Yonsei Med J.
2007 Apr;48(2):321-324. 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.2.321.
Acute Marchiafava-Bignami Disease: Diffusion-Weighted MRI in Cortical and Callosal Involvement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, St. Vincent Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Gyenggi-do, Korea. Ihn@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1779538
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2007.48.2.321
Abstract
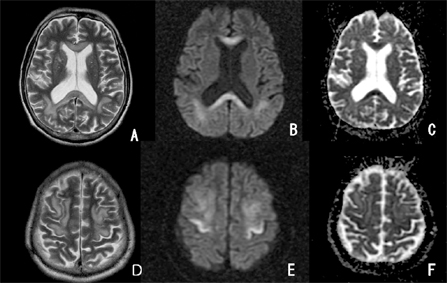
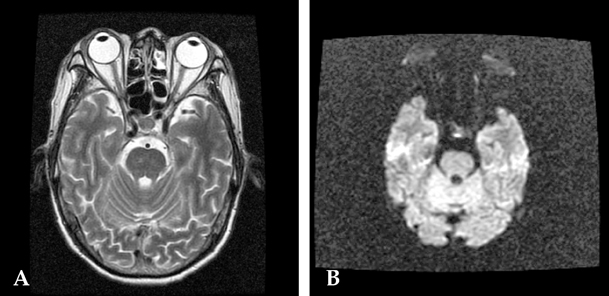
- Marchiafava-Bignami disease (MBD) is a fatal disorder characterized by demyelination of the corpus callosum. MRI, suggestive of corpus callosum demyelination with associated white matter involvement in both cerebral hemispheres, indicates a diagnosis of MBD. In this case, MR diffusion-weighted findings taken at an acute stage of MBD revealed lesions not only in the corpus callosum but also in the cerebral cortex. Lower apparent diffusion coefficient values of the corpus callosum and cortical lesions were associated with poor clinical outcome.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chang KH, Cha SH, Han MH, Park SH, Nah DL, Hong JH. Marchiafava-Bignami disease: serial changes in corpus callosum on MRI. Neuroradiology. 1992. 34:480–482.2. Kawarabuki K, Sakakibara T, Hirai M, Yoshioka Y, Yamamoto Y, Yamaki T. Marchiafava-Bignami disease: magnetic resonance imaing findings in corpus callosum and subcortical white matter. Eur J Radiol. 2003. 48:175–177.3. Arbelaez A, Pajon A, Castillo M. Acute Marchiafava-Bignami disease: MR findings in two patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003. 24:1955–1957.4. Inagaki T, Saito K. A case of Marchiafava-Bignami disease demonstrated by MR diffusion-weighted image. No To Shinkei. 2000. 52:633–637.5. Johkura K, Naito M, Naka T. Cortical involvement in Marchiafava-Bignami disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005. 26:670–673.6. Menegon P, Sibon I, Pachai C, Orgogozo JM, Dousset V. Marchiafava-Bignami disease: diffusion-weighted MRI in corpus callosum and cortical lesions. Neurology. 2005. 65:475–477.7. Lechevalier B, Andersson JC, Morin P. Hemispheric disconnection syndrome with a 'crossed avoiding' reaction in a case of Marchiafava-Bignami disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977. 40:483–497.8. Ellison D, Love S, Chimelli L, Harding BN, Lowe J, Vinters HV. Neuropathology. A reference text of CNS pathology. 2004. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Mosby;489–490.9. Yamashita M, Yamamoto T. Wernicke encephalopathy with symmetric pericentral involvement : MR findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1995. 19:306–308.10. Hlaihel C, Gonnaud PM, Champin S, Rousset H, Tran-Minh VA, Cotton F. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in Marchiafava-Bignami disease: follow-up studies. Neuroradiology. 2005. 47:520–524.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cortical Involvement of Marchiafava-Bignami Disease: A Case Report
- Acute Marchiafava-Bignami Disease With Typical White Matter Involvement on Diffusion Weighted MRI
- Callosal and Cortical Involvement in Acute Marchiafava-Bignami Disease
- Magnetic Resonance Finding of Acute Marchiafava-Bignami Disease with Diffuse Involvement: A Case Report
- A Case of Marchiafava-Bignami Disease with Reversible Brain MRI Findings of Corpus Callosal Lesions