J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs.
2016 Mar;27(1):81-94. 10.12799/jkachn.2016.27.1.81.
Exploring Psycho-social Determinants to Child Neglect and Abuse among Caregivers with Young Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea. yrtak@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2391748
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12799/jkachn.2016.27.1.81
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The objective of this study was to investigate the relations among psycho-social factors regarding child neglect and abuse using the data from the 2013 Korea National Survey on Children and Youth.
METHODS
Data from a sample of 1,062 primary caregivers with young children were analyzed with the SPSS and AMOS programs to examine the interrelationships among depression, parenting stress, marital satisfaction, parent-child attachment, and child neglect or maltreatment.
RESULTS
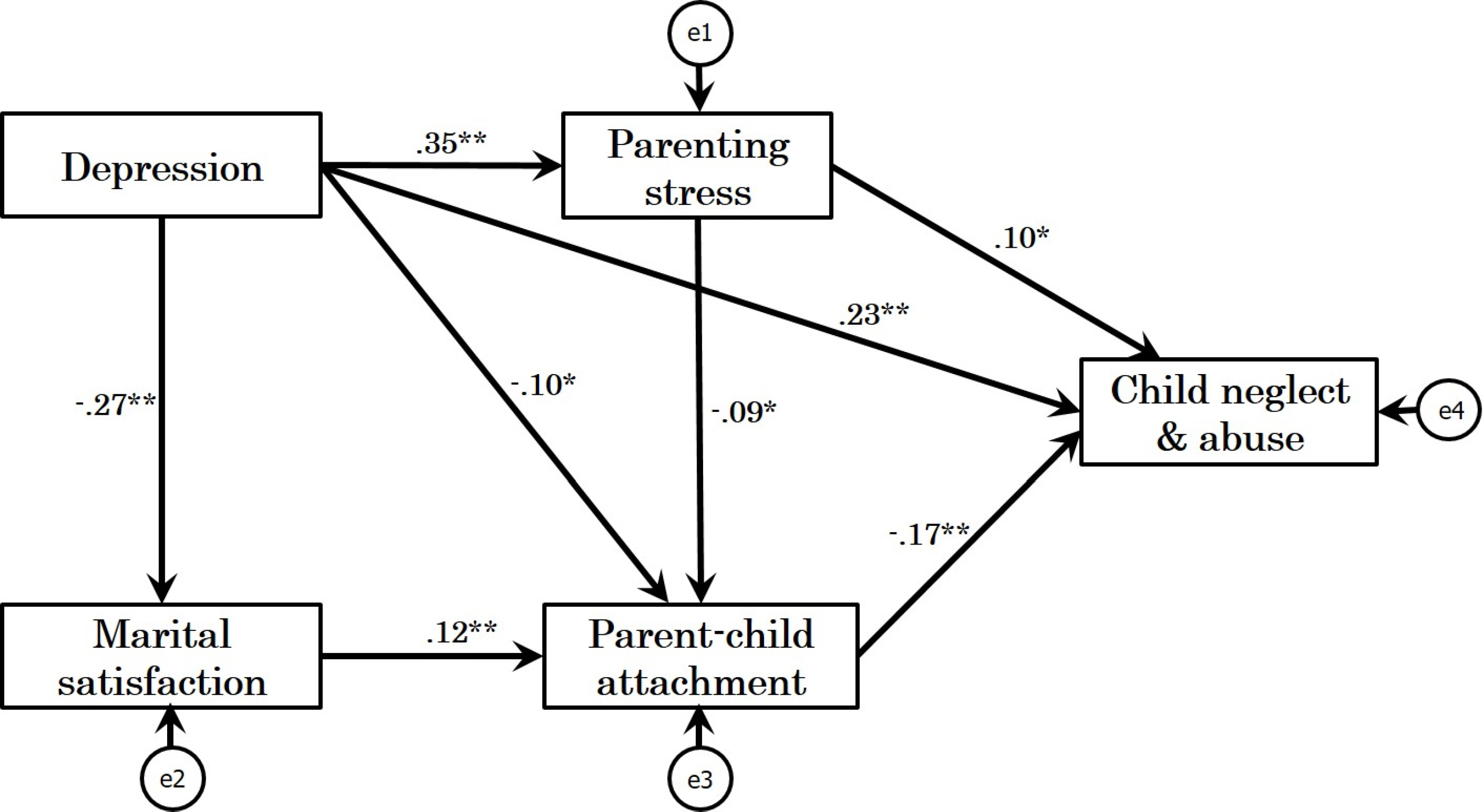
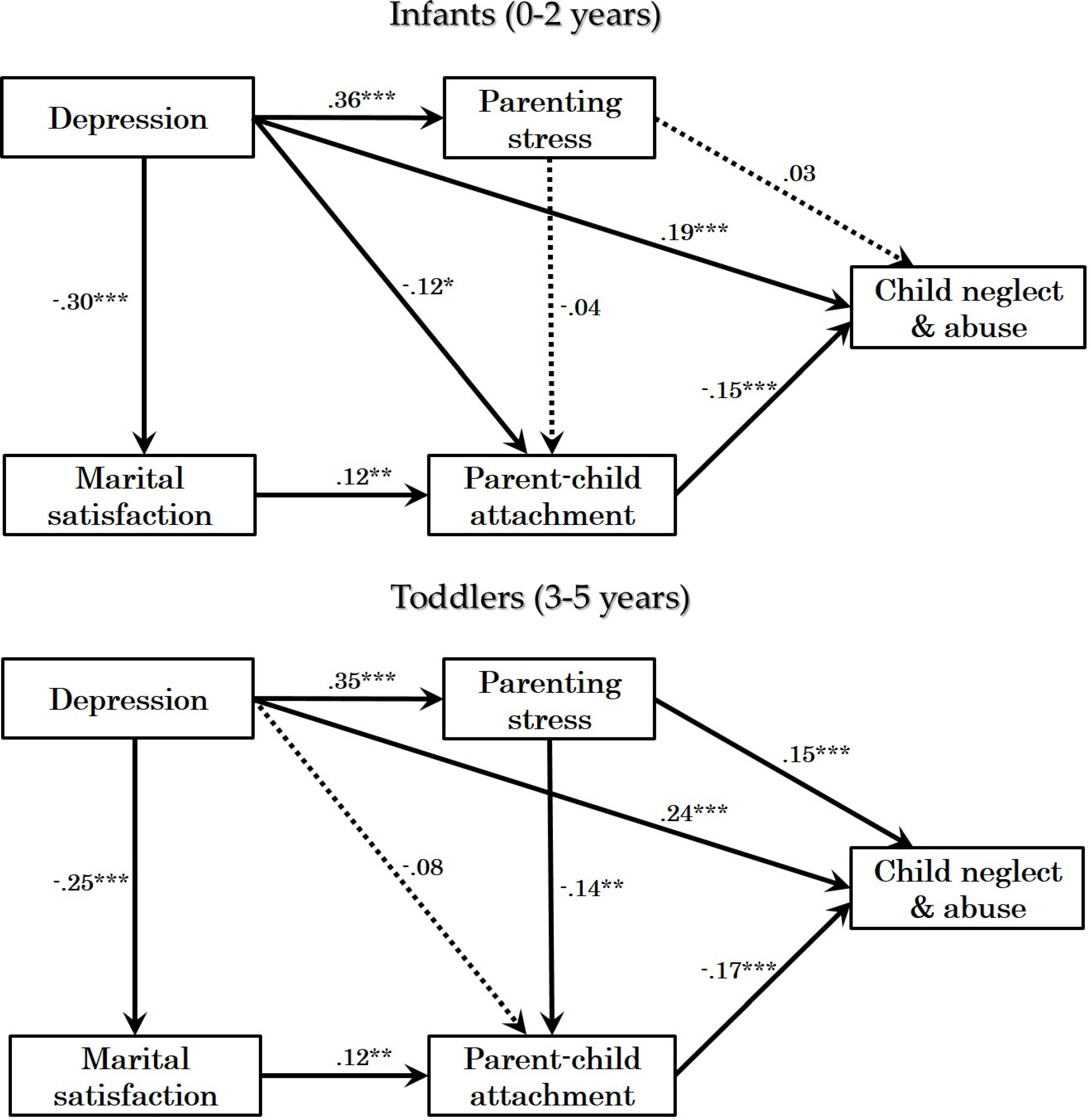
Depression, stress, and attachment had a direct influence on child neglect and abuse. Satisfaction with marital relationship, parenting stress, and attachment were found to play mediating roles in accounting for child neglect and abuse, explaining 12% of the variance. The results of multi group path analysis showed that some coefficients were different according to the age group of the children. For caregivers with infants, parenting stress did not predict either attachment or child maltreatment, whereas for caregivers with toddlers, depression did not have a significant effect on attachment.
CONCLUSION
In order to prevent child maltreatment, efforts should be made to develop community-based psycho-social support interventions focused on marital relationship as well as parent-child dyads and to provide practical child care support.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Statistics Korea. Report on child abuse [Internet]. Seoul: Statistics Korea;2014. [cited 2016 January 26]. Available from:. http://kosis.kr/common/meta_onedepth.jsp?vwcd=MT_OTITLE&listid=117_1 1764.2. US. Department of Health and Human Services, Children’s Bureau. Understanding the effects of maltreatment on brain development. Washington DC: Child welfare information gateway;2015. p. 19 p.3. Glaser D. Child abuse and neglect and the brain-a review. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 2000; 41(1):97–116. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1469-7610.00551.
Article4. Norman RE, Byambaa M, De R, Butchart A, Scott J, Vos T. The long-term health consequences of child physical abuse, emotional abuse, and neglect: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Medicine. 2012; 9(11):e1001349. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001349.
Article5. Stoltenborgh M, Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ, van IJzendoorn MH. The neglect of child neglect: a meta-analytic review of the prevalence of neglect. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology. 2012; 48(3):345–355. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00127-012-0549-y.
Article6. Berthelot N, Ensink K, Bernazzani O, Normandin L, Luyten P, Fonagy P. Intergenerational transmission of attachment in abused and neglected mothers: The role of trauma-specific reflective functioning. Infant Mental Health Journal. 2015; 36(2):200–212. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/imhj.21499.
Article7. Stith SM, Liu T, Davies LC, Boykin EL, Alder MC, Harris JM. . Risk factors in child maltreatment: A meta-analytic review of the literature. Aggression and Violent Behavior. 2009; 14(1):13–29. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2006.03.006.
Article8. Lee SJ, Taylor CA, Bellamy JL. Paternal depression and risk for child neglect in father-involved families of young children. Child Abuse & Neglect. 2012; 36(5):461–469. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2012.04.002.
Article9. Kim JH, Lee JY, Sung JH. The influences of mother’s psychological characteristics and parenting related factors on two-year-old infants’ development: The mediating role of parenting styles. Korean Journal of Child Studies. 2013; 34(6):77–96. http://dx.doi.org/10.5723/kjcs.2013.34.6.77.10. Gray PH, Edwards DM, O’Callaghan MJ, Cuskelly M, Gibbons K. Parenting stress in mothers of very preterm infantsinflu-ence of development, temperament and maternal depression. Early Human Development. 2013; 89(9):625–629. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2013.04.005.11. Park DY. The influences of mother’s psychological characteristics on verbal abuse of early children mother’s. Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society. 2013; 14(9):4368–4379. http://dx.doi.org/10.5762/kais.2013.14.9.4368.
Article12. Davis RN, Davis MM, Freed GL, Clark SJ. Fathers' depression related to positive and negative parenting behaviors with 1-year-old children. Pediatrics. 2011; 127(4):612–618. http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2010-1779.
Article13. Kim AR, Tak YR. Maternal role development in neonatal intensive care unit graduate mothers of premature infant. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2015; 21(4):308–320. http://dx.doi.org/10.4069/kjwhn.2015.21.4.308.
Article14. Bowlby J. A secure base: Parent-child attachment and healthy human development. New York, NY: Basic Books;1988. p. 224 p.15. Pillhofer M, Spangler G, Bovenschen I, Kuenster AK, Gabler S, Fallon B. . Pilot study of a program delivered within the regular service system in Germany: Effect of a short-term attachment-based intervention on maternal sensitivity in mothers at risk for child abuse and neglect. Child Abuse & Neglect. 2015; 42:163–173. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2014.07.007.
Article16. Parfitt Y, Ayers S, Pike A, Jessop DC, Ford E. A prospective study of the parent-baby bond in men and women 15 months after birth. Journal of Reproductive and Infant Psychology. 2014; 32(5):441–456. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/02646838.2014.956301.
Article17. Muzik M, Bocknek EL, Broderick A, Richardson P, Rosenblum KL, Thelen K. . Mother-infant bonding impairment across the first 6 months postpartum: the primacy of psychopathology in women with childhood abuse and neglect histories. Archives of Women's Mental Health. 2013; 16(1):29–38. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00737-012-0312-0.18. Hayes LJ, Goodman SH, Carlson E. Maternal antenatal depression and infant disorganized attachment at 12 months. Attachment & Human Development. 2013; 15(2):133–153. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/14616734.2013.743256.
Article19. Han TS, Hwang HJ. The effects of mother’s demographic characteristics, emotionality, marital conflicts and parenting related variables on preschool attachment. Korean Journal of Early Childhood Education. 2010; 30(5):99–119. http://dx.doi.org/10.18023/kjece.2010.30.5.005.20. Hopkins J, Gouze KR, Lavigne JV. Direct and indirect effects of contextual factors, caregiver depression, and parenting on attachment security in preschoolers. Attachment & Human Development. 2013; 15(2):155–173. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/14616734.2013.750702.
Article21. Kwon MK, Bang KS. Relationship of prenatal stress and depression to maternal-fetal attachment and fetal growth. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2011; 41(2):276–283. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.2.276.
Article22. Trillingsgaard T, Baucom KJW, Heyman RE. Predictors of change in relationship satisfaction during the transition to parenthood. Family Relations. 2014; 63(5):667–679. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/fare.12089.
Article23. Najman JM, Khatun M, Mamun A, Clavarino A, Williams GM, Scott J. . Does depression experienced by mothers leads to a decline in marital quality: A 21-year longitudinal study. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology. 2013; 49(1):121–132. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00127-013-0749-0.
Article24. Noh JY, Hwang HS. The effects of mothers' parenting stress and parental satisfaction on attachment formation with their children. Korean Journal of Human Ecology. 2012; 21(1):27–40. http://dx.doi.org/10.5934/kjhe.2012.21.1.27.
Article25. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs 2013 Korea national survey on children and youth 2013. Policy Paper. Sejong: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2013 December. Report No.: 2013-92.26. Straus MA, Hamby SL, Finkelhor D, Moore DW, Runyan D. Identification of child maltreatment with the parent-child conflict tactics scales: Development and psychometric data for a national sample of American parents. Child Abuse & Neglect. 1998; 22(4):249–270. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0145-2134(97)00174-9.
Article27. Kline RB. Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. 3rd ed. New York, NY: The Guilford Press;2010. p. 432 p.28. Cheung GW, Rensvold RB. Evaluating goodness-of-fit indexes for testing measurement invariance. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal. 2002; 9(2):233–255. http://dx.doi.org/10.1207/s15328007sem0902_5.
Article29. Thomason E, Volling BL, Flynn HA, McDonough SC, Marcus SM, Lopez JF. . Parenting stress and depressive symptoms in postpartum mothers: Bidirectional or unidirectional effects? Infant Behavior and Development. 2014; 37(3):406–415. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.infbeh.2014.05.009.
Article30. Maguire-Jack K, Negash T. Parenting stress and child maltreatment: The buffering effect of neighborhood social service availability and accessibility. Children and Youth Services Review. 2016; 60:27–33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2015.11.016.
Article