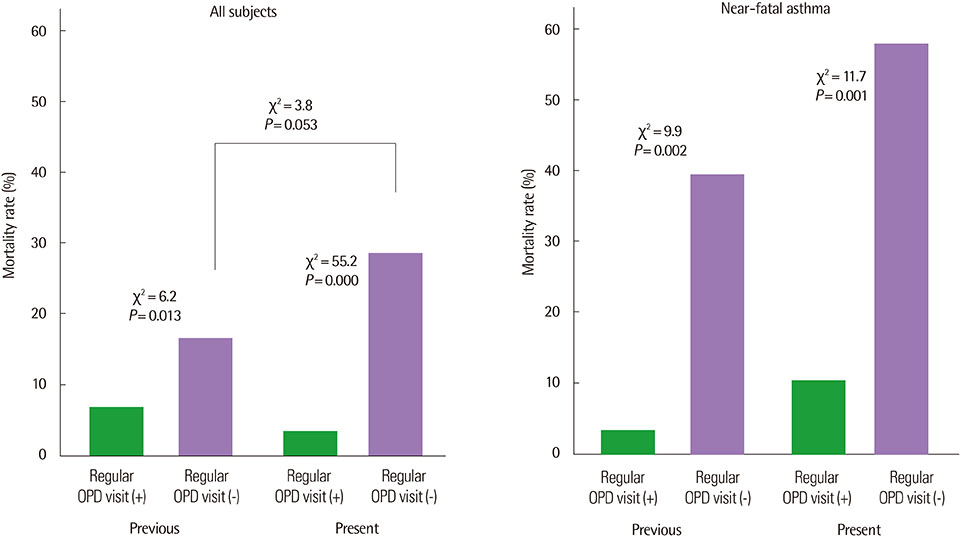
Sex, age, near-fatal asthma, and mortality (9.8% vs. 9.6%) were not significantly different between the previous (n=225) and present (n=397) studies. However, rehospitalization rate was significantly lower in the present study (29.3% vs. 52.4%, P=0.000). The patients in the present study used inhaled steroid more frequently (78.5% vs. 68.0%, P=0.006), had better asthma knowledge (P=0.000), and higher proportion of regular hospital visitors to total subjects (75.6% vs. 64.9%, P=0.004) than did the previous patients. The regular hospital visitors (n=300) showed a significantly lower mortality (3.3% vs. 28.9%, P=0.000), better knowledge (P=0.000) and higher inhaled steroid use (85.8% vs. 54.1%, P=0.000) than did the other group (n=97) in the present study.
CONCLUSION
Clinical outcomes after recovery from severe asthma exacerbation in the present study were better than the previous one. Our efforts to educate patients might contribute to these better results.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Marquette CH, Saulnier F, Leroy O, Wallaert B, Chopin C, Demarcq JM, et al. Long-term prognosis of near-fatal asthma. A 6-year follow-up study of 145 asthmatic patients who underwent mechanical ventilation for a near-fatal attack of asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992; 146:76–81.
Article2. Ulrik CS, Backer V, Søes-Petersen U, Lange P, Harving H, Plaschke PP. The patient's perspective: adherence or non-adherence to asthma controller therapy? J Asthma. 2006; 43:701–704.
Article3. Barnes PJ. Asthma. In : Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J, editors. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 19th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education;2015. p. 1669–1681.4. Kikuchi Y, Okabe S, Tamura G, Hida W, Homma M, Shirato K, et al. Chemosensitivity and perception of dyspnea in patients with a history of near-fatal asthma. N Engl J Med. 1994; 330:1329–1334.
Article5. Jang AS, Choi IS. Increased perception of dyspnea by inhalation of short acting beta2 agonist in patients with asthma of varying severity. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2000; 84:79–83.
Article6. Molfino NA, Nannini LJ, Rebuck AS, Slutsky AS. The fatality-prone asthmatic patient. Follow-up study after near-fatal attacks. Chest. 1992; 101:621–623.7. Jung HY, Choi IS, Lee WJ, Ban HJ, Lee SJ. Clinical outcomes after recovery from severe asthma exacerbation: the second report. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 29:27–32.8. Kwon SS, Kim MH, Cho YJ. Factors associated with mortality after asthma admission in the intensive care unit of a tertiary referral hospital. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015; 3:432–438.
Article9. British Thoracic Society. British guideline on the management of asthma: a national clinical guideline [Internet]. London: British Thoracic Society;2012. cited 2016 Jun 8. Available from: https://www.brit-thoracic.org.uk/document-library/clinical-information/asthma/btssign-asthma-guideline-2012/.10. Choi IS, Park SC, Jang AS, Kang KW, Lim H. Risk factors of near - fatal asthma. Korean J Med. 1999; 57:52–59.11. Crapo RO, Morris AH, Gardner RM. Reference spirometric values using techniques and equipment that meet ATS recommendations. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981; 123:659–664.12. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. National Asthma Education Program. Expert Panel Report. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991; 88(3 Pt 2):425–534.13. Bai TR, Cooper J, Koelmeyer T, Paré PD, Weir TD. The effect of age and duration of disease on airway structure in fatal asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 162(2 Pt 1):663–669.
Article14. Wennergren G, Kristjánsson S, Strannegård IL. Decrease in hospitalization for treatment of childhood asthma with increased use of antiinflammatory treatment, despite an increase in prevalence of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996; 97:742–748.
Article15. Donahue JG, Weiss ST, Livingston JM, Goetsch MA, Greineder DK, Platt R. Inhaled steroids and the risk of hospitalization for asthma. JAMA. 1997; 277:887–891.
Article16. Jónasson G, Lødrup Carlsen KC, Leegaard J, Carlsen KH, Mowinckel P, Halvorsen KS. Trends in hospital admissions for childhood asthma in Oslo, Norway, 1980-95. Allergy. 2000; 55:232–239.
Article17. Suissa S, Ernst P, Benayoun S, Baltzan M, Cai B. Low-dose inhaled corticosteroids and the prevention of death from asthma. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343:332–336.
Article18. Thomson NC, Chaudhuri R, Livingston E. Asthma and cigarette smoking. Eur Respir J. 2004; 24:822–833.
Article19. Kauppi P, Kupiainen H, Lindqvist A, Tammilehto L, Kilpeläinen M, Kinnula VL, et al. Overlap syndrome of asthma and COPD predicts low quality of life. J Asthma. 2011; 48:279–285.
Article20. Taylor DM, Auble TE, Calhoun WJ, Mosesso VN Jr. Current outpatient management of asthma shows poor compliance with International Consensus Guidelines. Chest. 1999; 116:1638–1645.
Article21. George MR, O'Dowd LC, Martin I, Lindell KO, Whitney F, Jones M, et al. A comprehensive educational program improves clinical outcome measures in inner-city patients with asthma. Arch Intern Med. 1999; 159:1710–1716.
Article22. Choi IS. Gender-specific asthma treatment. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011; 3:74–80.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Outcomes after Recovery from Severe Asthma Exacerbation: the Second Report
- Clinical Outcomes after Recovery from Severe Exacerbation in Asthma
- Factors Affecting Recovery Time of Pulmonary Function in Hospitalized Patients With Acute Asthma Exacerbations
- Severe asthma exacerbation associated with COVID-19 in children: A case report
- Clinical and Pathophysiological Characteristics of Severe Asthma