Clin Nutr Res.
2017 Apr;6(2):136-144. 10.7762/cnr.2017.6.2.136.
A Case Report of the Nutrition Support for a Patient with HELLP Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nutrition Care, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 03722, Korea. nutrpine@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Nutrition Services, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 06273, Korea.
- 3Department of Pharmacy, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 06273, Korea.
- 4Department of Food and Nutrition, Soongeui Women's College, Seoul 04628, Korea.
- 5Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 06273, Korea.
- KMID: 2383702
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7762/cnr.2017.6.2.136
Abstract
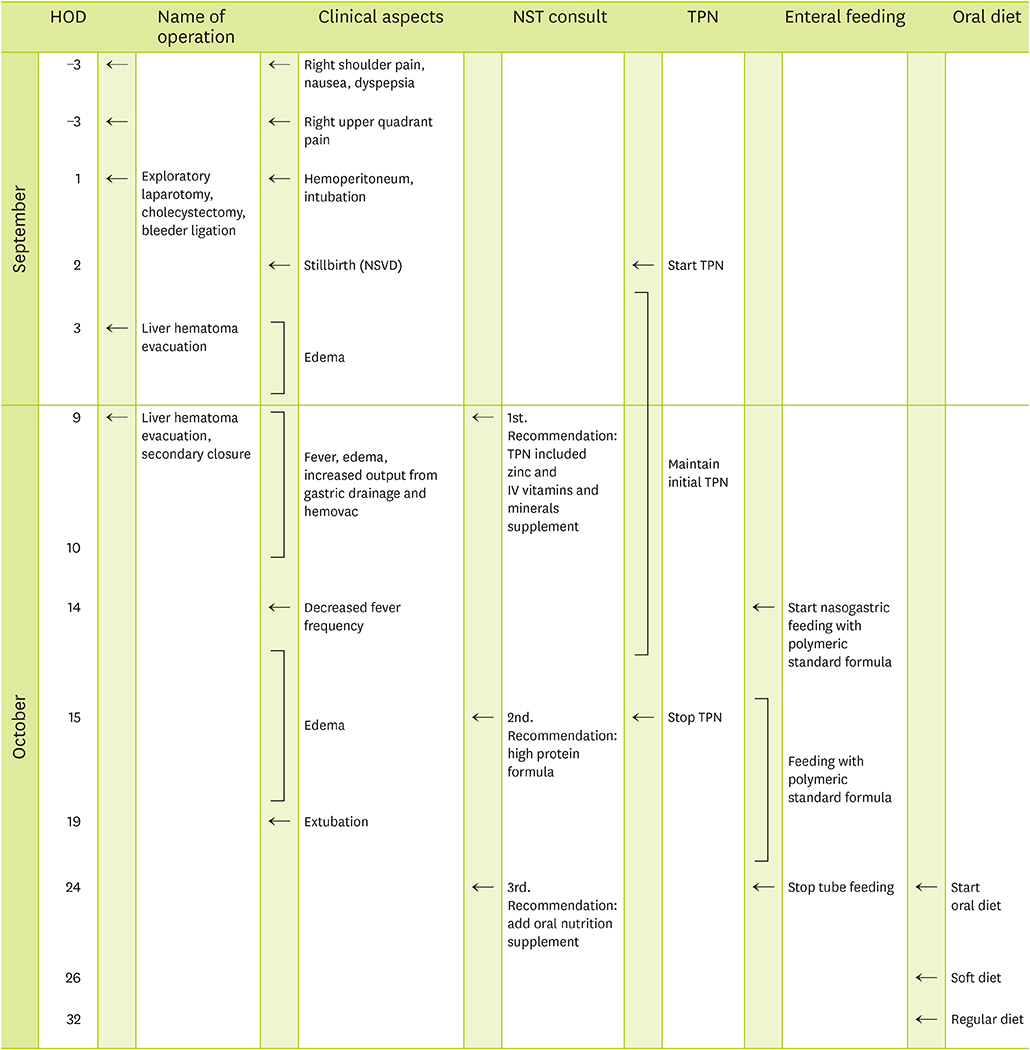
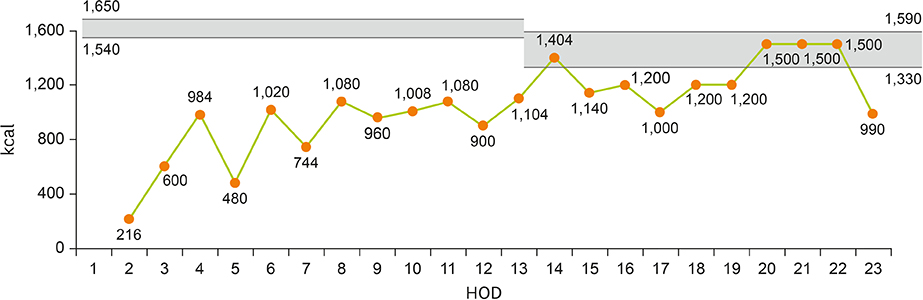
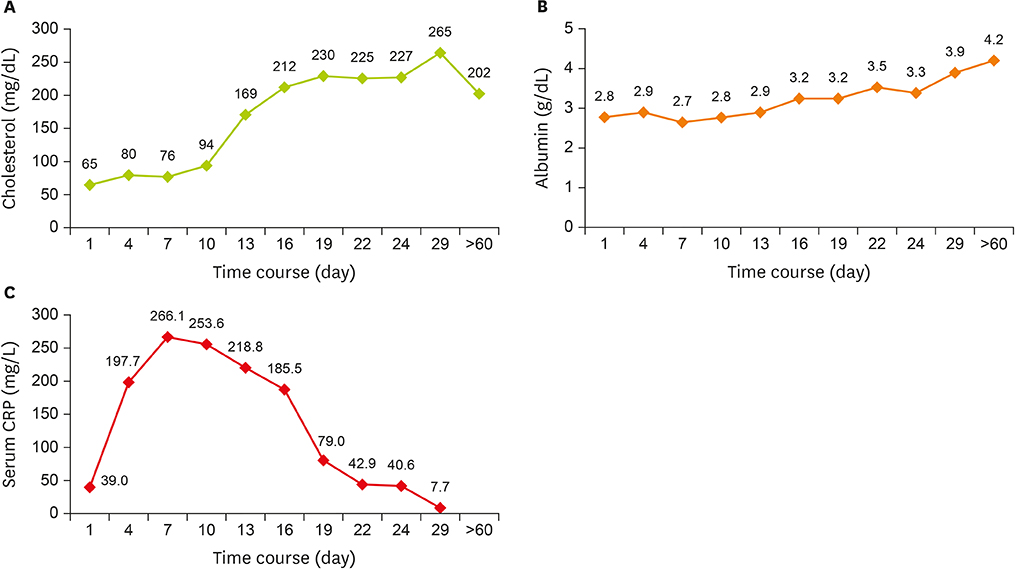
- A 30-year-old female patient, 18 weeks gestational age, with no prior medical history was admitted to hospital complaining severe right upper quadrant pain. The patient was admitted to intensive care unit (ICU) after emergency surgery to treat intraperitoneal hemorrhage caused by rupture of liver hematoma. Despite the absence of high blood pressure, the patient was diagnosed with hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count (HELLP) syndrome on the basis of abnormal levels of blood aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase, lactate dehydrogenase, total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, C-reactive protein (CRP) and platelet along with liver damage and proteinuria. While in ICU, the patient was given total parenteral nutrition (TPN) and enteral nutrition (EN) for -20 days because oral feeding was impractical. In the early stage, TPN supply was not sufficient to meet the elevated nutritional demand induced by disease and surgery. Nevertheless, continuous care of nutrition support team enabled satisfactory EN and, subsequently, oral feeding which led to improvement in patient outcome.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aspartic Acid
Bilirubin
Blood Platelets
C-Reactive Protein
Emergencies
Enteral Nutrition
Female
Gestational Age
HELLP Syndrome*
Hematoma
Hemolysis
Hemorrhage
Humans
Hypertension
Intensive Care Units
L-Lactate Dehydrogenase
Liver
Parenteral Nutrition
Parenteral Nutrition, Total
Platelet Count
Pregnancy
Proteinuria
Rupture
Aspartic Acid
Bilirubin
C-Reactive Protein
L-Lactate Dehydrogenase
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lachmeijer AM, Arngrímsson R, Bastiaans EJ, Frigge ML, Pals G, Sigurdardóttir S, Stéfansson H, Pálsson B, Nicolae D, Kong A, Aarnoudse JG, Gulcher JR, Dekker GA, ten Kate LP, Stéfansson K. A genome-wide scan for preeclampsia in the Netherlands. Eur J Hum Genet. 2001; 9:758–764.
Article2. Weinstein L. Syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count: a severe consequence of hypertension in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982; 142:159–167.
Article3. Sibai BM. The HELLP syndrome (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets): much ado about nothing? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990; 162:311–316.
Article4. Sibai BM. Imitators of severe pre-eclampsia/eclampsia. Clin Perinatol. 2004; 31:835–852.
Article5. Martin JN Jr, Blake PG, Perry KG Jr, McCaul JF, Hess LW, Martin RW. The natural history of HELLP syndrome: patterns of disease progression and regression. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991; 164:1500–1509.
Article6. Martin JN Jr, Rinehart BK, May WL, Magann EF, Terrone DA, Blake PG. The spectrum of severe preeclampsia: comparative analysis by HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzyme levels, and low platelet count) syndrome classification. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999; 180:1373–1384.
Article7. Geary M. The HELLP syndrome. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1997; 104:887–891.
Article8. Aarnoudse JG, Houthoff HJ, Weits J, Vellenga E, Huisjes HJ. A syndrome of liver damage and intravascular coagulation in the last trimester of normotensive pregnancy. A clinical and histopathological study. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1986; 93:145–155.
Article9. Pokharel SM, Chattopadhyay SK, Jaiswal R, Shakya P. HELLP syndrome--a pregnancy disorder with poor prognosis. Nepal Med Coll J. 2008; 10:260–263.10. Haram K, Svendsen E, Abildgaard U. The HELLP syndrome: clinical issues and management. A review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2009; 9:8.
Article11. McWhirter JP, Pennington CR. Incidence and recognition of malnutrition in hospital. BMJ. 1994; 308:945–948.
Article12. Ziegler TR. Parenteral nutrition in the critically ill patient. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:1088–1097.
Article13. Heyland DK, Montalvo M, MacDonald S, Keefe L, Su XY, Drover JW. Total parenteral nutrition in the surgical patient: a meta-analysis. Can J Surg. 2001; 44:102–111.14. McClave SA, Taylor BE, Martindale RG, Warren MM, Johnson DR, Braunschweig C, McCarthy MS, Davanos E, Rice TW, Cresci GA, Gervasio JM, Sacks GS, Roberts PR, Compher C; Society of Critical Care Medicine; American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. Guidelines for the provision and assessment of nutrition support therapy in the adult critically ill patient: Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.). JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2016; 40:159–211.
Article15. Singer P, Berger MM, Van den Berghe G, Biolo G, Calder P, Forbes A, Griffiths R, Kreyman G, Leverve X, Pichard C. ESPEN. ESPEN guidelines on parenteral nutrition: intensive care. Clin Nutr. 2009; 28:387–400.
Article16. Manzanares W, Dhaliwal R, Jiang X, Murch L, Heyland DK. Antioxidant micronutrients in the critically ill: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2012; 16:R66.
Article17. Mirtallo J, Canada T, Johnson D, Kumpf V, Petersen C, Sacks G, Seres D, Guenter P. Task Force for the Revision of Safe Practices for Parenteral Nutrition. Safe practices for parenteral nutrition. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2004; 28:S39–S70.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of the HELLP Syndrome treated with Postpartum Plasmapheresis
- Anesthetic Management of a Patient with Postpartum HELLP Syndrome: A case report
- Epidural Analgesia for Labor Pain Management in a Parturient with HELLP Syndrome: A case report
- Acute Airway Obstruction by a Retropharyngeal Hematoma when Performing Internal Jugular Vein Cannulation in a Patient with HELLP Syndrome: A case report
- Hepatic Infarction in HELLP Syndrome: A Case Report