Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2017 Jun;21(2):82-90. 10.13104/imri.2017.21.2.82.
MR Findings of Seizure-Related Cerebral Cortical Lesions during Periictal Period
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. choids@gnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2385604
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.2.82
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study investigated the MRI, MR angiography (MRA) and MR perfusion findings of seizure-related cerebral cortical lesions during the periictal period.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From a retrospective review of the institutional database between 2011 and 2014, a total of 21 patients were included in this study. Two radiologists assessed periictal MRI, including MRA and MR perfusion, in patients with seizure-related cortical lesions. The parameters examined include: location of cortical abnormality, multiplicity of the affected cortical region, cerebral vascular dilatation, perfusion abnormality and other parenchymal lesions.
RESULTS
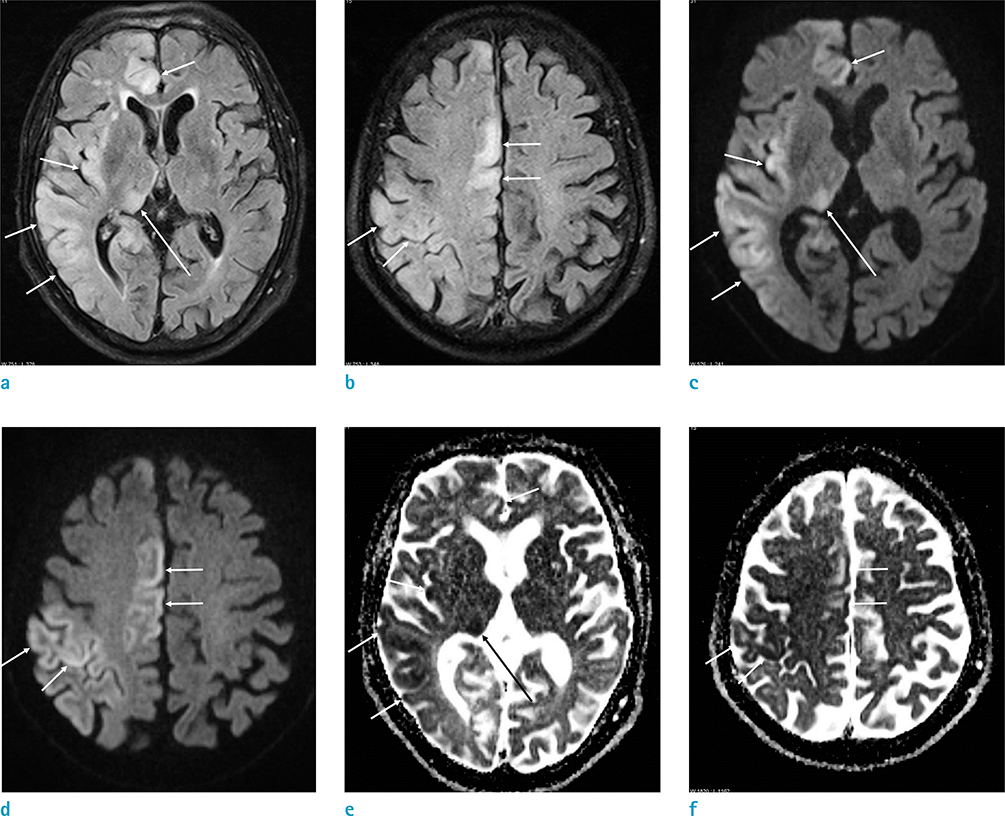
All patients showed T2 hyperintense cerebral cortical lesions with accompanying diffusion restriction, either unilateral (18/21, 85.7%) or bilateral (3/21, 14.3%). Of the 21 patients enrolled, 10 (47.6%) had concurrent T2 hyperintense thalamic lesions, and 10 (47.6%) showed hippocampal involvement. Of the 17 patients (81%) who underwent MRA, 13 (76.5%) showed vascular dilatation with increased flow signal in the cerebral arteries of the affected cortical regions. On MR perfusion, all 5 patients showed cortical hyperperfusion, corresponding to the region of cortical abnormalities.
CONCLUSION
Seizure-related cerebral cortical lesions are characterized by T2 and diffusion hyperintensities, with corresponding cerebral hyperperfusion and vascular dilatation. These findings can be helpful for making an accurate diagnosis in patients with seizure.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Annegers JF. The epidemiology of epilepsy. In : Wyllie E, editor. The treatment of epilepsy: principles and practice. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2001. p. 131–138.2. Cole AJ. Status epilepticus and periictal imaging. Epilepsia. 2004; 45:Suppl 4. 72–77.3. Briellmann RS, Wellard RM, Jackson GD. Seizure-associated abnormalities in epilepsy: evidence from MR imaging. Epilepsia. 2005; 46:760–766.4. Cianfoni A, Caulo M, Cerase A, et al. Seizure-induced brain lesions: a wide spectrum of variably reversible MRI abnormalities. Eur J Radiol. 2013; 82:1964–1972.5. Davis DP, Robertson T, Imbesi SG. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomography in the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke. J Emerg Med. 2006; 31:269–277.6. Mathews MS, Smith WS, Wintermark M, Dillon WP, Binder DK. Local cortical hypoperfusion imaged with CT perfusion during postictal Todd's paresis. Neuroradiology. 2008; 50:397–401.7. Weinand ME, Carter LP, el-Saadany WF, Sioutos PJ, Labiner DM, Oommen KJ. Cerebral blood flow and temporal lobe epileptogenicity. J Neurosurg. 1997; 86:226–232.8. Moritani T, Smoker WR, Sato Y, Numaguchi Y, Westesson PL. Diffusion-weighted imaging of acute excitotoxic brain injury. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:216–228.9. Warach S, Levin JM, Schomer DL, Holman BL, Edelman RR. Hyperperfusion of ictal seizure focus demonstrated by MR perfusion imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1994; 15:965–968.10. Chan S, Chin SS, Kartha K, et al. Reversible signal abnormalities in the hippocampus and neocortex after prolonged seizures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996; 17:1725–1731.11. Goyal MK, Sinha S, Ravishankar S, Shivshankar JJ. Peri-ictal signal changes in seven patients with status epilepticus: interesting MRI observations. Neuroradiology. 2009; 51:151–161.12. Huang YC, Weng HH, Tsai YT, et al. Periictal magnetic resonance imaging in status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res. 2009; 86:72–81.13. Holmes GL. Seizure-induced neuronal injury: animal data. Neurology. 2002; 59:S3–S6.14. Wang Y, Majors A, Najm I, et al. Postictal alteration of sodium content and apparent diffusion coefficient in epileptic rat brain induced by kainic acid. Epilepsia. 1996; 37:1000–1006.15. Kim JA, Chung JI, Yoon PH, et al. Transient MR signal changes in patients with generalized tonicoclonic seizure or status epilepticus: periictal diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:1149–1160.16. Bouilleret V, Nehlig A, Marescaux C, Namer IJ. Magnetic resonance imaging follow-up of progressive hippocampal changes in a mouse model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2000; 41:642–650.17. Szabo K, Poepel A, Pohlmann-Eden B, et al. Diffusion-weighted and perfusion MRI demonstrates parenchymal changes in complex partial status epilepticus. Brain. 2005; 128:1369–1376.18. Nevander G, Ingvar M, Auer R, Siesjo BK. Status epilepticus in well-oxygenated rats causes neuronal necrosis. Ann Neurol. 1985; 18:281–290.19. Toledo M, Munuera J, Sueiras M, Rovira R, Alvarez-Sabin J, Rovira A. MRI findings in aphasic status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2008; 49:1465–1469.20. Calistri V, Caramia F, Bianco F, Fattapposta F, Pauri F, Bozzao L. Visualization of evolving status epilepticus with diffusion and perfusion MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:671–673.21. Hayward NM, Ndode-Ekane XE, Kutchiashvili N, Grohn O, Pitkanen A. Elevated cerebral blood flow and vascular density in the amygdala after status epilepticus in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2010; 484:39–42.22. Unrath A, Muller HP, Ludolph AC, Kassubek J. Reversible cortical diffusion restriction, hyperperfusion and T2-hyperintensity caused by two different types of epileptic seizure. Clin Neuroradiol. 2012; 22:239–243.23. Zhao M, Suh M, Ma H, Perry C, Geneslaw A, Schwartz TH. Focal increases in perfusion and decreases in hemoglobin oxygenation precede seizure onset in spontaneous human epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2007; 48:2059–2067.24. Wasterlain CG, Fujikawa DG, Penix L, Sankar R. Pathophysiological mechanisms of brain damage from status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 1993; 34:Suppl 1. S37–S53.25. Nagasaka T, Shindo K, Hiraide M, Sugimoto T, Shiozawa Z. Ipsilateral thalamic MRI abnormality in an epilepsy patient. Neurology. 2002; 58:641–644.26. Shipp S. The functional logic of cortico-pulvinar connections. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2003; 358:1605–1624.27. Katramados AM, Burdette D, Patel SC, Schultz LR, Gaddam S, Mitsias PD. Periictal diffusion abnormalities of the thalamus in partial status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2009; 50:265–275.28. Eid T, Ghosh A, Wang Y, et al. Recurrent seizures and brain pathology after inhibition of glutamine synthetase in the hippocampus in rats. Brain. 2008; 131:2061–2070.29. Tuan Huynh NN, Hiroyoshi A, Shozo N, Takashi T, Hideo T, Akira M. Reversible focal radiological changes due to non-convulsive status epilepticus of the right parietooccipital lobe. Turk Neurosurg. 2013; 23:278–281.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Perfusion MR Imaging of Seizure-related Cerebral Cortical Lesion: A Case Report
- MR Findings of Hypoxic Brain Damage: Relation to Time Elapse and Prognosis of Patients
- Lobar Intracerebral Hemorrhage Associated With Cortical Superficial Siderosis
- MR findings of brain damage due to perinatal hypoxia
- Acute Marchiafava-Bignami Disease: Diffusion-Weighted MRI in Cortical and Callosal Involvement