J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Sep;32(9):1548-1551. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.9.1548.
Autotransplantation of the Heart for Recurrent Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Korea. cs99kjw@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Gyeongsang National University Jinju Hospital, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Gyeongsang National University Jinju Hospital, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 2385964
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.9.1548
Abstract
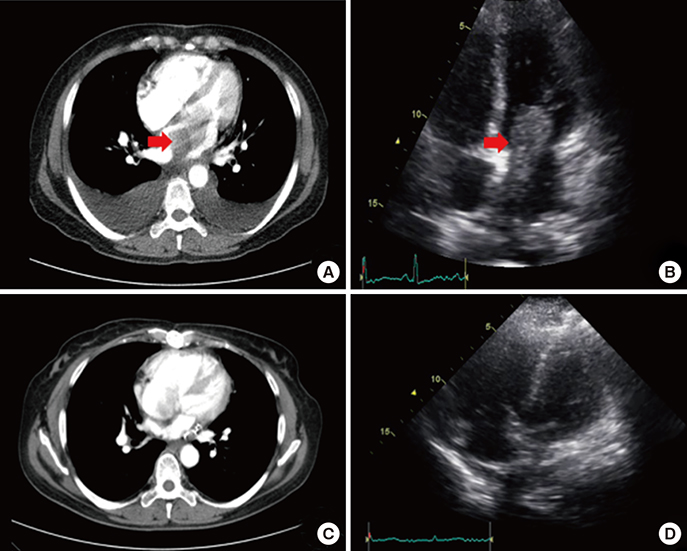
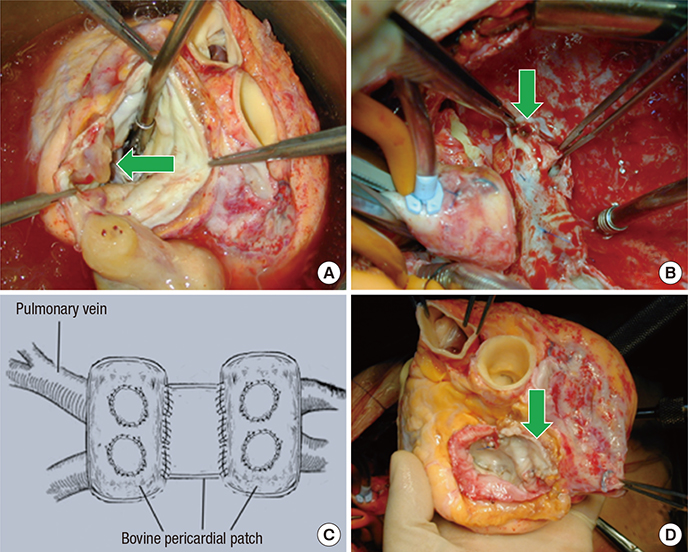
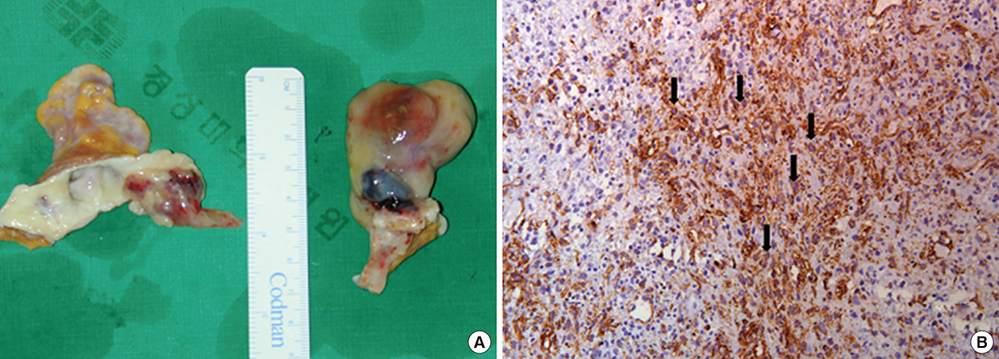
- We report a rare case of dyspnea caused by a cardiac tumor in a 53-year-old woman. The patient had undergone a cardiac tumor (inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, 6.2 × 4.2 × 3.3 cm) resection at our institute 13 months earlier. We performed preoperative evaluations which revealed a cardiac tumor originating from the posterior wall of the left atrium. Cardiac autotransplantation surgery (cardiac explantation, ex vivo tumor resection, cardiac reconstruction, and cardiac reimplantation) was successfully performed for the complete resection of the recurrent tumor without major postoperative complications. The patient showed good physical conditions for 21 months after the surgery. Cardiac autotransplantation is a safe and feasible technique for the complete resection of complex left atrial tumors.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Reardon MJ, Walkes JC, Defelice CA, Wojciechowski Z. Cardiac autotransplantation for surgical resection of a primary malignant left ventricular tumor. Tex Heart Inst J. 2006; 33:495–497.2. Conklin LD, Reardon MJ. Autotransplantation of the heart for primary cardiac malignancy: development and surgical technique. Tex Heart Inst J. 2002; 29:105–108.3. Gowdamarajan A, Michler RE. Therapy for primary cardiac tumors: is there a role for heart transplantation? Curr Opin Cardiol. 2000; 15:121–125.4. Cooley DA, Reardon MJ, Frazier OH, Angelini P. Human cardiac explantation and autotransplantation: application in a patient with a large cardiac pheochromocytoma. Tex Heart Inst J. 1985; 12:171–176.5. Ramlawi B, Al-Jabbari O, Blau LN, Davies MG, Bruckner BA, Blackmon SH, Ravi V, Benjamin R, Rodriguez L, Shapira OM, et al. Autotransplantation for the resection of complex left heart tumors. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014; 98:863–868.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of Nasal Septum after Septoplasty: A Case Report
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of Kidney
- Adult Intussusception Caused by Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Jejunum
- A Case of Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Maxillary Sinus
- Postoperative Recurrent Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Retroperitoneum: Case Report