Korean J Ophthalmol.
2017 Aug;31(4):372-374. 10.3341/kjo.2017.0014.
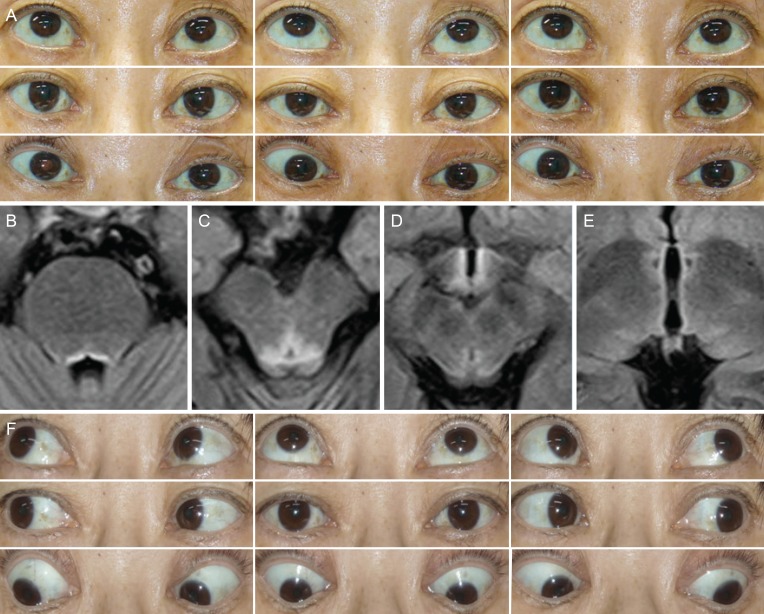
Wernicke's Encephalopathy Presenting with Bilateral Complete Horizontal and Downward Gaze Palsy in a Malnourished Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. mmk@med.yu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2385590
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.0014
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Miller NR, Subramanian PS, Patel VR, editors. Walsh and Hoyt's clinical neuro-ophthalmology: the essentials. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer;2016. p. 339.2. Kim K, Shin DH, Lee YB, et al. Evolution of abnormal eye movements in Wernicke's encephalopathy: correlation with serial MRI findings. J Neurol Sci. 2012; 323:77–79. PMID: 22940074.
Article3. Bhidayasiri R, Plant GT, Leigh RJ. A hypothetical scheme for the brainstem control of vertical gaze. Neurology. 2000; 54:1985–1993. PMID: 10822441.
Article4. Chern JJ, Relyea K, Edmond JC, et al. Transient selective downward gaze paralysis complicating posterior fossa tumor resection in children: report of 2 cases. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2009; 3:467–471. PMID: 19485729.5. Kim JY, Heo DW, Lee HJ, Lee YH. A case of thiamine (vitamin B1)-deficient optic neuropathy associated with Wernicke's encephalopathy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:1954–1959.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Wernicke's Encephalopathy after Long-Term Intravenous Feeding
- A Case of Bilateral Sudden Deafness Caused by Wernicke Encephalopathy
- A Case of Bilateral Horizontal Gaze Palsy due to Pontine Hemorrhage
- Bilateral Hearing Loss in Wernicke Encephalopathy
- A Case of Wernicke's Encephalopathy Presenting as Acute Bilateral Wrist Drop