J Neurocrit Care.
2017 Jun;10(1):49-52. 10.18700/jnc.160092.
Status Epilepticus after Catheter Drainage of Basal Ganglia Hemorrhage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. myoungsim@naver.com
- 2Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2385888
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18700/jnc.160092
Abstract
- No abstract available.
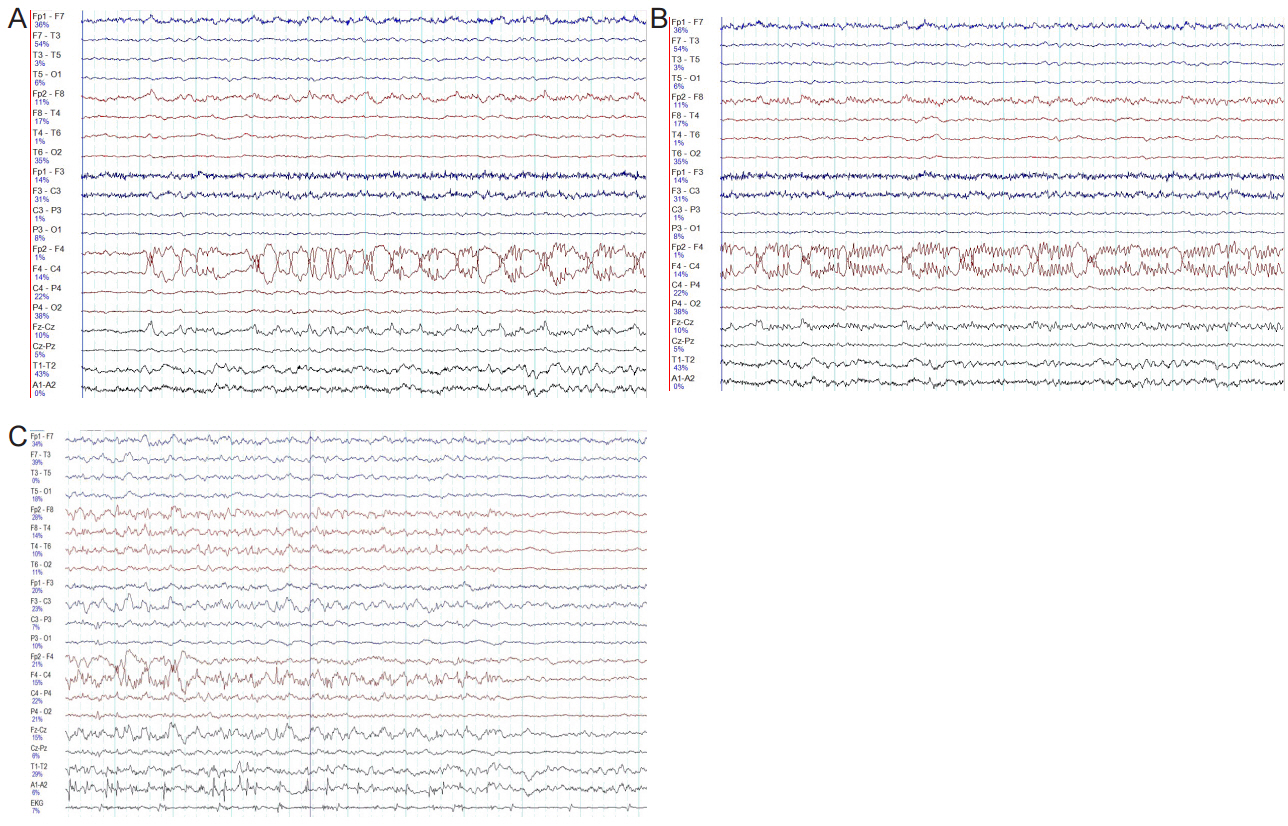
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bladin CF, Alexandrov AV, Bellavance A, Bornstein N, Chambers B, Coté R, et al. Seizures after stroke: a prospective multicenter study. Arch Neurol. 2000; 57:1617–22.2. Neshige S, Kuriyama M, Yoshimoto T, Takeshima S, Himeno T, Takamatsu K, et al. Seizures after intracerebral hemorrhage; risk factor, recurrence, efficacy of antiepileptic drug. J Neurol Sci. 2015; 359:318–22.
Article3. Chen X, Chen W, Ma A, Wu X, Zheng J, Yu X, et al. Frameless stereotactic aspiration and subsequent fibrinolytic therapy for the treatment of spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage. Br J Neurogurg. 2011; 25:369–75.
Article4. Vespa P, McArthur D, Miller C, O’Phelan K, Frazee J, Kidwell C, et al. Frameless stereotactic aspiration and thrombolysis of deep intracerebral hemorrhage is associated with reduction of hemorrhage volume and neurological improvement. Neurocrit Care. 2005; 2:274–81.
Article5. De Herdt V, Dumont F, Henon H, Derambure P, Vonck K, Leys D, et al. Early seizures in intracerebral hemorrhage: incidence, associated factors, and outcome. Neurology. 2011; 77:1794–800.
Article6. Ferlazzo E, Gasparini S, Beghi E, Sueri C, Russo E. Epilepsy in cerebrovascular diseases: review of experimental and clinical data with meta-analysis of risk factors. Epilepsia. 2016; 57:1205–14.
Article7. Woo KM, Yang SY, Cho KT. Seizures after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012; 52:312–9.
Article8. Zhang C, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhang JG, Hu W, Ge M, et al. Risk factors for post-stroke seizures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsy res. 2014; 108:1806–16.
Article9. Fiorella D, Arthur A, Bain M, Mocco J. Minimally invasive surgery for intracerebral and intraventricular hemorrhage: rationale, review of existing data and emerging technologies. Stroke. 2016; 47:1399–406.10. You NK, Ahn JY, Cho JH, Hong CK, Joo JY. Navigation-assisted aspiration and thrombolysis of deep intracerebral hemorrhage. Korean J Cerebrovasc Surg. 2007; 9:172–6.11. Kwon WK, Park DH, Park KJ, Kang SH, Lee JH, Cho TH, et al. Prognostic factors of clinical outcome after neuronavigationassisted hematoma drainage in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2014; 123:83–9.
Article12. Hanley DF, Thompson RE, Muschelli J, Rosenblum M, McBee N, Lane K, et al. Safety and efficacy of minimally invasive surgery plus alteplase in intracerebral haemorrhage evacuation (MISTIE): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016; 15:1228–37.
Article13. Fiorella D, Arthur AS, Mocco JD. 305 The INVEST Trial: a randomized, controlled trial to investigate the safety and efficacy of image-guided minimally invasive endoscopic surgery with apollo vs best medical management for supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 2016; 63 Suppl 1:187.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Traumatic Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Bilateral Basal Ganglia
- Bilateral Traumatic Hemorrhage of the Basal Ganglia
- Simultaneous Multiple Basal Ganglia and Cerebellar Hemorrhage: Case Report
- Persistent Autonomic Hyperfunction Following Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- Transsylvian-Transinsular Approach for Deep-Seated Basal Ganglia Hemorrhage: An Experience at a Single Institution