J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2017 Jun;24(2):80-86. 10.4184/jkss.2017.24.2.80.
Survival Analysis Based on the Incidence of a New Fracture in an Adjacent Vertebra After Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea. jhkim@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2385643
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2017.24.2.80
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
To evaluate the factors affecting the incidence of new vertebral fractures and the survival rate associated with the occurrence of a new fracture in an adjacent vertebra after vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty for single-vertebral body fracture due to osteoporosis. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: It is controversial whether adjacent-vertebra fractures after vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty are due to the natural course of osteoporosis or are a complication of vertebroplasty.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From May 2002 to January 2010, among 490 cases of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for the fracture of a single vertebral body due to osteoporosis, 250 cases were analyzed retrospectively, and a survival rate analysis was performed based on the incidence of a new fracture in an adjacent vertebral body. The survival rate analysis was conducted based on age at the time of surgery, gender, surgical method, leakage of cement into the vertebral disc, compression rate before surgery, recovery of vertebral height after surgery, bone density before surgery, surgeon, the presence of diabetes, and smoking. The average follow-up period was 13.8 months (range, 1 month to 7 years and 11 months) and the mean age at the time of surgery was 72.1 years (range, 47-92 years).
RESULTS
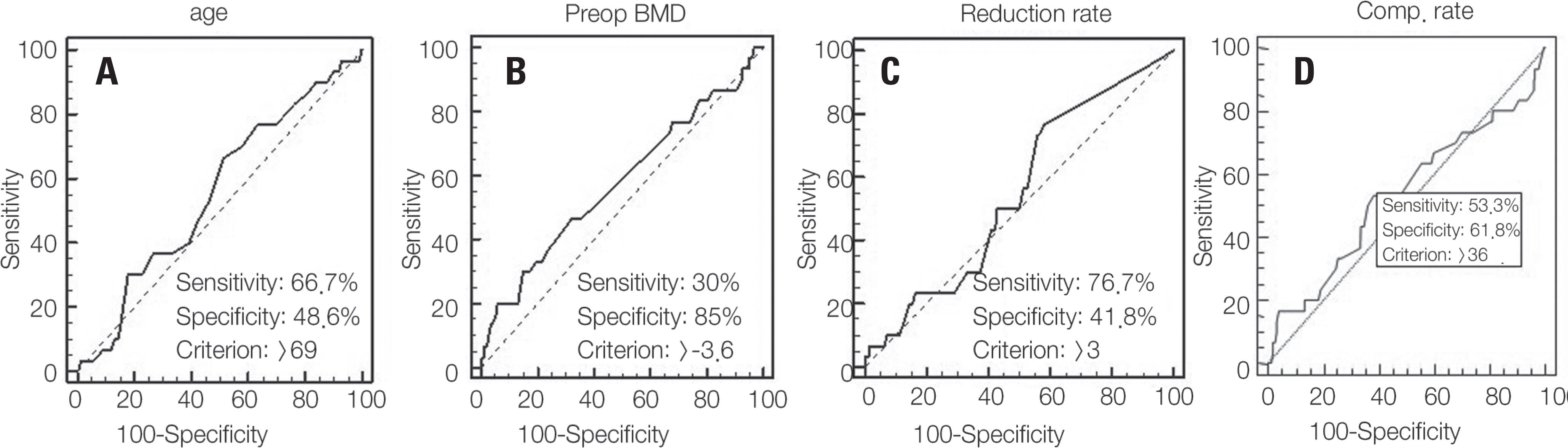
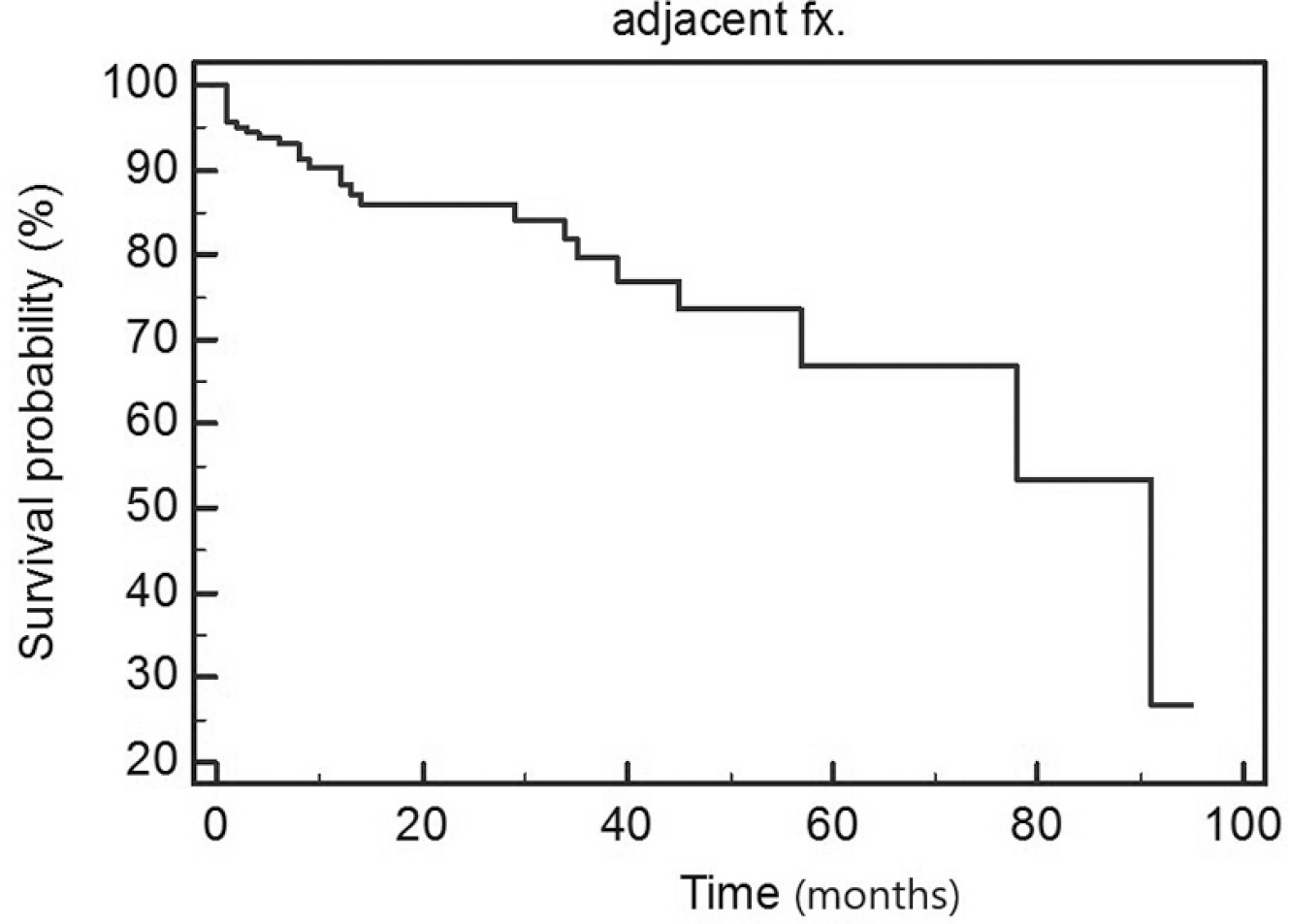
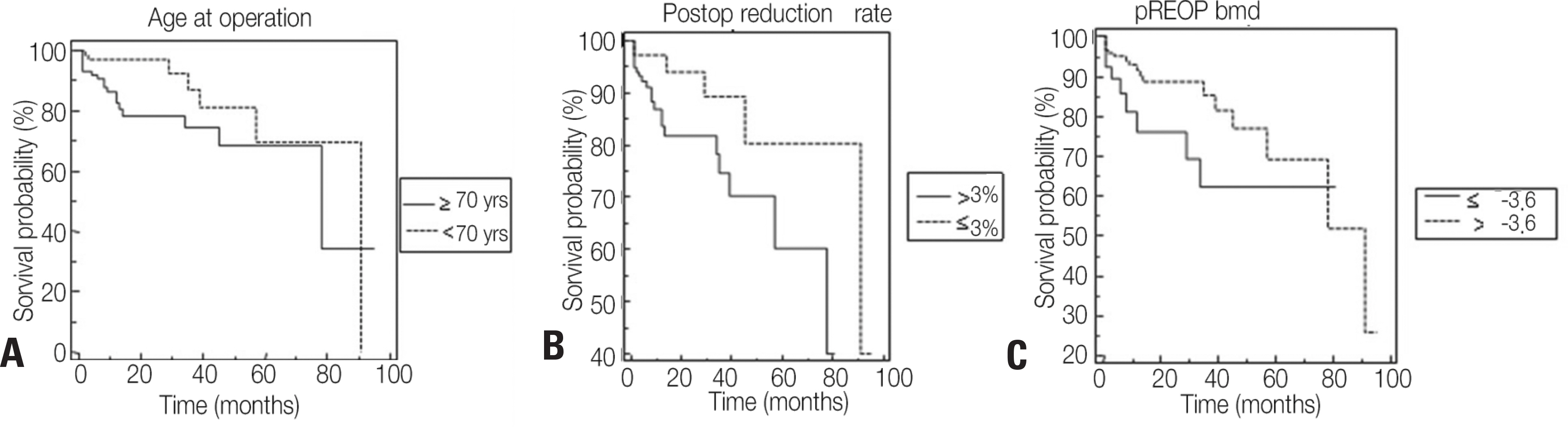
Among the 250 cases, a new fracture in an adjacent vertebral body occurred in 30 cases (12%). The 1-year survival rate of patients undergoing vertebroplastry or kyphoplasty for a vertebral fracture was 88.4%, the 5-year rate was 66.8%, and the 7-year rate was 53.5%. When the cases were analyzed according to whether the patient's age at the time of surgery was under or over 70 years, the survival rate was significantly higher in the under-70 group (p=0.026). Moreover, when analyzing the survival rate using a 3% vertebral height recovery rate after surgery as baseline, the group that showed 3% or less had a significantly higher survival rate (p=0.04); moreover, the survival rate was significantly higher in patients with a bone density higher than −3.6 (p=0.046). In multiple factor analysis, age at the time of surgery (p=0.022) and the vertebral height recovery rate after surgery (p=0.046) were found to be statistically significant factors.
CONCLUSIONS
The survival rate associated with a new fracture in an adjacent vertebra after vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures was significantly decreased at 1, 5, and 7 years. Based on the survival rate analysis, the most crucial factors were age and the vertebral height recovery rate after surgery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, et al. Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty. Neurochirurgie. 1987; 33:166–8.2. Diamond TH, Champion B, Clark WA. Management of acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a nonrandomized trial comparing percutaneous vetebroplasty with conservative therapy. Am J Med. 2003; 114:257–65.3. Kallmes DF, Comstock BA, Heagerty PJ, et al. A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic spinal fractures. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:569–79.
Article4. Buchbinder R, Osborne RH, Ebeling PR, et al. A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:557–68.
Article5. Lo YP, Chen WJ, Chen LH, et al. New vertebral fracture after vertebroplasty. J Traum. 2008; 65:1439–45.
Article6. Ahn Y, Lee JH, Lee HY, et al. Predictive factors for subse-quent vertebral fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008; 9:129–36.
Article7. Jensen ME, Evans AJ, Mathis JM, et al. Percutaneous poly-methylmethacrylate vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression fractures: technical aspects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997; 18:1897–904.8. Gardos F, Hardy N, Cayrlle G, et al. Treatment of vertebral compression fractures by vertebroplasty. Rev Rhum (Engl Ed). 1997; 64:38.9. Trout AT, Kallmes DF, Kaufmann TJ. New fractures after vertebroplasty: adjacent fractures occur significantly sooner. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:217–23.10. Uppin AA, Hirsch JA, Centenera LV, et al. Occurrence of new vertebral body fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoprosis. Radiology. 2003; 226:119–24.11. Yang S, Liu Y, Yang H, et al. Risk factors and correlation of secondary adjacent vertebral compression fracture in percutaneous kyphoplasty. Int J Surg. 2016. 138–42.
Article12. Laredo JD, Hamz B. Complication of percutaneous vertebroplasty and their prevention. Skeletal Radiol. 2004; 33:493–505.
Article13. Liebschner MA, Rosenberg WS, Keaveny TM. Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffnes after vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:1547–54.14. Baroud G, Nemes J, Ferguson SJ, et al. Material changes in osteoporotic human cancellous bone following infil-tration with acrylic bone cement for a vertebral cement augmentation. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2003; 6:133–9.
Article15. Berlemann U, Ferguson SJ, Nolte LP, et al. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty. A biomechanical investigation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84:748–52.16. Lin EP, Ekholm S, Hiwatashi A, et al. Vertebroplasty: cement leakage into the disc increases the risk of new fracture of adjacent vertebral body. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; 25:175–80.17. Chen YD, Teng MM, Chang CY, et al. Intrathecal cement leakage as a rare and serious complication of percutane-ous vertebroplasty: case report and literature review. Chin J Radiol. 2007; 32:141–5.18. Kim MH, Andrew S, Min SH, et al. Risk factors of new compression fractures in adjacent vertebrae after percutane-ous vertebroplasty. Asian Spine J. 2011; 5:180–7.
Article19. Papnastassious ID, Phillips FM, Van Meirhaeghe J, et al. Comparing effects of kyphoplasty, vertebroplasty, and non-surgical management in a systematic review of randomized and non-randomized controlled studies. Eur Spine J. 2012. 1826–43.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparisons of Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty for Thoracolumbar Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures
- The Incidence of Recurrent Vertebral Fracture after Kyphoplasty or Vertebroplasty
- Minimally Invasive Treatment of Painful Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures
- Analysis of the Cement Distribution Pattern and Other Risk Factors that Affect the Incidence of Recompression Fractures of Vertebral Bodies after Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty
- Vertebral Recompression after Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty