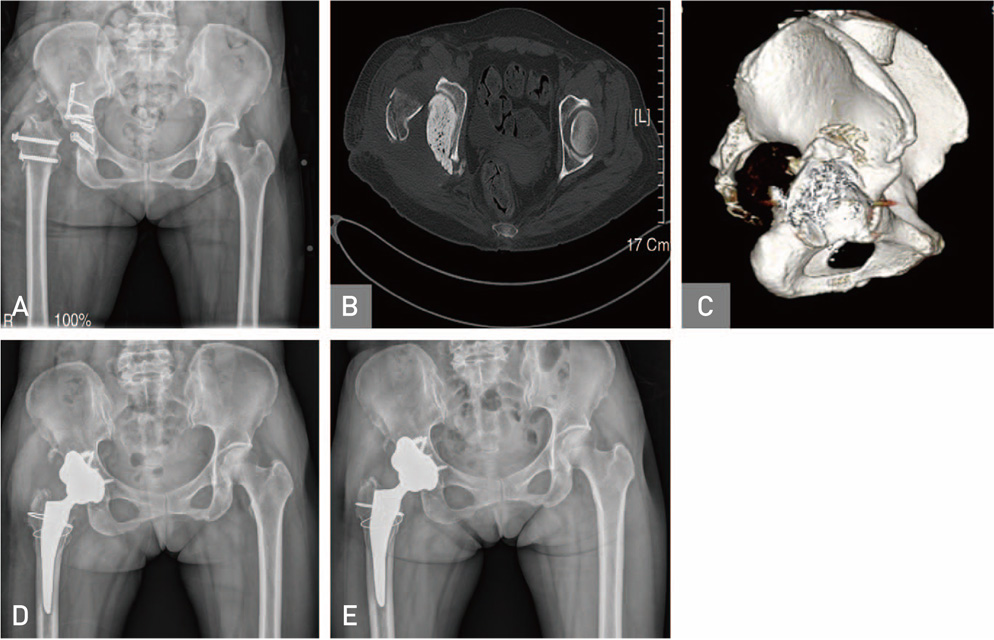
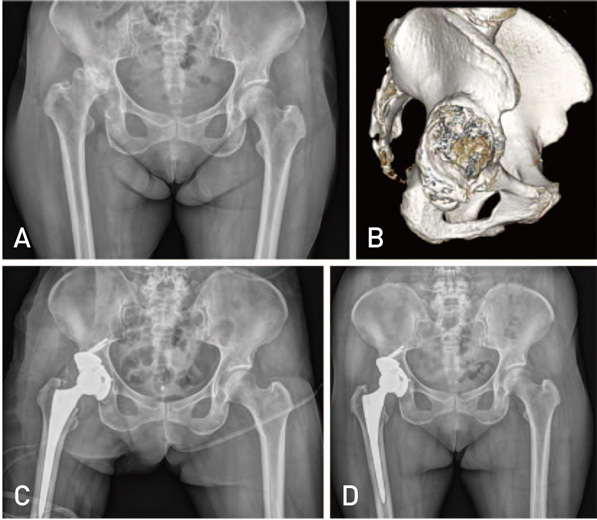
Hip Pelvis.
2017 Sep;29(3):168-175. 10.5371/hp.2017.29.3.168.
Acetabular Defect Reconstruction with Trabecular Metal Augments: Study with Minimum One-year Follow-up
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea. shonwy@hotmail.com wonyong@kumc.or.kr
- KMID: 2389522
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2017.29.3.168
Abstract
- PURPOSE
High rates of mechanical failure have been reported in type III acetabular defects. Recently porous trabecular metal augments have been introduced with, excellent biomechanical characteristics and biocompatibility, allowing early stability and greater bone ingrowth. The aim of the study was to assess the short term clinical and radiological outcome of the trabecular metal augments.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We performed, 22 revision total hip arthroplasties (THA) and 6 primary THA (total 28) using trabecular metal augments to reconstruct acetabular defect between 2011 to 2015. Among 28 patients, 18 were males, 10 females. Mean age of patients was 61.21 years. Paprosky classification for acetabular bone defects was used. Eighteen cases were classified as grade 3 A and 10 cases as grade 3B. Hip center was calculated in each case preoperatively and compared postoperatively to check whether it has been brought down. Clinical outcome assessed using Harris hip score (HHS) and radiological outcomes as osteolysis in acetabular zones and osseointegration, according to Moore's criteria.
RESULTS
HHS improved from 58.00 to 86.20. Centre of rotation of hip joint corrected from 38.90 mm preoperatively to 23.85 mm postoperatively above the interteardrop line. Among 28 patients, 18 patients had three or more signs of osseointegration (Moore's criteria), during final follow up and 10 had one/two signs. No radiolucency, osteolysis, or loosening found during follow up radiographic examination.
CONCLUSION
Our study showed that trabecular metal augments were highly satisfactory in short term. However, long term study is required for better evaluation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Pretreatment on Grit-Blasted Titanium Alloy for Enhanced Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
Seong Hwa Hong, Jinwoo Nam, Hee Joong Kim, Jeong Joon Yoo
Clin Orthop Surg. 2019;11(3):361-368. doi: 10.4055/cios.2019.11.3.361.
Reference
-
1. Necas L, Katina S, Uhlarova J, Colton CL. Survival analysis of total hip and knee replacement in Slovakia 2003-2011. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2013; 80:Suppl. 1–85.2. Templeton JE, Callaghan JJ, Goetz DD, Sullivan PM, Johnston RC. Revision of a cemented acetabular component to a cementless acetabular component. A ten to fourteen-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83-A:1706–1711.3. Jain S, Grogan RJ, Giannoudis PV. Options for managing severe acetabular bone loss in revision hip arthroplasty. A systematic review. Hip Int. 2014; 24:109–122.
Article4. Gill TJ, Sledge JB, Müller ME. The Bürch-Schneider anti-protrusio cage in revision total hip arthroplasty: indications, principles and long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998; 80:946–953.5. Herrera A, Martínez AA, Cuenca J, Canales V. Management of types III and IV acetabular deficiencies with the longitudinal oblong revision cup. J Arthroplasty. 2006; 21:857–864.
Article6. Bobyn JD, Stackpool GJ, Hacking SA, Tanzer M, Krygier JJ. Characteristics of bone ingrowth and interface mechanics of a new porous tantalum biomaterial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999; 81:907–914.
Article7. Paprosky WG, Perona PG, Lawrence JM. Acetabular defect classification and surgical reconstruction in revision arthroplasty. A 6-year follow-up evaluation. J Arthroplasty. 1994; 9:33–44.
Article8. Engh CA, Massin P, Suthers KE. Roentgenographic assessment of the biologic fixation of porous-surfaced femoral components. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; (257):107–128.
Article9. Moore MS, McAuley JP, Young AM, Engh CA Sr. Radiographic signs of osseointegration in porous-coated acetabular components. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 444:176–183.
Article10. Whitehouse MR, Masri BA, Duncan CP, Garbuz DS. Continued good results with modular trabecular metal augments for acetabular defects in hip arthroplasty at 7 to 11 years. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015; 473:521–527.
Article11. Antoniades J, Pellegrini VD Jr. Cross-sectional anatomy of the ilium: implications for acetabular component placement in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470:3537–3541.
Article12. Della Valle CJ, Berger RA, Rosenberg AG, Galante JO. Cementless acetabular reconstruction in revision total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; (420):96–100.
Article13. Whaley AL, Berry DJ, Harmsen WS. Extra-large uncemented hemispherical acetabular components for revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83-A:1352–1357.
Article14. D'Antonio JA, Capello WN, Borden LS, et al. Classification and management of acetabular abnormalities in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; (243):126–137.15. Berry DJ. Revision total hip arthroplasty: uncemented acetabular components. In : Callaghan JJ, Rosenberg AG, Rubash HE, editors. The adult hip. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2007. p. 1371–1381.16. van Haaren EH, Heyligers IC, Alexander FG, Wuisman PI. High rate of failure of impaction grafting in large acetabular defects. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89:296–300.
Article17. Benazzo F, Botta L, Scaffino MF, et al. Trabecular titanium can induce in vitro osteogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem cells without osteogenic factors. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014; 102:2061–2071.
Article18. Marin E, Fusi S, Pressacco M, Paussa L, Fedrizzi L. Characterization of cellular solids in Ti6Al4V for orthopaedic implant applications: Trabecular titanium. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2010; 3:373–381.
Article19. Van Kleunen JP, Lee GC, Lementowski PW, Nelson CL, Garino JP. Acetabular revisions using trabecular metal cups and augments. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24:6 Suppl. 64–68.
Article20. Del Gaizo DJ, Kancherla V, Sporer SM, Paprosky WG. Tantalum augments for Paprosky IIIA defects remain stable at midterm followup. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470:395–401.
Article21. Weeden SH, Schmidt RH. The use of tantalum porous metal implants for Paprosky 3A and 3B defects. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22:6 Suppl 2. 151–155.
Article22. Gustke KA, Levering MF, Miranda MA. Use of jumbo cups for revision of acetabulae with large bony defects. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29:199–203.
Article23. Patel JV, Masonis JL, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH. The fate of cementless jumbo cups in revision hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003; 18:129–133.
Article24. Schreurs BW, Luttjeboer J, Thien TM, et al. Acetabular revision with impacted morselized cancellous bone graft and a cemented cup in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. A concise follow-up, at eight to nineteen years, of a previous report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009; 91:646–651.
Article25. Nehme A, Lewallen DG, Hanssen AD. Modular porous metal augments for treatment of severe acetabular bone loss during revision hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; (429):201–208.
Article26. Unger AS, Lewis RJ, Gruen T. Evaluation of a porous tantalum uncemented acetabular cup in revision total hip arthroplasty: clinical and radiological results of 60 hips. J Arthroplasty. 2005; 20:1002–1009.
Article27. Abolghasemian M, Tangsataporn S, Sternheim A, Backstein D, Safir O, Gross AE. Combined trabecular metal acetabular shell and augment for acetabular revision with substantial bone loss: a mid-term review. Bone Joint J. 2013; 95-B:166–172.28. Banerjee S, Issa K, Kapadia BH, Pivec R, Khanuja HS, Mont MA. Systematic review on outcomes of acetabular revisions with highly-porous metals. Int Orthop. 2014; 38:689–702.
Article29. DeLee JG, Charnley J. Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976; 121:20–32.
Article30. Röder C, Eggli S, Aebi M, Busato A. The validity of clinical examination in the diagnosis of loosening of components in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003; 85:37–44.
Article31. Sporer SM, Paprosky WG. The use of a trabecular metal acetabular component and trabecular metal augment for severe acetabular defects. J Arthroplasty. 2006; 21:6 Suppl 2. 83–86.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acetabular Reconstruction in Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Acetabular Cup Revision
- Acetabular Reconstruction using Acetabular Roof Reinforcement Ring
- Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Tantalum Augment in Patients with Paprosky III or IV Acetabular Bone Defects: A Minimum 2-year Follow Up Study
- Assessment of Surgical Treatment of Acetabular Fracture after Minimum Five-year Follow-up