Yonsei Med J.
2014 May;55(3):651-659. 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.3.651.
Histogram Analysis of Hepatobiliary Phase MR Imaging as a Quantitative Value for Liver Cirrhosis: Preliminary Observations
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Research Institute of Radiological Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. gafield@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Radiology, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, San Diego, CA, USA.
- KMID: 2068674
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.3.651
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate whether histogram analysis of the hepatobiliary phase on gadoxetate enhanced-MRI could be used as a quantitative index for determination of liver cirrhosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
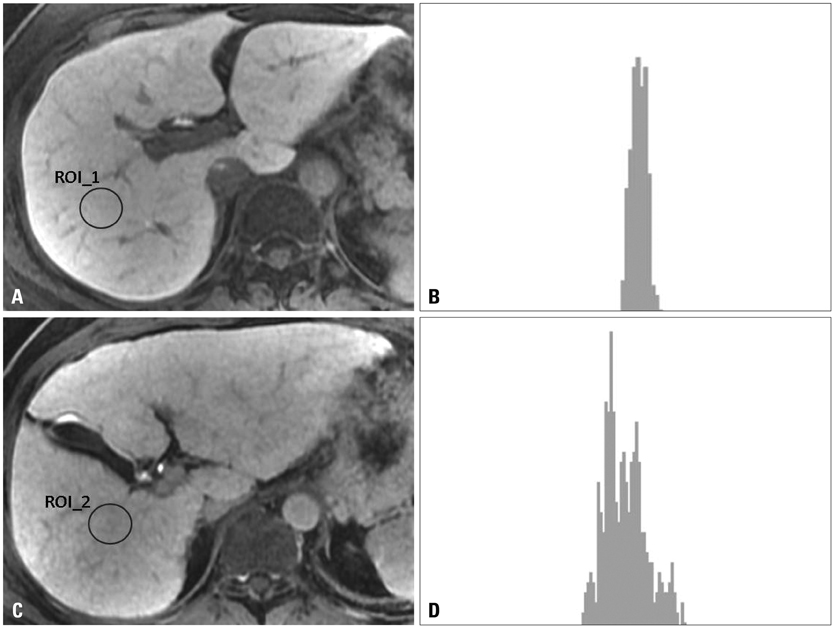
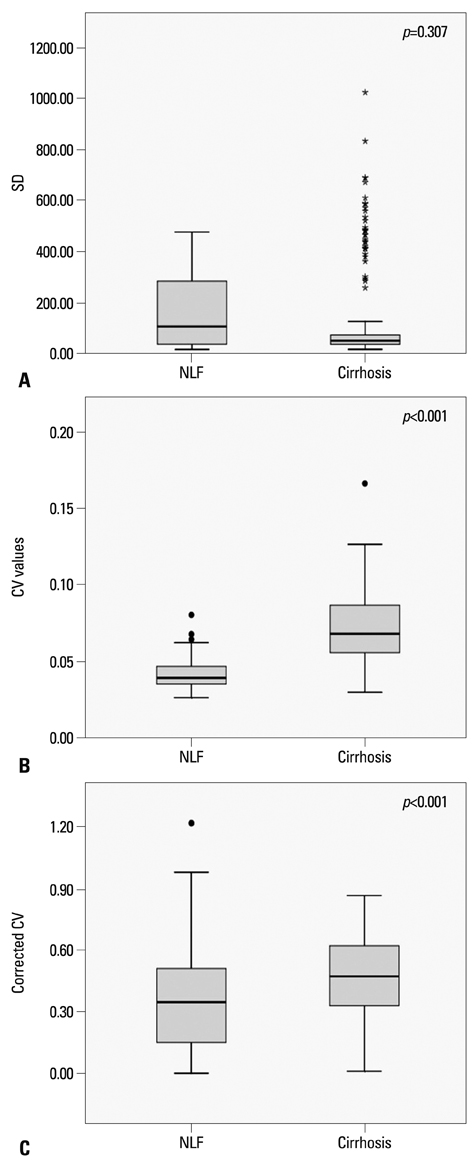
A total of 63 patients [26 in a normal liver function (NLF) group and 37 in a cirrhotic group] underwent gadoxetate-enhanced MRI, and hepatobiliary phase images were obtained at 20 minutes after contrast injection. The signal intensity of the hepatic parenchyma was measured at four different regions of interest (ROI) of the liver, avoiding vessels and bile ducts. Standard deviation (SD), coefficient of variation (CV), and corrected CV were calculated on the histograms at the ROIs. The distributions of CVs calculated from the ROI histogram were examined and statistical analysis was carried out.
RESULTS
The CV value was 0.041+/-0.009 (mean CV+/-SD) in the NLF group, while that of cirrhotic group was 0.071+/-0.020. There were statistically significant differences in the CVs and corrected CV values between the NLF and cirrhotic groups (p<0.001). The most accurate cut-off value among CVs for distinguishing normal from cirrhotic group was 0.052 (sensitivity 83.8% and specificity 88.5%). There was no statistically significant differences in SD between NLF and cirrhotic groups (p=0.307).
CONCLUSION
The CV of histograms of the hepatobiliary phase on gadoxetate-enhanced MRI may be useful as a quantitative value for determining the presence of liver cirrhosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Histogram Analysis of Diffusion Kurtosis Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Diagnosis of Hepatic Fibrosis
Ruo-Fan Sheng, Kai-Pu Jin, Li Yang, He-Qing Wang, Hao Liu, Yuan Ji, Cai-Xia Fu, Meng-Su Zeng
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(5):916-922. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.5.916.
Reference
-
1. Afdhal NH, Nunes D. Evaluation of liver fibrosis: a concise review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004; 99:1160–1174.
Article2. Schuppan D, Afdhal NH. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet. 2008; 371:838–851.
Article3. Buti M, San Miguel R, Brosa M, Cabasés JM, Medina M, Angel Casado M, et al. Estimating the impact of hepatitis C virus therapy on future liver-related morbidity, mortality and costs related to chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2005; 42:639–645.
Article4. Talwalkar JA. Economic impact of hospitalization for end-stage liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:1562.
Article5. Tokita H, Fukui H, Tanaka A, Kamitsukasa H, Yagura M, Harada H, et al. Risk factors for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with chronic hepatitis C who achieved a sustained virological response to interferon therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 20:752–758.
Article6. Froehlich F, Lamy O, Fried M, Gonvers JJ. Practice and complications of liver biopsy. Results of a nationwide survey in Switzerland. Dig Dis Sci. 1993; 38:1480–1484.7. Perrault J, McGill DB, Ott BJ, Taylor WF. Liver biopsy: complications in 1000 inpatients and outpatients. Gastroenterology. 1978; 74:103–106.
Article8. Terjung B, Lemnitzer I, Dumoulin FL, Effenberger W, Brackmann HH, Sauerbruch T, et al. Bleeding complications after percutaneous liver biopsy. An analysis of risk factors. Digestion. 2003; 67:138–145.
Article9. Ito K, Mitchell DG. Imaging diagnosis of cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis. Intervirology. 2004; 47:134–143.
Article10. Schwenzer NF, Springer F, Schraml C, Stefan N, Machann J, Schick F. Non-invasive assessment and quantification of liver steatosis by ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance. J Hepatol. 2009; 51:433–445.
Article11. Vitellas KM, Tzalonikou MT, Bennett WF, Vaswani KK, Bova JG. Cirrhosis: spectrum of findings on unenhanced and dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging. Abdom Imaging. 2001; 26:601–615.
Article12. Hammerstingl R, Zangos S, Schwarz W, Rosen T, Bechstein WO, Balzer T, et al. Contrast-enhanced MRI of focal liver tumors using a hepatobiliary MR contrast agent: detection and differential diagnosis using Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced versus Gd-DTPA-enhanced MRI in the same patient. Acad Radiol. 2002; 9:Suppl 1. S119–S120.13. Talwalkar JA, Yin M, Fidler JL, Sanderson SO, Kamath PS, Ehman RL. Magnetic resonance imaging of hepatic fibrosis: emerging clinical applications. Hepatology. 2008; 47:332–342.
Article14. Bluemke DA, Sahani D, Amendola M, Balzer T, Breuer J, Brown JJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of MR imaging with liver-specific contrast agent: U.S. multicenter phase III study. Radiology. 2005; 237:89–98.
Article15. Aguirre DA, Behling CA, Alpert E, Hassanein TI, Sirlin CB. Liver fibrosis: noninvasive diagnosis with double contrast material-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 2006; 239:425–437.
Article16. Lucidarme O, Baleston F, Cadi M, Bellin MF, Charlotte F, Ratziu V, et al. Non-invasive detection of liver fibrosis: is superparamagnetic iron oxide particle-enhanced MR imaging a contributive technique? Eur Radiol. 2003; 13:467–474.
Article17. Hamm B, Staks T, Mühler A, Bollow M, Taupitz M, Frenzel T, et al. Phase I clinical evaluation of Gd-EOB-DTPA as a hepatobiliary MR contrast agent: safety, pharmacokinetics, and MR imaging. Radiology. 1995; 195:785–792.
Article18. Reimer P, Rummeny EJ, Shamsi K, Balzer T, Daldrup HE, Tombach B, et al. Phase II clinical evaluation of Gd-EOB-DTPA: dose, safety aspects, and pulse sequence. Radiology. 1996; 199:177–183.
Article19. Ni Y, Marchal G, Lukito G, Yu J, Mühler A, Baert AL. MR imaging evaluation of liver enhancement by Gd-EOB-DTPA in selective and total bile duct obstruction in rats: correlation with serologic, microcholangiographic, and histologic findings. Radiology. 1994; 190:753–758.
Article20. Tsuda N, Okada M, Murakami T. New proposal for the staging of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: evaluation of liver fibrosis on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI. Eur J Radiol. 2010; 73:137–142.
Article21. Watanabe H, Kanematsu M, Goshima S, Kondo H, Onozuka M, Moriyama N, et al. Staging hepatic fibrosis: comparison of gadoxetate disodium-enhanced and diffusion-weighted MR imaging--preliminary observations. Radiology. 2011; 259:142–150.
Article22. Sãftoiu A, Gheonea DI, Ciurea T. Hue histogram analysis of real-time elastography images for noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 189:W232–W233.23. Maeda K, Utsu M, Kihaile PE. Quantification of sonographic echogenicity with grey-level histogram width: a clinical tissue characterization. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1998; 24:225–234.
Article24. Aubé C, Oberti F, Korali N, Namour MA, Loisel D, Tanguy JY, et al. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1999; 30:472–478.
Article25. Brancatelli G, Federle MP, Ambrosini R, Lagalla R, Carriero A, Midiri M, et al. Cirrhosis: CT and MR imaging evaluation. Eur J Radiol. 2007; 61:57–69.26. Ito K, Mitchell DG, Siegelman ES. Cirrhosis: MR imaging features. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2002; 10:75–92.27. Yin M, Talwalkar JA, Glaser KJ, Manduca A, Grimm RC, Rossman PJ, et al. Assessment of hepatic fibrosis with magnetic resonance elastography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 5:1207–1213.
Article28. Asbach P, Klatt D, Hamhaber U, Braun J, Somasundaram R, Hamm B, et al. Assessment of liver viscoelasticity using multifrequency MR elastography. Magn Reson Med. 2008; 60:373–379.
Article29. Huwart L, Sempoux C, Salameh N, Jamart J, Annet L, Sinkus R, et al. Liver fibrosis: noninvasive assessment with MR elastography versus aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index. Radiology. 2007; 245:458–466.
Article30. Annet L, Peeters F, Abarca-Quinones J, Leclercq I, Moulin P, Van Beers BE. Assessment of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in liver fibrosis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007; 25:122–128.
Article31. Faria SC, Ganesan K, Mwangi I, Shiehmorteza M, Viamonte B, Mazhar S, et al. MR imaging of liver fibrosis: current state of the art. Radiographics. 2009; 29:1615–1635.
Article32. Jirák D, Dezortová M, Taimr P, Hájek M. Texture analysis of human liver. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2002; 15:68–74.
Article33. Kato H, Kanematsu M, Zhang X, Saio M, Kondo H, Goshima S, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis: preliminary evaluation of MRI texture analysis using the finite difference method and an artificial neural network. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 189:117–122.
Article34. Kitao A, Matsui O, Yoneda N, Kozaka K, Shinmura R, Koda W, et al. The uptake transporter OATP8 expression decreases during multistep hepatocarcinogenesis: correlation with gadoxetic acid enhanced MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2011; 21:2056–2066.
Article35. Tsuboyama T, Onishi H, Kim T, Akita H, Hori M, Tatsumi M, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: hepatocyte-selective enhancement at gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging--correlation with expression of sinusoidal and canalicular transporters and bile accumulation. Radiology. 2010; 255:824–833.
Article36. Nassif A, Jia J, Keiser M, Oswald S, Modess C, Nagel S, et al. Visualization of hepatic uptake transporter function in healthy subjects by using gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 2012; 264:741–750.
Article37. Bashir MR, Husarik DB, Ziemlewicz TJ, Gupta RT, Boll DT, Merkle EM. Liver MRI in the hepatocyte phase with gadolinium-EOB-DTPA: does increasing the flip angle improve conspicuity and detection rate of hypointense lesions? J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012; 35:611–616.
Article38. Stelter L, Grieser C, Fernándes CM, Rothe JH, Streitparth F, Seehofer D, et al. Flip angle modulations in late phase Gd-EOB-DTPA MRI improve the identification of the biliary system. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:e991–e995.
Article39. Bashir MR, Merkle EM. Improved liver lesion conspicuity by increasing the flip angle during hepatocyte phase MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2011; 21:291–294.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum to "Histogram Analysis of Hepatobiliary Phase MR Imaging as a Quantitative Value for Liver Cirrhosis: Preliminary Observations" by Choi JY, et al. (Yonsei Med J 2014;55:651-9.)
- The Proper Scan Delay of the Hepatobiliary Phase of Gadoxetic Acid-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Evaluate Small-Sized (< or = 3 cm) Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Liver
- Focal Hepatic Nodules with High Signal Intensity on T1-weighted MR Imaging: Differentiation of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma from Dysplastic Nodule by Quantitative Analysis of Multi-phase Contrast-enhanced DynamicMR Imaging
- Usefulness of Gadobenate Dimeglumine - Enhanced Hepatobiliary Phase MR Imaging on Predicting Histological Grade of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- A Slowly Growing Mass Around a Cirrhotic Liver: Usefulness of the Hepatobiliary Phase in the Diagnosis of Ectopic Liver