J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci.
2017 Jun;33(2):80-87. 10.14368/jdras.2017.33.2.80.
Physical properties of a new resin-based root canal sealer in comparison with AH Plus Jet
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Republic of Korea. drbozon@gwnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2388013
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14368/jdras.2017.33.2.80
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to assess the physical properties of a novel resin-based endodontic sealer, Any-Seal, in comparison with AH Plus Jet.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
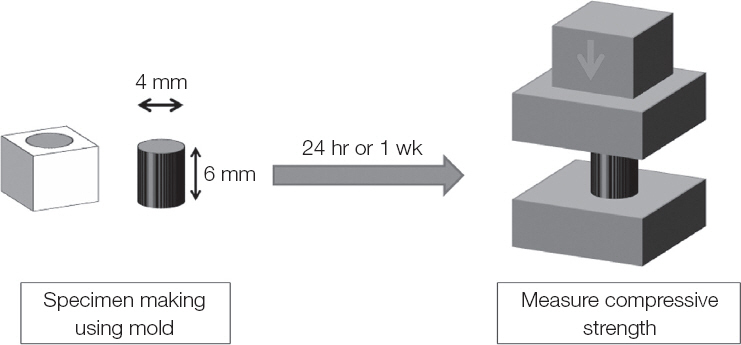
Flow, radiopacity and compressive strength were examined according to ISO 6876/2001. For flow test, 0.05 mL of sealer was placed between glass plate and 100 g weight were applied. Ten minutes after mixing the sealers, the load was removed and the diameters of the compressed sealer discs were measured. For radiopacity, 10 mm diameter and 1 mm thickness sample were fabricated and took radiograph with an aluminum step-wedge and analyzed using imaging program. For compressive strength test, 4 mm × 6 mm cylindrical specimen was fabricated and tested after 24 hours and 1 week using Universal testing machine.
RESULTS
Both tested sealers were consistent with ISO 6876/2001 in the flow and radiopacity test. The flow values of both sealers were not significantly different (P > 0.05). AH Plus Jet had significantly higher radiopacity (P < 0.05). AH Plus Jet showed higher compressive strength at both time intervals (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSION
Any-Seal showed low compressive strength until after 1 week, so its physical and biological aspect should be evaluated more before clinical use.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ørstavik D, Eriksen HM, Beyer-Olsen EM. Adhesive properties and leakage of root canal sealers in vitro. Int Endod J. 1983; 16:59–63. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.1983.tb01297.x.2. Branstetter J, von Fraunhofer JA. The physical properties and sealing action of endodontic sealer cements:a review of the literature. J Endod. 1982; 8:312–6. DOI: 10.1016/S0099-2399(82)80280-X.3. Grossman LI. Endodontic practice. 12th ed. New Delhi: Wolters Kluwer Publishers;2010. p. 301.4. Ørstavik D. Physical properties of root canal sealers:measurement of flow, working time, and compressive strength. Int Endod J. 1983; 16:99–107. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.1983.tb01307.x.5. Marín-Bauza GA, Silva-Sousa YT, da Cunha SA, Rached-Junior FJ, Bonetti-Filho I, Sousa-Neto MD, Miranda CE. Physicochemical properties of endodontic sealers of different bases. J Appl Oral Sci. 2012; 20:455–61. DOI: 10.1590/S1678-77572012000400011.6. Schroeder A. The impermeability of root canal filling material and first demonstrations of new root filling materials. SSO Schweiz Monatsschr Zahnheilkd. 1954; 64:921–31.7. De-Deus G, Scelza MZ, Neelakantan P, Sharma S, Neves Ade A, Silva EJ. Three-dimensional quantitative porosity characterization of syringe-versus hand-mixed set epoxy resin root canal sealer. Braz Dent J. 2015; 26:607–11. DOI: 10.1590/0103-6440201300074. PMID: 26963204.8. Cotti E, Petreucic V, Re D, Simbula G. Cytotoxicity evaluation of a new resin-based hybrid root canal sealer:an in vitro study. J Endod. 2014; 40:124–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.09.038. PMID: 24332003.9. You SY, Bae KS, Baek SH, Kum KY, Shon WJ, Lee W. Lifespan of one nickel-titanium rotary file with reciprocating motion in curved root canals. J Endod. 2010; 36:1991–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2010.08.040. PMID: 21092819.10. Ørstavik D. Materials used for root canal obturation:technical, biological and clinical testing. Endod Topics. 2005; 12:25–38. DOI: 10.1111/j.1601-1546.2005.00197.x.11. Zhou HM, Shen Y, Zheng W, Li L, Zheng YF, Haapasalo M. Physical properties of 5 root canal sealers. J Endod. 2013; 39:1281–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.06.012. PMID: 24041392.12. Collares FM, Klein M, Santos PD, Portella FF, Ogliari F, Leitune VC, Samuel SM. Influence of radiopaque fillers on physicochemical properties of a model epoxy resin-based root canal sealer. J Appl Oral Sci. 2013; 21:533–9. DOI: 10.1590/1679-775720130334. PMID: 24473719. PMCID: PMC3891277.13. Ruiz-Linares M, Bailón-Sánchez ME, Baca P, Valderrama M, Ferrer-Luque CM. Physical properties of AH Plus with chlorhexidine and cetrimide. J Endod. 2013; 39:1611–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.08.002. PMID: 24238458.14. Weisman MI. A study of the flow rate of ten root canal sealers. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1970; 29:255–61. DOI: 10.1016/0030-4220(70)90094-0.15. Watts D, Combe EC, Greener EH. The rheological properties of polyelectrolyte cements II. Glass ionomers. J Oral Rehabil. 1981; 8:61–7. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.1981.tb00476.x. PMID: 6935395.16. Vermilyea SG, de Simon LB, Huget EF. The rheologic properties of endodontic sealers. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1978; 46:711–6. DOI: 10.1016/0030-4220(78)90468-1.17. Uhrich JM, Moser JB, Heuer MA. The rheology of selected root canal sealer cements. J Endod. 1978; 4:373–9. DOI: 10.1016/S0099-2399(78)80212-X.18. Lacey S, Pitt Ford TR, Watson TF, Sherriff M. A study of the rheological properties of endodontic sealers. Int Endod J. 2005; 38:499–504. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2005.00953.x. PMID: 16011766.19. Ørstavik D. Endodontic materials. Adv Dent Res. 1988; 2:12–24. DOI: 10.1177/08959374880020010301.20. Sonntag D, Ritter A, Burkhart A, Fischer J, Mondrzyk A, Ritter H. Experimental amine-epoxide sealer:a physicochemical study in comparison with AH Plus and EasySeal. Int Endod J. 2015; 48:74756. DOI: 10.1111/iej.12372. PMID: 25117941.21. Beyer-Olsen EM, Ørstavik D. Radiopacity of root canal sealers. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1981; 51:320–8. DOI: 10.1016/0030-4220(81)90062-1.22. Bowen RL, Cleek GW. X-ray-opaque reinforcing fillers for composite materials. J Dent Res. 1969; 48:79–82. DOI: 10.1177/00220345690480013101. PMID: 5252105.23. Bortoluzzi EA, Guerreiro-Tanomaru JM, TanomaruFilho M, Duarte MA. Radiographic effect of different radiopacifiers on a potential retrograde filling material. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009; 108:628–32. DOI: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.04.044. PMID: 19699115.24. Vivan RR, Ordinola-Zapata R, Bramante CM, Bernardineli N, Garcia RB, Hungaro Duarte MA, de Moraes IG. Evaluation of the radiopacity of some commercial and experimental root-end filling materials. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009; 108:e35–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.07.037. PMID: 19913718.25. Marin-Bauza GA, Rached-Junior FJ, Souza-Gabriel AE, Sousa-Neto MD, Miranda CE, Silva-Sousa YT. Physicochemical properties of methacrylate resinbased root canal sealers. J Endod. 2010; 36:1531–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2010.05.002. PMID: 20728722.26. Cañadas PS, Berástegui E, Gaton-Hernández P, Silva LA, Leite GA, Silva RS. Physicochemical properties and interfacial adaptation of root canal sealers. Braz Dent J. 2014; 25:435–41. DOI: 10.1590/0103-6440201300037.27. Belli S, Ozcan E, Derinbay O, Eldeniz AU. A comparative evaluation of sealing ability of a new, self-etching, dual-curable sealer:hybrid root SEAL (MetaSEAL). Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008; 106:e45–e52. DOI: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.07.027. PMID: 18801670.28. Borges RP, Sousa-Neto MD, Versiani MA, RachedJúnior FA, De-Deus G, Miranda CE, Pécora JD. Changes in the surface of four calcium silicatecontaining endodontic materials and an epoxy resin-based sealer after a solubility test. Int Endod J. 2012; 45:419–28. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01992.x. PMID: 22150403.29. Viapiana R, Flumignan DL, Guerreiro-Tanomaru JM, Camilleri J, Tanomaru-Filho M. Physicochemical and mechanical properties of zirconium oxide and niobium oxide modified Portland cementbased experimental endodontic sealers. Int Endod J. 2014; 47:437–48. DOI: 10.1111/iej.12167. PMID: 24033490 .
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The influence of AH-26 and zinc oxide-eugenol root canal sealer on the shear bond strength of composite resin to dentin
- Calcium silicate-based root canal sealers: a literature review
- Cytotoxicity of resin-based root canal sealer, adseal
- Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of newly developed calcium phosphate-based root canal sealers
- A micro-computed tomographic evaluation of root canal filling with a single gutta-percha cone and calcium silicate sealer