J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2013 Dec;15(4):316-319. 10.7461/jcen.2013.15.4.316.
Simultaneous Multiple Basal Ganglia and Cerebellar Hemorrhage: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Hwaseong, Korea. kosaken@lycos.co.kr
- KMID: 1810791
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2013.15.4.316
Abstract
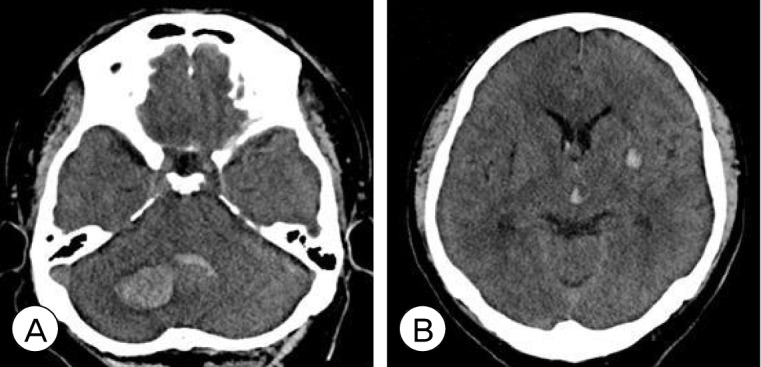
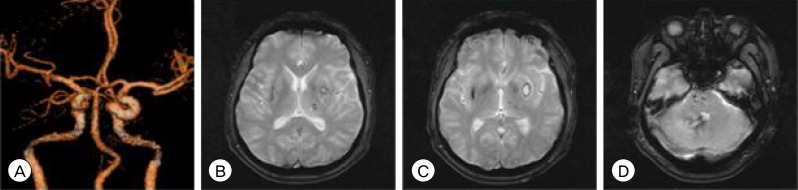
- A 35-year-old man presented with simultaneous multiple intracranial hematomas in the right cerebellar dentate nucleus and left basal ganglia. The hematomas were visible by computed tomography performed within two hours of the patient's arrival. The initial computed tomography showed acute hemorrhage in the left basal ganglia and dentate nucleus in cerebellum. The patient then experienced a change of consciousness due to newly developed hydrocephalus, and emergent extra-ventricular drainage was performed. By discharge, fortunately, the patient was fully recovered.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bae H, Jeong D, Doh J, Lee K, Yun I, Byun B. Recurrence of bleeding in patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Cerebrovasc Dis. 1999; Mar-Apr. 9(2):102–108. PMID: 9973653.
Article2. Balasubramaniam S, Nadkarni TD, Goel A. Simultaneous thalamic and cerebellar hypertensive haemorrhages. Neurol India. 2007; Apr-Jun. 55(2):183–184. PMID: 17558137.
Article3. Bamford J, Sandercock P, Dennis M, Warlow C, Jones L, McPherson K, et al. A prospective study of acute cerebrovascular disease in the community: The Oxfordshire Community Stroke Project 1981-86. 1. Methodology, demography and incident cases of first-ever stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988; 11. 51(11):1373–1380. PMID: 3266234.
Article4. Bayramoğlu M, Karatas M, Leblebici B, Cetin N, Sozay S, Turhan N. Hemorrhagic transformation in stroke patients. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2003; 1. 82(1):48–52. PMID: 12510185.
Article5. Becker C, Howard G, McLeroy KR, Yatsu FM, Toole JF, Coull B, et al. Community hospital-based stroke programs: North Carolina, Oregon, and New York. II: Description of study population. Stroke. 1986; Mar-Apr. 17(2):285–293. PMID: 3083536.
Article6. Butcher K, Laidlaw J. Current intracerebral haemorrhage management. J Clin Neurosci. 2003; 3. 10(2):158–167. PMID: 12637041.
Article7. Kabuto M, Kubota T, Kobayashi H, Nakagawa T, Arai Y, Kitai R. Simultaneous bilateral hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhages-Two case reports. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1995; 8. 35(8):584–586. PMID: 7566389.8. Kohshi K, Abe H, Tsuru E. Simultaneous hypertensive intracerebral hematomas: Two case reports. J Neurol Sci. 2000; 12. 181(1-2):137–139. PMID: 11099724.
Article9. Kojima S, Omura T, Wakamatsu W, Kishi M, Yamazaki T, Iida M, et al. Prognosis and disability of stroke patients after 5 years in Akita, Japan. Stroke. 1990; 1. 21(1):72–77. PMID: 2300993.
Article10. Lin YT, Lo YK, Kuo HC, Chang YT, Chang MH, Li JY. Stroke registry in Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 2002; 7. 65(7):307–313. PMID: 12365647.11. Mauriño J, Saposnik G, Lepera S, Rey RC, Sica RE. Multiple simultaneous intracerebral hemorrhages: Clinical features and outcome. Arch Neurol. 2001; 4. 58(4):629–632. PMID: 11295994.12. Ozdemir O, Calisaneller T, Yildirim E, Altinors N. Simultaneous supra and infratentorial hypertensive intracerebral haemorrhage. J Clin Neurosci. 2007; 8. 14(8):775–777. PMID: 17493816.
Article13. Silliman S, McGill J, Booth R. Simultaneous bilateral hypertensive putaminal hemorrhages. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2003; 1. 12(1):44–46. PMID: 17903903.
Article14. Sorimachi T, Ito Y, Morita K, Fujii Y. Microbleeds on gradient-echo T2(*)-weighted MR images from patients with multiple simultaneous intracerebral haemorrhages. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2007; 2. 149(2):171–176. discussion 176-7. PMID: 17211554.15. Takeuchi S, Takasato Y, Masaoka H, Hayakawa T, Yatsushige H, Sugawara T. Simultaneous multiple hypertensive intracranial hemorrhages. J Clin Neurosci. 2011; 9. 18(9):1215–1218. PMID: 21752649.
Article16. Tanno H, Ono J, Suda S, Karasudani H, Yamakami I, Isobe K, et al. [Simultaneous, multiple hypertensive intracerebral hematomas: Report of 5 cases and review of literature]. No shinkei Geka. 1989; 3. 17(3):223–228. Japanese. PMID: 2671770.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multiple, Simultaneous, Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhages in the Pons and Basal Ganglia: A Case Report
- Multiple Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Case Report
- A Case of Bilateral Simultaneous Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Basal Ganglia
- Bilateral Traumatic Hemorrhage of the Basal Ganglia
- Cerebellar Lesions of Uremic Encephalopathy on MRI in Hemodialyzed Diabetic Patient: A Case Report