J Korean Soc Radiol.
2017 Aug;77(2):101-104. 10.3348/jksr.2017.77.2.101.
A Slowly Growing Mass Around a Cirrhotic Liver: Usefulness of the Hepatobiliary Phase in the Diagnosis of Ectopic Liver
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, St. Vincent's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea. bellenina@daum.net
- 2Department of Hospital Pathology, St. Vincent's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2386746
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2017.77.2.101
Abstract
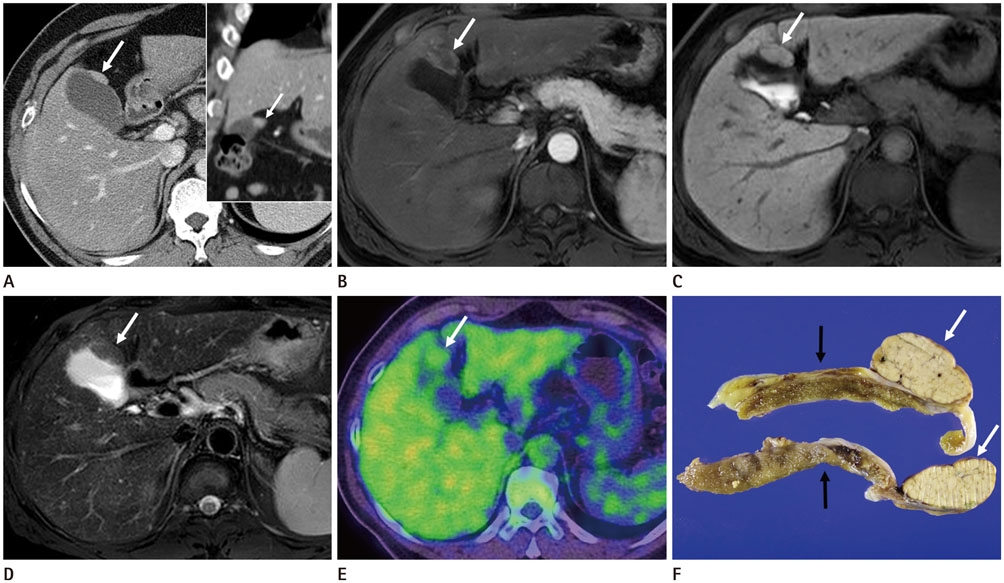
- An ectopic liver is a rare congenital abnormality that is difficult to detect before surgery due to its small size. A 53-year-old man had liver cirrhosis and received regular surveillance. An ovoid mass on the surface of the gallbladder separated from the liver proper was found on computed tomography (CT). The mass had grown slowly over five years of surveillance. Upon further evaluation, the mass exhibited iso-signal intensity compared to liver on T2-weighted images, precontrast T1-weighted images, and the hepatobiliary phase of gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Surgical resection was performed, and the mass was diagnosed as an ectopic liver with normal liver parenchyma without cirrhotic changes. This case demonstrates that ectopic liver with normal liver tissue can develop in a patient with liver cirrhosis and can grow in the absence of a tumor. MRI with gadoxetic acid is useful to identify this condition correctly.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Martinez CA, de Resende HC Jr, Rodrigues MR, Sato DT, Brunialti CV, Palma RT. Gallbladder-associated ectopic liver: a rare finding during a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2013; 4:312–315.2. Arslan Y, Altintoprak F, Serin KR, Kivilcim T, Yalkin O, Ozkan OV, et al. Rare entity: ectopic liver tissue in the wall of the gallbladder-a case report. World J Clin Cases. 2014; 2:924–926.3. Beltran MA, Barria C, Pujado B, Barrera R, Mendez P, Pozo C. Hepatic heterototopic tissue on the gallbladder wall: an incidental finding with pathological potential. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2007; 16:347–349.4. Hamdani SD, Baron RL. Ectopic liver simulating a mass in the gallbladder wall: imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994; 162:647–648.5. Arakawa M, Kimura Y, Sakata K, Kubo Y, Fukushima T, Okuda K. Propensity of ectopic liver to hepatocarcinogenesis: case reports and a review of the literature. Hepatology. 1999; 29:57–61.6. Bal A, Yilmaz S, Yavas BD, Ozdemir C, Ozsoy M, Akici M, et al. A rare condition: ectopic liver tissue with its unique blood supply encountered during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015; 9:47–50.7. Choi JY, Lee JM, Sirlin CB. CT and MR imaging diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: part I. Development, growth, and spread: key pathologic and imaging aspects. Radiology. 2014; 272:635–654.8. Van Beers BE, Pastor CM, Hussain HK. Primovist, eovist: what to expect? J Hepatol. 2012; 57:421–429.9. Choi JY, Lee JM, Sirlin CB. CT and MR imaging diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: part II. Extracellular agents, hepatobiliary agents, and ancillary imaging features. Radiology. 2014; 273:30–50.10. Leone N, De Paolis P, Carrera M, Carucci P, Musso A, David E, et al. Ectopic liver and hepatocarcinogenesis: report of three cases with four years’ follow-up. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 16:731–735.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Histogram Analysis of Hepatobiliary Phase MR Imaging as a Quantitative Value for Liver Cirrhosis: Preliminary Observations
- Hepatic Enhancement on Gd-BOPTA-enhanced MR Imaging: Comparison between Cirrhotic and Normal Livers
- Experiment of Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury of the Cirrhotic Liver in the Murine Mouse Model
- Postprandial Hepatic Volume Change: Spiral CT Evaluation in Case of Liver Cirrhosis
- Hepatic Cavernous Hemangioma in Cirrhotic Liver: Imaging Findings