J Bacteriol Virol.
2017 Mar;47(1):41-53. 10.4167/jbv.2017.47.1.41.
Influence of Chemical- and Natural-Based Lotions on Bacterial Communities in Human Forearm Skin
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Beauty Art, Seokyeong University, Seoul, Korea. baakdoo@skuniv.ac.kr
- 2Department of Nano Convergence, Seokyeong University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2384419
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2017.47.1.41
Abstract
- Purpose
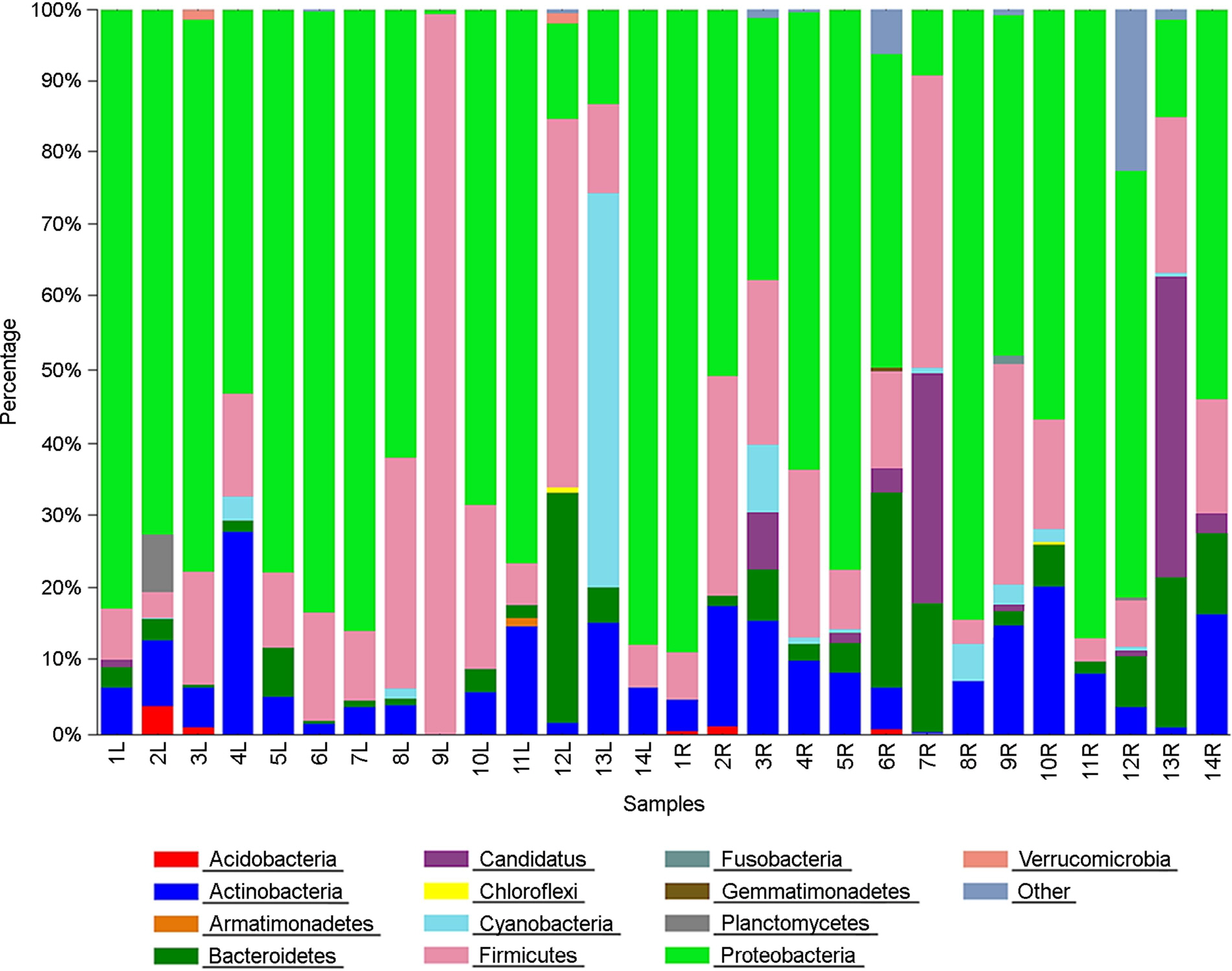
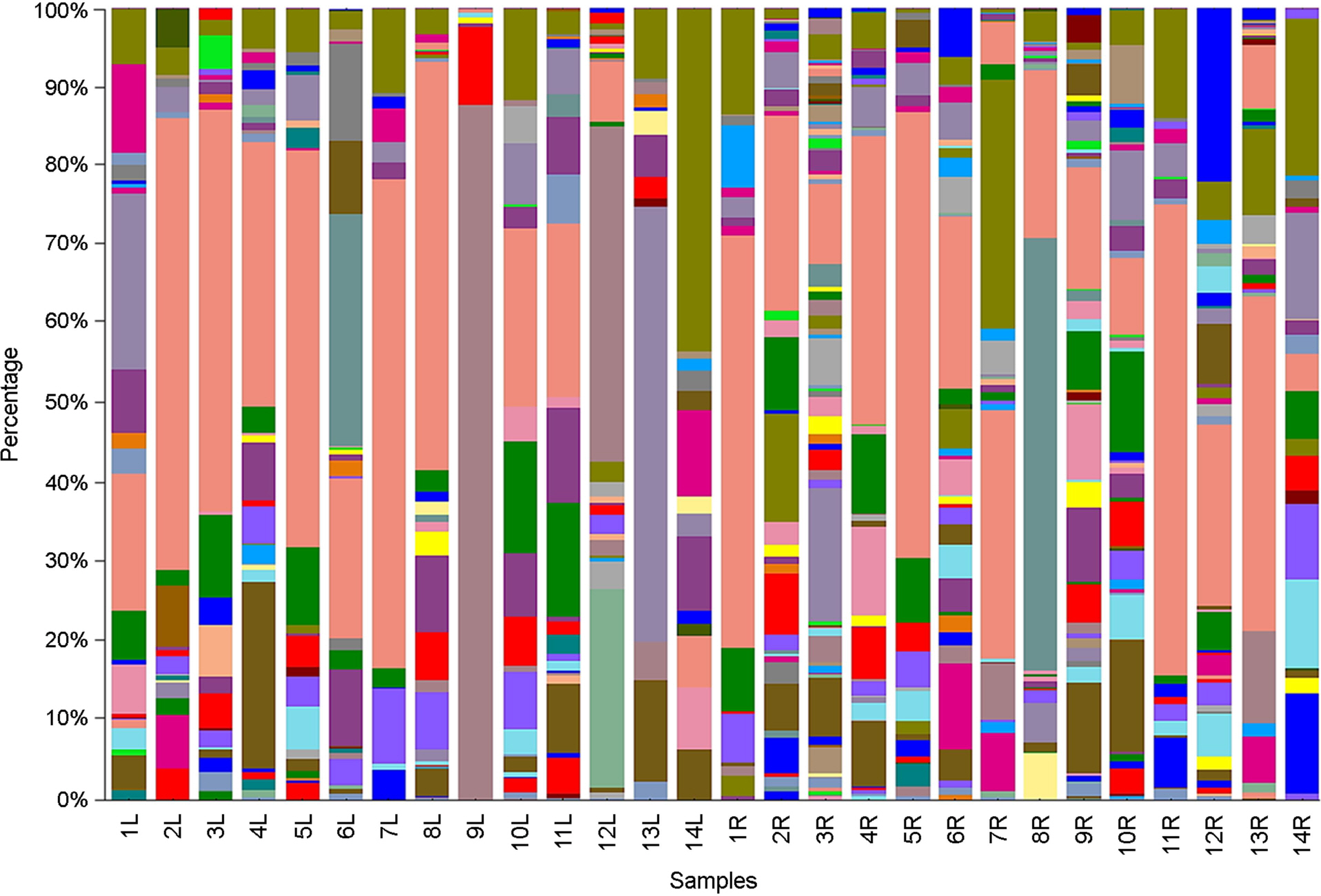
of this study was to evaluate the influence of a lotion on the bacterial community in the human forearm skin. The chemical- and natural-based lotions were applied on the left and right inner forearm skins, respectively, of 14 participants, who cleansed forearm skin using sterilized cotton swabs. The germs on cotton swabs were analyzed using libraries of PCR amplicons. The genetic diversity of the bacterial communities detected on the natural-based lotion-applied skin (NLS) was significantly higher than that of the bacterial communities on the chemical-based lotion-applied skin (CLS) in all participants, except two. The diversity was estimated based on operational taxonomic unit (OTU), Chao1, Shannon, and Simpson indices. Bacterial communities obtained from the CLS and NLS were phylogenetically separated into 5 and 3 monophyletic groups, respectively, based on lotion types. The taxonomic distribution of the bacterial communities, which were composed of 198 genera in 14 phyla in the CLS and NLS, respectively, was irregularly and biasedly separated into 2 groups based on the lotion types. Among the 14 phyla, Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria were found to be relatively dominant, and 15 of the 198 genera, including Methylobacterium, Propionibacterium, Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Bacillus were relatively dominant (>0.5%). The taxonomic distribution of dominant bacterial communities from CLS and NLS was irregularly and biasedly separated without relation to the lotion types. In conclusion, the chemical- and natural-based lotions were responsible for changing or influencing the genetic diversity, phylogenetic separation, and taxonomic distribution of skin bacterial communities.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Correction: Influence of Chemical- and Natural-Based Lotions on Bacterial Communities in Human Forearm Skin
Doo Hyun Park
J Bacteriol Virol. 2017;47(2):110-110. doi: 10.4167/jbv.2017.47.2.110.
Reference
-
1). Segre JA. Epidermal barrier formation and recovery in skin disorders. J Clin Invest. 2006; 116:1150–8.
Article2). Grice EA, Kong HH, Conlan S, Deming CB, Davis J, Young AC. Topographical and temporal diversity of the human skin microbiome. Science. 2009; 324:1190–2.
Article3). Roth RR, James WD. Microbial ecology of the skin. Ann Rev Microbiol. 1988; 42:441–64.
Article4). Elias PM. The skin barrier as an innate immune element. Semin Immunopathol. 2007; 29:3–14.
Article5). Cogen AL, Nizet V, Gallo RL. Skin microbiota: A source of disease or defence? Br J Dermatol. 2008; 158:442–55.
Article6). Till AE, Goulden V, Cunliffe WJ, Holland KT. The cutaneous microflora of adolescent, persistent and late-onset acne patients does not differ. Br J Dermatol. 2000; 142:885–92.7). Grice EA, Segre JA. The skin microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011; 9:244–53.
Article8). Yarwood JM, Bartels DJ, Volper EM, Greenberg EP. Quorum sensing in Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. J Bacteriol. 2004; 186:1838–50.9). Pesci EC, Pearson JP, Seed PC, Iglewski BH. Regulation of las and rhl quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1997; 179:3127–32.
Article10). Fuqua C, Winans SC, Greenberg EP. Census and consensus in bacterial ecosystems: the LuxR-LuxI family of quorum-sensing transcriptional regulators. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1996; 50:727–51.
Article11). Latifi A, Foglino M, Tanaka K, Williams P, Lazdunski A. A hierarchical quorum sensing cascade in Pseudomonas aeruginosa links the transcriptional activators LasR and R hIR (VsmR) to expression of the stationary-phase sigma factor Rpos. Mol Microbiol. 1996; 21:1137–46.12). de Almeida e Borges LF, Silva BL, Gontijo Filho PP. Hand washing: Changes in the skin flora. Am J Infect Control. 2007; 35:417–20.13). Wibowo C, Ng KM. Product-centered processing: manufacture of chemical-based consumer products. Am Inst Chem Eng J. 2002; 48:1212–30.
Article14). Gfatter R, Hackl P, Braun F. Effects of soap and detergents on skin surface pH, stratum corneum hydration and fat content in infants. Dermatology. 1997; 195:258–62.
Article15). Chen Q. Evaluate the effectiveness of the natural cosmetic product compared to chemical-based products. Int J Chem. 2009; 1:57–9.
Article16). Hoolnad KT, Bojar RA. Cosmetics: what is their influence on the skin microflora? Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002; 3:445–9.17). Boireau-Adamezyk E, Baillet-Guffroy A, Stamatas GN. Age-dependent changes in stratum corneum barrier function. Skin Res Technol. 2014; 20:409–15.
Article18). Wick G, Grunbeck-Loebenstein B. The aging immune system: primary and secondary alterations of immune reactivity in the elderly. Exp Gerontol. 1997; 32:401–13.
Article19). Proksch E, Fölster-Holst R, Jensen JM. Skin barrier function, epidermal proliferation and differentiation in eczema. J Dermatol Sci. 2006; 43:159–69.
Article20). Harding CR, Watkinson A, Rawlings AV, Scott IR. Dry skin, moisturization and corneodesmolysis. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2000; 22:21–52.
Article21). Gomez-Alvarez V, Teal TK, Schmidt TM. Systematic artifacts in metagenomes from complex microbial communities. ISME J. 2009; 3:1314–7.
Article22). Chou HH, Holmes MH. DNA sequence quality trimming and vector removal. Bioinformatics. 2001; 17:1093–104.
Article23). Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011; 28:2731–9.
Article24). Fredricks DN. Microbial ecology of human skin in health and disease. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2001; 6:167–9.
Article25). Holland KT, Bojar RA. Cosmetics: what is their influence on the skin microflora? Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002; 3:445–9.26). Gao Z, Tseng CH, Pei Z, Blaser MJ. Molecular analysis of human forearm superficial skin bacterial biota. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104:2927–32.
Article27). Grice EA, Kong HH, Renaud G, Young AC, Bouffard GG, Blakesley RW, et al. A diversity profile of the human skin microbiota. Genome Res. 2008; 18:1043–50.
Article28). Eloe-Fadrosh EA, Rasko DA. The human microbiome: from symbiosis to pathogenesis. Annu Rev Med. 2013; 64:145–63.
Article29). Leeming JP, Holland KT, Cunliffe WJ. The microbial ecology of pilosebaceous units isolated from human skin. J Gen Microbiol. 1984; 130:803–7.
Article30). de Almeida e Borges LF, Silva BL, Gontijo Filho PP. Hand washing changes in the skin flora. Am J Infect Control. 2007; 35:417–20.31). Kampf G, Kramer A. Epidemiologic background of hand hygiene and evaluation of the most important agents for scrubs and rubs. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004; 17:863–93.
Article32). Bowe WP, Puqliese S. Cosmetic benefits of natural ingredients. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014; 13:1021–5.33). You JY, Park SH, Hwang IA, Jo SJ, Huh CH, Youn SW, et al. A clinical study on the effect of a cream containing ramulus mori extract and tea tree oil on acne vulgaris and aerobic skin flora. Korean J Dermatol. 2003; 41:1136–41.34). Blanpain C, Fuchs E. Epidermal homeostasis: a balancing act of stem cells in the skin. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009; 10:207–17.
Article35). Zoetendal EG, Vaughan EE, de Vos WM. A microbial world within us. Mol Microbiol. 2006; 59:1639–50.
Article36). Costello EK, Lauber CL, Hamady M, Fierer N, Gordon JI, Knight R. Bacterial community variation in human body habitats across space and time. Science. 2009; 326:1694–7.
Article37). Leyden JJ, McGinley KJ, Nordstrom KM, Webster GF. Skin microflora. J Invest Dermatol. 1987; 88:65s–72s.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correction: Influence of Chemical- and Natural-Based Lotions on Bacterial Communities in Human Forearm Skin
- Reconstruction of Hand and Forearm Injury using Reverse Ulnar Artery Forearm Flap: Six Cases Report
- A Case of Allergic Contact Dermatitis to Antiseptics
- A case of chemical meningitis after myelography
- Chemical burn due to weed killer, Gramoxone@(paraquat dichloride)