Anesth Pain Med.
2017 Jul;12(3):213-219. 10.17085/apm.2017.12.3.213.
Comparing the effects of vecuronium and cisatracurium on electrophysiologic monitoring during neurosurgery: a randomized controlled study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jjeong.lee@samsung.com
- KMID: 2388834
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2017.12.3.213
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
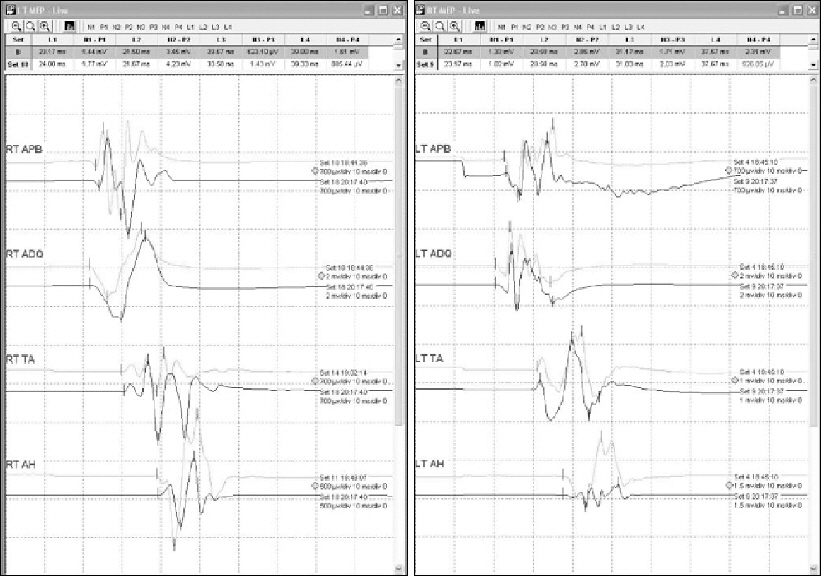
The differences between neuromuscular blocking (NMB) drugs on the efficacy of intraoperative motor-evoked potential (MEP) monitoring have not been established through clinical study. We compared the effects of vecuronium and cisatracurium on the efficacy of intraoperative MEP monitoring.
METHODS
We enrolled 72 patients who had undergone neurosurgery with MEP monitoring. We randomly allocated the subjects into one of two groups, in whom we maintained continuous intravenous vecuronium (Group V) or cisatracurium (Group C) infusion during the surgeries; the target partial NMB for maintenance was T1/Tc 50% (T1, first twitch of TOF response; Tc, control response of T1 before NMB drug injection). We compared the means and coefficients of variation (CV, %) of all measured MEP amplitudes and the frequencies of NMB drug dose changes.
RESULTS
The means and CVs of MEP amplitude and latency in all four limbs did not differ significantly between the groups, although we did change the continuous NMB drug doses in group V significantly less often than in group C.
CONCLUSIONS
There were no significant differences between vecuronium and cisatracurium on the MEP variability and mean amplitudes. However, cisatracurium needed more frequent dose changes to maintain T1/Tc 50%.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mendiratta A, Emerson RG. Neurophysiologic intraoperative monitoring of scoliosis surgery. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2009; 26:62–9. DOI: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e31819f9049. PMID: 19279500.2. Sloan TB, Heyer EJ. Anesthesia for intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring of the spinal cord. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2002; 19:430–43. DOI: 10.1097/00004691-200210000-00006.3. Minahan RE, Riley LH 3rd, Lukaczyk T, Cohen DB, Kostuik JP. The effect of neuromuscular blockade on pedicle screw stimulation thresholds. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:2526–30. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-200010010-00016.4. Blair EA, Teeple E Jr, Sutherland RM, Shih T, Chen D. Effect of neuromuscular blockade on facial nerve monitoring. Am J Otol. 1994; 15:161–7. PMID: 8172295.5. Cai YR, Xu J, Chen LH, Chi FL. Electromyographic monitoring of facial nerve under different levels of neuromuscular blockade during middle ear microsurgery. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009; 122:311–4.6. Lang EW, Beutler AS, Chesnut RM, Patel PM, Kennelly NA, Kalkman CJ, et al. Myogenic motor-evoked potential monitoring using partial neuromuscular blockade in surgery of the spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21:1676–86. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-199607150-00013.7. Sloan TB. Muscle relaxant use during intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring. J Clin Monit Comput. 2013; 27:35–46. DOI: 10.1007/s10877-013-9490-1. PMID: 23015366.8. Burmester M, Mok Q. Randomised controlled trial comparing cisatracurium and vecuronium infusions in a paediatric intensive care unit. Intensive Care Med. 2005; 31:686–92. DOI: 10.1007/s00134-005-2615-3. PMID: 15815895.9. Pühringer FK, Heier T, Dodgson M, Erkola O, Goonetilleke P, Hofmockel R, et al. Double-blind comparison of the variability in spontaneous recovery of cisatracurium- and vecuronium-induced neuromuscular block in adult and elderly patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2002; 46:364–71. DOI: 10.1034/j.1399-6576.2002.460406.x. PMID: 11952434.10. Sparr HJ, Beaufort TM, Fuchs-Buder T. Newer neuromuscular blocking agents: how do they compare with established agents? Drugs. 2001; 61:919–42. DOI: 10.2165/00003495-200161070-00003. PMID: 11434449.11. van Dongen EP, ter Beek HT, Schepens MA, Morshuis WJ, Langemeijer HJ, de Boer A, et al. Within-patient variability of myogenic motor-evoked potentials to multipulse transcranial electrical stimulation during two levels of partial neuromuscular blockade in aortic surgery. Anesth Analg. 1999; 88:22–7. DOI: 10.1213/00000539-199901000-00005. PMID: 9895060.12. Kim WH, Lee JJ, Lee SM, Park MN, Park SK, Seo DW, et al. Comparison of motor-evoked potentials monitoring in response to transcranial electrical stimulation in subjects undergoing neurosurgery with partial vs no neuromuscular block. Br J Anaesth. 2013; 110:567–76. DOI: 10.1093/bja/aes395. PMID: 23378247.13. Melloni C, Devivo P, Launo C, Mastronardi P, Novelli GP, Romano E. Cisatracurium versus vecuronium: a comparative, double blind, randomized, multicenter study in adult patients under propofol/fentanyl/N2O anesthesia. Minerva Anestesiol. 2006; 72:299–308. PMID: 16675938.14. Prielipp RC, Coursin DB, Scuderi PE, Bowton DL, Ford SR, Cardenas VJ Jr, et al. Comparison of the infusion requirements and recovery profiles of vecuronium and cisatracurium 51W89 in intensive care unit patients. Anesth Analg. 1995; 81:3–12. DOI: 10.1213/00000539-199507000-00002. PMID: 7598277.15. Belmont MR, Lien CA, Quessy S, Abou-Donia MM, Abalos A, Eppich L, et al. The clinical neuromuscular pharmacology of 51W89 in patients receiving nitrous oxide/opioid/barbiturate anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1995; 82:1139–45. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-199505000-00008. PMID: 7741288.16. Shanks CA. Pharmacokinetics of the nondepolarizing neuromuscular relaxants applied to calculation of bolus and infusion dosage regimens. Anesthesiology. 1986; 64:72–86. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-198601000-00011. PMID: 2935053.17. Magorian T, Flannery KB, Miller RD. Comparison of rocuronium, succinylcholine, and vecuronium for rapid-sequence induction of anesthesia in adult patients. Anesthesiology. 1993; 79:913–8. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-199311000-00007. PMID: 7902034.18. Motamed C, Kirov K, Combes X, Duvaldestin P. Comparison between the Datex-Ohmeda M-NMT module and a force-displacement transducer for monitoring neuromuscular blockade. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2003; 20:467–9. DOI: 10.1097/00003643-200306000-00007. PMID: 12803264.19. Dahaba AA, von Klobucar F, Rehak PH, List WF. The neuromuscular transmission module versus the relaxometer mechanomyograph for neuromuscular block monitoring. Anesth Analg. 2002; 94:591–6. DOI: 10.1097/00000539-200203000-00021. PMID: 11867381.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A comparison of the clinical duration and recovery characteristics of cisatracurium after priming using rocuronium or cisatracurium: preliminary study
- The dose effect of ephedrine on the onset time and intubating conditions after cisatracurium administration
- Streptozotocin Diabetes Attenuates the Effects of Nondepolarizing Neuromuscular Relaxants on Rat Muscles
- Bradycardia following Administration of Vecuronium in a Parturient Undergoing Cesarean Section
- Comparison of Maximum Inspiratory Pressure and Train of Four Ratio at Neuromuscular Recovery of Vecuronium after Neuroleptanesthesia