Ann Rehabil Med.
2017 Apr;41(2):306-312. 10.5535/arm.2017.41.2.306.
Correlation of Serum Creatine Kinase Level With Pulmonary Function in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea. sposta@yuhs.ac
- 2Rehabilitation Institute of Neuromuscular Disease, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2389490
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2017.41.2.306
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the relationship between serum creatine kinase (CK) level and pulmonary function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD).
METHODS
A total of 202 patients with DMD admitted to the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital were enrolled from January 1, 1999 to March 31, 2015. Seventeen patients were excluded. Data collected from the 185 patients included age, height, weight, body mass index, pulmonary function tests including forced vital capacity (FVC), peak cough flow, maximal expiratory pressure (MEP), and maximal inspiratory pressure (MIP), and laboratory measurements (serum level of CK, CK-MB, troponin-T, and B-type natriuretic peptide). FVC, MEP, and MIP were expressed as percentages of predicted normal values.
RESULTS
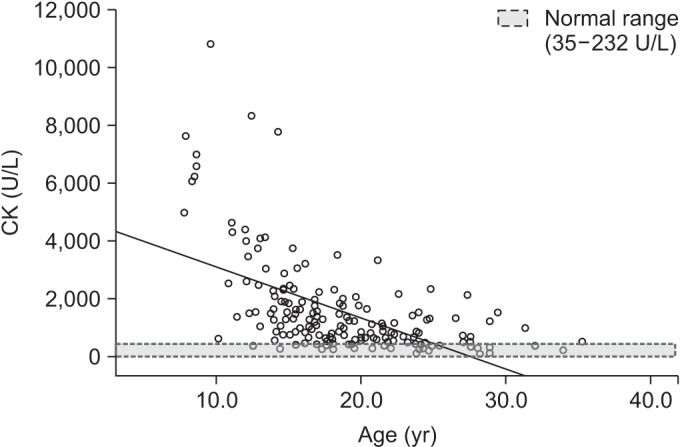
Serum CK activities were elevated above normal levels, even in the oldest DMD group. Serum CK level was strongly correlated with pulmonary functions of sitting FVC (p<0.001), supine FVC (p<0.001), MIP (p=0.004), and MEP (p<0.001).
CONCLUSION
Serum CK level is a reliable screening test even in patients with advanced DMD, and is a strong predictor of pulmonary functions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Helderman-van den Enden AT, Madan K, Breuning MH, van der Hout AH, Bakker E, de Die-Smulders CE, et al. An urgent need for a change in policy revealed by a study on prenatal testing for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013; 21:21–26. PMID: 22669413.
Article2. Deconinck N, Dan B. Pathophysiology of Duchenne muscular dystrophy: current hypotheses. Pediatr Neurol. 2007; 36:1–7. PMID: 17162189.
Article3. Zatz M, Rapaport D, Vainzof M, Passos-Bueno MR, Bortolini ER, Pavanello Rde C, et al. Serum creatine-kinase (CK) and pyruvate-kinase (PK) activities in Duchenne (DMD) as compared with Becker (BMD) muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1991; 102:190–196. PMID: 2072118.
Article4. Inkley SR, Oldenburg FC, Vignos PJ Jr. Pulmonary function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy related to stage of disease. Am J Med. 1974; 56:297–306. PMID: 4813648.
Article5. Hapke EJ, Meek JC, Jacobs J. Pulmonary function in progressive muscular dystrophy. Chest. 1972; 61:41–47. PMID: 5049500.
Article6. Rideau Y, Jankowski LW, Grellet J. Respiratory function in the muscular dystrophies. Muscle Nerve. 1981; 4:155–164. PMID: 7207506.
Article7. Hahn A, Bach JR, Delaubier A, Renardel-Irani A, Guillou C, Rideau Y. Clinical implications of maximal respiratory pressure determinations for individuals with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1997; 78:1–6. PMID: 9014949.
Article8. Morris JF, Koski A, Johnson LC. Spirometric standards for healthy nonsmoking adults. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971; 103:57–67. PMID: 5540840.
Article9. Polgar G, Promadhat V. Pulmonary function testing in children: techniques and standards. Philadelphia: Saunders;1971.10. Wilson SH, Cooke NT, Edwards RH, Spiro SG. Predicted normal values for maximal respiratory pressures in Caucasian adults and children. Thorax. 1984; 39:535–538. PMID: 6463933.
Article11. Phillips MF, Quinlivan RC, Edwards RH, Calverley PM. Changes in spirometry over time as a prognostic marker in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 164:2191–2194. PMID: 11751186.
Article12. Pearce JM, Pennington RJ, Walton JN. Serum enzyme studies in muscle disease. II: Serum creatine kinase activity in muscular dystrophy and in other myopathic and neuropathic disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1964; 27:96–99. PMID: 14167093.13. Haas M, Vlcek V, Balabanov P, Salmonson T, Bakchine S, Markey G, et al. European Medicines Agency review of ataluren for the treatment of ambulant patients aged 5 years and older with Duchenne muscular dystrophy resulting from a nonsense mutation in the dystrophin gene. Neuromuscul Disord. 2015; 25:5–13. PMID: 25497400.
Article14. Finkel RS, Flanigan KM, Wong B, Bonnemann C, Sampson J, Sweeney HL, et al. Phase 2a study of ataluren-mediated dystrophin production in patients with nonsense mutation Duchenne muscular dystrophy. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e81302. PMID: 24349052.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Duchenne Type Muscular Dystrophy: Report of 8 Cases
- A clinical study on Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- A Paucisymptomatic HyperCKemia Patient Diagnosed with Manifesting Female Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Carrier
- Clinical Implications of Pulmonary Function Test and Maximum Static Pressure in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- Pathologically and Genetically Diagnosed Subclinical Symptomatic Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Carrier: Broadened Spectrum of Clinical Phenotype